Abstract
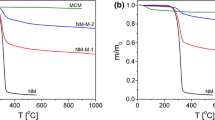
It is known that the energy of the amorphous state of itraconazole loaded in ordered mesoporous materials is high relative to that of the crystalline state and is responsible for enhanced solubility and dissolution rate. We investigated the effects of particle size (0.7–5 μm), mesostructure (2D p6mm, cubic Ia-3d and cubic Fm-3m) and pore size (2.2–15.4 nm) of mesoporous silicas on the release performance of itraconazole. Results indicated that the release performance was not influenced by the particle sizes tested here, that the release performance increased with increasing pore diameter due to the lower probability of drug molecules colliding to recrystallize in large pores, and that the release performance was decreased in the cage-type pore structure (Fm-3m) compared to that in the cylindrical pore structures (p6mm and Ia-3d) because of the small entrance to the cagelike pores that retards the drug release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pouton CW. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Delivery Rev, 1997, 25: 47–58
Loftsson T, Brewster ME. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J Pharm Sci, 1996, 85: 1017–1025
Rabinow BE. Nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2004, 3: 785–796
Van Speybroeck M, Mols R, Mellaerts R, Thi TD, Martens JA, Humbeeck JV, Annaert P, Mooter GVD, Augustijns P. Combined use of ordered mesoporous silica and precipitation inhibitors for improved oral absorption of the poorly soluble weak base itraconazole. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2010, 75: 354–365
Hancock BC, Zografi G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J Pharm Sci, 1997, 86: 1–12
Yanagisawa T, Shimizu T, Kuroda K, Chuzo K. The preparation of alkyltriinethylaininonium & ndash; kaneinite complexes and their conversion to microporous materials. B Chem Soc Jpn, 1990, 63: 988–992
Zhao D, Feng J, Huo Q, Melosh N, Fredrickson GH, Chmelka BF, Stucky GD. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science, 1998, 279: 548–552
Beck JS, Vartuli JC, Roth WJ, Leonowicz ME, Kresge CT, Schmitt KD, Chu CTW, Olson DH, Sheppard EW. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J Am Chem Soc, 1992, 114: 10834–10843
Ukmar T, Planinšek O. Ordered mesoporous silicates as matrices for controlled release of drugs. Acta Pharmaceut, 2010, 60: 373–385
Che S, Liu Z, Ohsuna T, Sakamoto K, Terasaki O, Tatsumi T. Synthesis and characterization of chiral mesoporous silica. Nature, 2004, 429: 281–284
Linton P, Alfredsson V. Growth and morphology of mesoporous SBA-15 particles. Chem Mater, 2008, 20: 2878–2880
Sayari A, Han BH, Yang Y. Simple synthesis route to monodispersed SBA-15 silica rods. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126: 14348–14349
Tan B, Rankin SE. Dual latex/surfactant templating of hollow spherical silica particles with ordered mesoporous shells. Langmuir, 2005, 21: 8180–8187
Linton P, Wennerstrom H, Alfredsson V. Controlling particle morphology and size in the synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 materials. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2010, 12: 3852–3858
Yu C, Fan J, Tian B, Zhao D. Morphology development of mesoporous materials: a colloidal phase separation mechanism. Chem Mater, 2004, 16: 889–898
Su B, Lu X, Lu Q. Oriented SBA-15-type silica films on polyimide films with laser-induced periodic microgrooves. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 9695–9699
Chen Q, Han L, Gao C, Che S. Synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica spheres (mmsss) with controlled particle size using gemini surfactant. Microporous Mesoporous Mat, 2010, 128: 203–212
Chen L, Zhu G, Zhang D, Zhao H, Guo M, Shi W, Qiu S. Novel mesoporous silica spheres with ultra-large pore sizes and their application in protein separation. J Mater Chem, 2009, 19: 2013–2017
Che S, Garcia-Bennett AE, Yokoi T, Sakamoto K, Kunieda H, Terasaki O, Tatsumi T. A novel anionic surfactant templating route for synthesizing mesoporous silica with unique structure. Nat Mater, 2003, 2: 801–805
Alberius PCA, Frindell KL, Hayward RC, Kramer EJ, Stucky GD, Chmelka BF. General predictive syntheses of cubic, hexagonal, and lamellar silica and titania mesostructured thin films. Chem Mater, 2002, 14: 3284–3294
Yu C, Yu Y, Zhao D. Highly ordered large caged cubic mesoporous silica structures templated by triblock PEO-PBO-PEO copolymer. Chem Commun, 2000, 7: 575–576
Ben T, Ren H, Ma S, Cao D, Lan J, Jing X, Wang W, Xu J, Deng F, Simmons JM, Qiu S, Zhu G. Targeted synthesis of a porous aromatic framework with high stability and exceptionally high surface area. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 121: 9621–9624
Wei J, Wang H, Deng Y, Sun Z, Shi L, Tu B, Luqman M, Zhao D. Solvent evaporation induced aggregating assembly approach to three-dimensional ordered mesoporous silica with ultralarge accessible mesopores. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 20369–20377
Zhu L, Wang D, Wei X, Zhu X, Li J, Tu C, Su Y, Wu J, Zhu B, Yan D. Multifunctional pH-sensitive superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanocomposites for targeted drug delivery and mr imaging. J Control Release, 2013, 169: 228–238
Chen Y, Chen H, Zhang S, Chen F, Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhu M, Wu H, Guo L, Feng J, Shi J. Multifunctional mesoporous nanoellipsoids for biological bimodal imaging and magnetically targeted delivery of anticancer drugs. Adv Funct Mater, 2011, 21: 270–278
Muhammad F, Guo M, Qi W, Sun F, Wang A, Guo Y, Zhu G. PH-triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracelluar dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 8778–8781
Vallet-Regi M, Rámila A, del Real RP, Pérez-Pariente J. A new property of MCM-41: drug delivery system. Chem Mater, 2000, 13: 308–311
Charnay C, Bégu S, Tourné-Péteilh C, Nicole L, Lerner DA, Devoisselle JM. Inclusion of ibuprofen in mesoporous templated silica: drug loading and release property. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2004, 57: 533–540
Mellaerts R, Mols R, Jammaer JAG, Aerts CA, Annaert P, Humbeeck JV, Mooter GVD, Augustijns P, Martens JA. Increasing the oral bioavailability of the poorly water soluble drug itraconazole with ordered mesoporous silica. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2008, 69: 223–230
Van Speybroeck M, Barillaro V, Thi TD, Mellaerts R, Martens J, Humbeeck JV, Vermant J, Annaert P, Mooter GVD, Augustijns P. Ordered mesoporous silica material SBA-15: a broad-spectrum formulation platform for poorly soluble drugs. J Pharm Sci, 2009, 98: 2648–2658
Salonen J, Kaukonen AM, Hirvonen J, Lehto VP. Mesoporous silicon in drug delivery applications. J Pharm Sci, 2008, 97: 632–653
Fan J, Yu C, Gao F, Lei J, Tian B, Wang L, Luo Q, Tu B, Zhou W, Zhao D. Cubic mesoporous silica with large controllable entrance sizes and advanced adsorption properties. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2003, 115: 3254–3258
Alba-Simionesco C, Coasne B, Dosseh G, Dudziak G, Gubbins KE, Radhakrishnan R, Sliwinska-Bartkowiak M. Effects of confinement on freezing and melting. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2006, 18: R15
Kresge C, Leonowicz M, Roth WJ, Vartuli JC, Beck JS. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature, 1992, 359: 710–712
Yano K, Fukushima Y. Particle size control of mono-dispersed super-microporous silica spheres. J Mater Chem, 2003, 13: 2577–2581
Wang Y, Zhang F, Wang Y, Ren J, Li C, Liu X, Guo Y, Guo Y, Lu G. Synthesis of length controllable mesoporous SBA-15 rods. Mater Chem Phys, 2009, 115: 649–655
Ding Y, Yin G, Liao X, Huang Z, Chen X, Yao Y, Li J. A convenient route to synthesize SBA-15 rods with tunable pore length for lysozyme adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mat, 2013, 170: 45–51
Kleitz F, Choi SH, Ryoo R. Cubic Ia3d large mesoporous silica: synthesis and replication to platinum nanowires, carbon nanorods and carbon nanotubes. Chem Commun, 2003: 2136–2137
Mellaerts R, Jammaer JA, Van Speybroeck M, Chen H, Humbeeck JV, Augustijns P, Mooter GVD, Martens JA. Physical state of poorly water soluble therapeutic molecules loaded into SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silica carriers: a case study with itraconazole and ibuprofen. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 8651–8659
Tozuka Y, Sasaoka S, Nagae A, Moribe K, Oguchi T, Yamamoto K. Rapid adsorption and entrapment of benzoic acid molecules onto mesoporous silica (FSM-16). J Colloid Interface Sci, 2005, 291: 471–476
Lee S, Nam K, Kim M, Jun S, Park JS, Woo JS, Hwang SJ. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersions of itraconazole by using aerosol solvent extraction system for improvement in drug solubility and bioavailability. Arch Pharm Res, 2005, 28: 866–874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Che, S. Enhanced release of the poorly soluble drug itraconazole loaded in ordered mesoporous silica. Sci. China Chem. 58, 400–410 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5333-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5333-x