Abstract
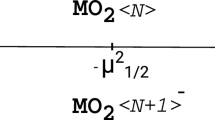
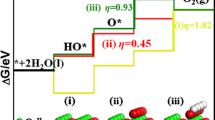
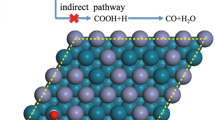
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 has the benefit of turning greenhouse gas emissions into useful resources. We performed a comparative study of the electrochemical reduction of CO2 on stepped Pb(211) and Sn(112) surfaces based on the results of density functional theory slab calculations. We mapped out the potential energy profiles for electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate and other possible products on both surfaces. Our results show that the first step is the formation of the adsorbed formate (HCOO*) species through an Eley-Rideal mechanism. The formate species can be reduced to HCOO− through a one-electron reduction in basic solution, which produces formic acid as the predominant product. The respective potentials of forming HCOO* are predicted to be −0.72 and −0.58 V on Pb and Sn. Higher overpotentials make other reaction pathways accessible, leading to different products. On Sn(112), CO and CH4 can be generated at −0.65 V following formate formation. In contrast, the limiting potential to access alternative reaction channels on Pb(211) is −1.33 V, significantly higher than that of Sn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scibioh MA, Viswanathan B. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide: a status report. Pro Indian Natn Sci Acad, 2004, 70: 407–462
D’Alessandro DM, Smit B, Long JR. Carbon dioxide capture: prospects for new materials. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 49: 6058–6082
Hori Y. Electrochemical CO2 reduction on metal electrodes. In: Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008. 89–189
Qiao JL, Liu YY, Hong F, Zhang JJ. A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43: 631–675
Jhong HR, Ma S, Kenis PJ. Electrochemical conversion of CO2 to useful chemicals: current status, remaining challenges, and future opportunities. Curr Opin Chem Eng, 2013, 2: 191–199
Lee J, Kwon Y, Machunda RL, Lee HJ. Electrocatalytic recycling of CO2 and small organic molecules. Chem Asian J, 2009, 4: 1516–1523
Genovese C, Ampelli C, Perathoner S, Centi G. Electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 on carbon nanotube-based electrodes for producing solar fuels. J Catal, 2013, 308: 237–249
Bernstein NJ, Akhade SA, Janik MJ. Density functional theory study of carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction on the Fe(100) surface. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2014, 16: 13708–13717
Friebel D, Mbuga F, Rajasekaran S, Miller DJ, Ogasawara H, Alonso-Mori R, Sokaras D, Nordlund D, Weng TC, Nilsson A. Structure, redox chemistry, and interfacial alloy formation in monolayer and multilayer Cu/Au(111) model catalysts for CO2 electro-reduction. J Phys Chem C, 2014, 118: 7954–7961
Terunuma Y, Saitoh A, Momose Y. Relationship between hydro-carbon production in the electrochemical reduction of CO2 and the characteristics of the Cu electrode. J Electroanal Chem, 1997, 434: 69–75
Goncalves M, Gomes A, Condeco J, Fernandes R, Pardal T, Sequeira C, Branco J. Selective electrochemical conversion of CO2 to C2 hydrocarbons. Energy Convers Manage, 2010, 51: 30–32
Schouten KJP, Kwon Y, van der Ham CJM, Qin Z, Koper MTM. A new mechanism for the selectivity to C-1 and C-2 species in the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on copper electrodes. Chem Sci, 2011, 2: 1902–1909
Hori Y, Murata A, Takahashi R. Formation of hydrocarbons in the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide at a copper electrode in aqueous solution. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1, 1989, 85: 2309–2326
Hori Y, Koga O, Yamazaki H, Matsuo T. Infrared spectroscopy of adsorbed CO and intermediate species in electrochemical reduction of CO2 to hydrocarbons on a Cu electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 1995, 40: 2617–2622
Hori Y, Takahashi I, Koga O, Hoshi N. Selective formation of C2 compounds from electrochemical reduction of CO2 at a series of copper single crystal electrodes. J Phys Chem B, 2002, 106: 15–17
Hori Y, Konishi H, Futamura T, Murata A, Koga O, Sakurai H, Oguma K. “Deactivation of copper electrode” in electrochemical reduction of CO2. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 50: 5354–5369
Hirunsit P. Electroreduction of carbon dioxide to methane on copper, copper-silver, and copper-gold catalysts: a DFT study. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117: 8262–8268
Nie X, Esopi MR, Janik MJ, Asthagiri A. Selectivity of CO2 reduction on copper electrodes: the role of the kinetics of elementary steps. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52: 2459–2462
Nie X, Luo W, Janik MJ, Asthagiri A. Reaction mechanisms of CO2 electrochemical reduction on Cu (111) determined with density functional theory. J Catal, 2014, 312: 108–122
Durand WJ, Peterson AA, Studt F, Abild-Pedersen F, Nørskov JK. Structure effects on the energetics of the electrochemical reduction of CO2 by copper surfaces. Surf Sci, 2011, 605: 1354–1359
Hansen HA, Montoya JH, Zhang YJ, Shi C, Peterson AA, Nørskov JK. Electroreduction of methanediol on copper. Catal Lett, 2013, 143: 631–635
Peterson AA, Abild-Pedersen F, Studt F, Rossmeisl J, Nørskov JK. How copper catalyzes the electroreduction of carbon dioxide into hydrocarbon fuels. Energ Environ Sci, 2010, 3: 1311–1315
Peterson AA, Nørskov JK. Activity descriptors for CO2 electro-reduction to methane on transition-metal catalysts. J Phys Chem Lett, 2012, 3: 251–258
Innocent B, Pasquier D, Ropital F, Hahn F, Leger JM, Kokoh KB. FTIR spectroscopy study of the reduction of carbon dioxide on lead electrode in aqueous medium. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2010, 94: 219–224
Kwon Y, Lee J. Formic acid from carbon dioxide on nanolayered electrocatalyst. Electrocatal, 2010, 1: 108–115
Koleli F, Balun D. Reduction of CO2 under high pressure and high temperature on Pb-granule electrodes in a fixed-bed reactor in aqueous medium. Appl Catal A-Gen, 2004, 274: 237–242
Innocent B, Liaigre D, Pasquier D, Ropital F, Leger JM, Kokoh KB. Electro-reduction of carbon dioxide to formate on lead electrode in aqueous medium. J Appl Electrochem, 2009, 39: 227–232
Zhang S, Kang P, Meyer TJ. Nano-structured tin catalysts for selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136: 1734–1737
Lv W, Zhang R, Gao P, Lei L. Studies on the faradaic efficiency for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate on tin electrode. J Power Sources, 2014, 253: 276–281
Kaneco S, Iwao R, Iiba K, Ohta K, Mizuno T. Electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide to formic acid on Pb in KOH/methanol electrolyte at ambient temperature and pressure. Energy, 1998, 23: 1107–1112
Del Castillo A, Alvarez-Guerra M, Irabien A. Continuous electroreduction of CO2 to formate using Sn gas diffusion electrodes. AIChE J, 2014, 60: 3557–3564
Grasemann M, Laurenczy G. Formic acid as a hydrogen source-recent developments and future trends. Energ Environ Sci, 2012, 5: 8171–8181
Bumroongsakulsawat P, Kelsall GH. Effect of solution pH on CO: formate formation rates during electrochemical reduction of aqueous CO2 at Sn cathodes. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 141: 216–225
Li WZ. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to small organic molecule fuels on metal catalysts. Chem Inform, 2012, 43: 55–76
Sullivan BP, Krist K, Guard H. Electrochemical and Electrocatalytic Reactions of Carbon Dioxide. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1992
Koleli F, Atilan T, Palamut N, Gizir AM, Aydin R, Hamann CH. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 at Pb- and Sn-electrodes in a fixed-bed reactor in aqueous K2CO3 and KHCO3 media. J Appl Electrochem, 2003, 33: 447–450
Nørskov JK, Bligaard T, Logadottir A, Bahn S, Hansen LB, Bollinger M, Bengaard H, Hammer B, Sljivancanin Z, Mavrikakis M. Universality in heterogeneous catalysis. J Catal, 2002, 209: 275–278
Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54: 11169–11186
King H. Crystal structures of the elements at 25 °C. J Phase Equilib, 1981, 2: 401–402
Craven JE. Band structure and fermi surface of white tin as derived from de Haas-van Alphen data. Phys Rev, 1969, 182: 693–702
Nørskov JK, Rossmeisl J, Logadottir A, Lindqvist L, Kitchin JR, Bligaard T, Jonsson H. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108: 17886–17892
Calle-Vallejo F, Koper MTM. Theoretical considerations on the electroreduction of CO to C2 species on Cu(100) electrodes. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52: 7282–7285
Cramer CJ. Essentials of computational chemistry: theories and models. Volume 9: charge distribution and spectroscopic properties. 2nd Ed. Weinheim: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2004. 305–351
Hara K, Kudo A, Sakata T. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide under high pressure on various electrodes in an aqueous electrolyte. J Electroanal Chem, 1995, 391: 141–147
Hori Y, Wakebe H, Tsukamoto T, Koga O. Electrocatalytic process of CO selectivity in electrochemical reduction of CO2 at metal electrodes in aqueous media. Electrochimica Acta, 1994, 39: 1833–1839
Azuma M, Hashimoto K, Hiramoto M, Watanabe M, Sakata T. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on various metal electrodes in low-temperature aqueous KHCO3 media. J Electrochem Soc, 1990, 137: 1772–1778
Prakash GKS, Viva FA, Olah GA. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Sn-Nafion coated electrode for a fuel-cell-like device. J Power Sources, 2013, 223: 68–73
Li H, Oloman C. The electro-reduction of carbon dioxide in a continuous reactor. J Appl Electrochem, 2005, 35: 955–965
Wu JJ, Harris B, Sharma PP, Zhou XD. Morphological stability of Sn electrode for electrochemical conversion of CO2. ECS Trans, 2013, 58: 71–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, C., Wang, H., Zhu, X. et al. A DFT study of CO2 electrochemical reduction on Pb(211) and Sn(112). Sci. China Chem. 58, 607–613 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5323-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5323-z