Abstract
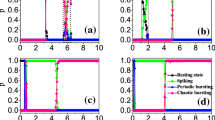
In this paper, we study how adaptive coupling with time-periodic growth speed (TPGS) affects the spiking synchronization of weighted adaptive Newman-Watts Hodgkin-Huxley neuron networks with time delays. It is found that the neuronal spiking intermittently exhibits synchronization transitions between desynchronization and in-phase synchronization or anti-phase synchronization as TPGS amplitude or frequency is varied, showing multiple synchronization transitions. These transitions depend on the values of time delay and can occur only when time delay is close to those values that can induce synchronization transitions when the growth speed is fixed. These results show that the adaptive coupling with TPGS has great influence on the spiking synchronization of the neuronal networks and thus plays a crucial role in the information processing and transmission in neural systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singer W. Synchronization of cortical activity and its putative role in information processing and learning. Annu Rev Physiol, 1993, 55: 349–374
Gray CM. The temporal correlation hypothesis of visual feature integration: Still alive and well. Neuron, 1999, 24: 31–47
Fries P, Nikolić D, Singer W. The gamma cycle. Trends Neurosci, 2007, 30: 309–316
Levy R, Hutchison WD, Lozano AM, Dostrovsky JO. High-frequency synchronization of neuronal activity in the sub-thalamic nucleus of Parkinsonian patients with limb tremor. J Neurosci, 2000, 20: 7766–7775
Mormann F, Kreuz T, Andrzejak RG, David P, Lehnertz K, Elger CE. Epileptic seizures are preceded by a decrease in synchronization. Epilepsy Res, 2003, 53:173–185
Zhou CS, Kurths J. Noise-induced synchronization and coherence resonance of a Hodgkin-Huxley model of thermally sensitive neurons. Chaos, 2003, 13: 401–409
Bahar S. Burst-enhanced synchronization in an array of noisy coupled neurons. Fluct Noise Lett, 2004, 4: L87–L96
Yoshioka M. Chaos synchronization in gap-junction-coupled neurons. Phys Rev E, 2005, 71: 065203
Wang QY, Lu QS, Chen GR. Subthreshold stimulus-aided temporal order and synchronization in a square lattice noisy neuronal network. EPL, 2007, 77: 10004
Hasegawa H. Synchronizations in small-world networks of spiking neurons: Diffusive versus sigmoid couplings. Phys Rev E, 2005, 72: 056139
Gong YB, Wang MS, Hou ZH, Xin HW. Optimal spike coherence and synchronization on complex Hodgkin-Huxley neuron networks. Chem Phys Chem, 2005, 6: 1042–1047
Gong YB, Xu B, Xu Q, Yang CL, Ren TQ, Hou ZH, Xin HW. Ordering spatiotemporal chaos in complex thermosensitive neuron networks. Phys Rev E, 2006, 73: 0 46137
Wei DQ, Luo XS. Ordering spatiotemporal chaos in discrete neural networks with small-world connections. EPL, 2007, 78: 68004
Zheng YH, Lu QS. Spatiotemporal patterns and chaotic burst synchronization in a small-world neuronal network. Phys A, 2008, 387:3719–3728
Wang QY, Lu QS, Chen GR. Ordered bursting synchronization and complex wave propagation in a ring neuronal network. Phys A, 2007, 374: 869–878
Ibarz B, Cao HJ, Sanjuán MAF. Bursting regimes in map-based neuron models coupled through fast threshold modulation. Phys Rev E, 2008, 77: 051918
Perc M. Optimal spatial synchronization on scale-free networks via noisy chemical synapses. Biophys Chem, 2009, 141:175–179
Shen Y, Hou ZH, Xin HW. Transition to burst synchronization in coupled neuron networks. Phys Rev E, 2008, 77: 031920
Postnova S, Voigt K, Braun HA. Neural synchronization at tonictobursting transitions. J Biol Phys, 2007, 33: 129–143
Dhamala M, Jirsa VK, Ding MZ. Enhancement of neural synchrony by time delay. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 94: 074104
Rossoni E, Chen YH, Ding MZ, Feng JF. Stability of synchronous oscillations in a system of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with delayed diffusive and pulsed coupling. Phys Rev E, 2005, 71: 061904
Ko TW, Ermentrout GB. Effects of axonal time delay on synchronization and wave formation in sparsely coupled neuronal oscillators. Phys Rev E, 2007, 76: 056206
Roxin A, Brunel N, Hansel D. Role of delays in shaping spatiotemporal dynamics of neuronal activity in large networks. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94: 238103
Wang QY, Perc M, Duan ZS, Chen GR. Delay-enhanced coherence of spiral waves in noisy Hodgkin-Huxley neuronal networks. Phys Lett A, 2008, 372: 5681–5687
Gosak M, Markovič R, Marhl M. The role of neural architecture and the speed of signal propagation in the process of synchronization of bursting neurons. Physica A, 2012, 391: 2764–2770
Wang QY, Perc M, Duan ZS, Chen GR. Delay-induced multiple stochastic resonances on scale-free neuronal networks. Chaos, 2009, 19: 023112
Hao YH, Gong YB, Lin X, Ma XG. Delay-induced coherence bi-resonance-like behavior in stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley neuron networks. Sci China Chem, 2010, 53: 1762–1766
Lin X, Gong YB, Wang Li, Ma XG. Coherence resonance and bi-resonance by time-periodic coupling strength in Hodgkin-Huxley neuron networks. Sci China Chem, 2012, 55: 256–261
Hao YH, Gong YB, Lin X. Multiple resonances with time delays in scale-free networks of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons subjected to non-Gaussian noise. Sci China Chem, 2011, 54: 782–787
Wang QY, Duan ZS, Perc M, Chen GR. Synchronization transitions on small-world neuronal networks: Effects of information transmission delay and rewiring probability. EPL, 2008, 83: 50008
Wang QY, Perc M, Duan ZS, Chen GR. Synchronization transitions on scale-free neuronal networks due to finite information transmission delays. Phys Rev E, 2009, 80: 026206
Wang QY, Chen GR, Perc M. Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6: e15851
Burić N, Todorović K, Vasović N. Synchronization of bursting neurons with delayed chemical synapses. Phys Rev E, 2008, 78: 036211
Wang QY, Lu QS, Chen GR, Feng ZS, Duan LX. Bifurcation and synchronization of synaptically coupled FHN models with time delay. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2009, 39: 918–925
Wang, QY Lu QS, Chen GR. Synchronization transition by synaptic delay in coupled fast spiking neurons. Int J Bifurcat Chaos, 2008, 18:1189–1198
Xie YH, Gong YB, Hao YH, Ma XG. Synchronization transitions on complex thermo-sensitive neuron networks with time delays. Biophys Chem, 2010, 146: 126–132
Gong YB, Xie YH, Lin X, Hao YH, Ma XG. Ordering chaos and synchronization transitions by chemical delay and coupling on scale-free neuronal networks. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2010, 43: 96–103
Hao YH, Gong YB, Wang L, Ma XG, Yang CL. Single or multiple synchronization transitions in scale-free neuronal networks with electrical or chemical coupling. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2011, 44: 260–268
Gong YB, Lin X, Wang L, Hao YH. Chemical synaptic coupling-induced delay-dependent synchronization transitions in scale-free neuronal networks. Sci China Chem, 2011, 54: 1498–1503
Haas JS, Nowotny T, Abarbanel HDI. Spike-timing-dependent plasticity of inhibitory synapses in the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol, 2006, 98: 3305–3313
Achour SB, Pascual O. Glia: The many ways to modulate synaptic plasticity. Neurochem Int, 2010, 57: 440–445
Gerrow K, Triller A. Synaptic stability and plasticity in a floating world. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2010, 20: 631–639
Seliger P, Young SC, Tsimring LS. Plasticity and learning in a network of coupled phase oscillators. Phys Rev E, 2002, 65: 041906
Huang D. Synchronization in adaptive weighted networks. Phys Rev E, 2006, 74: 046208
Zhu JF, Zhao M, Yu W, Zhou CS, Wang BH. Better synchronizability in generalized adaptive networks. Phys Rev E, 2010, 81: 026201
Wu D, Zhu SQ, Luo XQ, Wu L. Effect of adaptive coupling on stochastic resonance of small-world networks. Phys Rev E, 2011, 84: 021102
Ma J, Jia Y, Wang C N, Li S R. The instability of the spiral wave induced by the deformation of elastic excitable media. J Phys A: Math Theor, 2008, 41: 385105
Sheheitli H, Rand R. Origin of arrhythmias in a heart model. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 2009, 14: 3707–3414
Wang C N, Yang L J, Yuan L H, Ma J. Deformation and death of spiral wave induced by asymmetrical diffusion in elastic media. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat, 2010, 15: 3913–3918
Newman MEJ, Watts DJ. Scaling and percolation in the small-world network model. Phys Rev E, 1999, 60: 7332–7342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Gong, Y., Xu, B. et al. Adaptive coupling-enhanced spiking synchronization in Newman-Watts neuronal networks with time delays. Sci. China Chem. 56, 648–655 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4836-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4836-6