Abstract
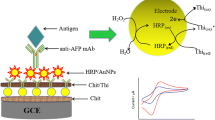
An effective electrochemical signal amplification strategy based on enzyme membrane modification and redox probe immobilization was proposed to construct an amperometric immunosensor. L-cysteine@ferrocene functionalized chitosan, which possessed not only efficient redox-activity but also excellent film-forming ability, was coated on the bare glass carbon electrode. Moreover, the thiol groups (-SH) in the ferrocenyl compound were used for gold nanoparticles immobilization via the strong bonding interaction, which could further be utilized for the immobilization of antibody biomolecules with well-retained bioactivities. Finally, glucose oxidase (GOD) as the enzyme membrane was employed to block the possible remaining active sites and avoid the nonspecific adsorption. With the excellent electrocatalytic properties of GOD towards glucose, the amplification of antigen-antibody interaction and the enhanced sensitivity could be achieved. Under the optimal conditions, the linear range of the proposed immunosensor for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) was from 0.05 to 100 ng/mL with a detection limit of 0.02 ng/mL (S/N = 3). Moreover, the immunosensor exhibited good selectivity, stability and reproducibility, which provided a promising potential for clinical immunoassay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wulfkuhle JD, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF. Proteomic applications for the early detection of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2003, 3: 267–275
Kitano H. Systems biology: A brief overview. Science, 2002, 295: 1662–1664
Srinivas PR, Kramer BS, Srivastava S. Trends in biomarker research for cancer detection. Lancet Oncol, 2001, 2: 698–704
Voller A, Bartlett A, Bidwell DE. Enzyme immunoassays with special reference to ELISA techniques. J Clin Pathol, 1978, 31: 507–520
Goldsmith SJ. Radioimmunoassay: Review of basic principles. Semin Nucl Med, 1975, 5: 125–152
Matsuya T, Tashiro S, Hoshino N, Shibata N, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K. A core-shell-type fluorescent nanosphere possessing reactive poly(ethylene glycol) tethered chains on the surface for zeptomole detection of protein in time-resolved fluorometric immunoassay. Anal Chem, 2003, 75: 6124–6132
Tadic SC, Dernick G, Juncker D, Buurman G, Kropshofer H, Michel B, Fattinger C, Delamarche E. High-sensitivity miniaturized immunoassays for tumor necrosis factor α using microfluidic systems. Lab Chip, 2004, 4: 563–569
Fu ZF, Hao C, Fei X, Ju HX. Flow-injection chemiluminescent immunoassay for α-fetoprotein based on epoxysilane modified glass microbeads. J Immunol Methods, 2006, 312: 61–67
Fu ZF, Yan F, Liu H, Yang ZJ, Ju HX. Channel-resolved multianalyte immunosensing system for flow-through chemiluminescent detection of α-fetoprotein and carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron, 2008, 23: 1063–1069
Schmalzing D, Nashabeh W. Capillary electrophoresis based immunoassays: A critical review. Electrophoresis, 1997, 18: 2184–2193
Niederkofler EE, Tubbs KA, Gruber K, Nedelkov D, Kiernan UA, Williams P, Nelson RW. Determination of β-2 microglobulin levels in plasma using a high-throughput mass spectrometric immunoassay system. Anal Chem, 2001, 73: 3294–3299
Hu SH, Zhang SC, Hu ZC, Xing Z, Zhang XR. Detection of multiple proteins on one spot by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and application to immuno-microarray with element-tagged antibodies. Anal Chem, 2007, 79: 923–929
Saito K, Kobayashi D, Sasaki M, Araake H, Kida T, Yagihashi A, Yajima T, Kameshima H, Watanabe N. Detection of human serum tumor necrosis factor-α in healthy donors, using a highly sensitive immuno-PCR assay. Clin Chem, 1999, 45: 665–669
Tan F, Yan F, Ju HX. A designer ormosil gel for preparation of sensitive immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on simple direct electron transfer. Electrochem Commun, 2006, 8: 1835–1839
Lai GS, Yan F, Ju HX. Dual signal amplification of glucose oxidasefunctionalized nanocomposites as a trace label for ultrasensitive simultaneous multiplexed electrochemical detection of tumor markers. Anal Chem, 2009, 81: 9730–9736
Cheng W, Yan F, Ding L, Ju HX, Yin YB. Cascade signal amplification strategy for subattomolar protein detection by rolling circle amplification and quantum dots tagging. Anal Chem, 2010, 82: 3337–3342
Yuan R, Zhuo Y, Chai YQ, Zhang Y, Sun AL. Determination of carcinoembryonic antigen using a novel amperometric enzyme-electrode based on layer-by-layer assembly of gold nanoparticles and thionine. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2007, 50: 97–104
Wu J, Tang JH, Dai Z, Yan F, Ju HX, Murr NE. A disposable electrochemical immunosensor for flow injection immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron, 2006, 22: 102–108
Dai Z, Yan F, Yu H, Hu XY, Ju HX. Novel amperometric immunosensor for rapid separation-free immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. J Immunol Methods, 2004, 287: 13–20
Dai Z, Chen J, Yan F, Ju HX. Electrochemical sensor for immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen based on thionine monolayer modified gold electrode. Cancer Detection and Prevention, 2005, 29: 233–240
Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Tang DP, Zhang Y, Wang N, Li XL, Zhu Q. A reagentless amperometric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/thionine/Nafion-membrane-modified gold electrode for determination of a-1-fetoprotein. Electrochem Commun, 2005, 7: 355–360
Song ZJ, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Yin B, Fu P, Wang JF. Multilayer structured amperometric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles and Prussian blue nanoparticles/nanocomposite functionalized interface. Electrochim Acta, 2010, 55: 1778–1784
Badia A, Carlini R, Fernandez A, Battaglini F, Mikkelsen SR, English AM. Intramolecular electron-transfer rates in ferrocene-derivatized glucose oxidase. J Am Chem Soc, 1993, 115: 7053–7060
Kandimalla VB, Tripathi VS, Ju H. Aconductiveormosil encapsulated with ferrocene conjugate and multiwall carbon nanotubes for biosensing application. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 1167–1174
Lin JH, Qu W, Zhang SS. Disposable biosensor based on enzyme immobilized on Au-chitosan-modified indium tin oxide electrode with flow injection amperometric analysis. Anal Biochem, 2007, 36: 288–293
Lu XB, Hu JQ, Yao X, Wang ZP, Li JH. Composite system based on chitosan and room temperature ionic liquid: Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin. Biomacromolecules, 2006, 7: 975–980
Chen J, Yan F, Dai Z, Ju HX. Reagentless amperometric immunosensors for human chorionic gonadotrophin based on direct electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase. Biosens Bioelectron, 2005, 21: 330–336
Cui RJ, Huang HP, Yin ZZ, Gao D, Zhu JJ. Horseradish peroxidase-functionalized gold nanoparticle label for amplified immunoanalysis based on gold nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes hybrids modified biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron, 2008, 23: 1666–1673
Li N, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Chen SH, An HZ, Li WJ. New Antibody immobilization strategy based on gold nanoparticles and azure I/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite membranes for an amperometric enzyme immunosensor. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 8443–8450
Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Sun AL, Zhang Y, Yang JZ. A tris (2,2′-bipyridyl) cobalt(III)-bovine serum albumin composite membrane for biosensors. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 5420–5429
Song ZJ, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Wang JF, Che X. Dual amplification strategy for the fabrication of highly sensitive amperometric immunosensor based on nanocomposite functionalized interface. Sens Actuators B, 2010, 145: 817–825
Frens G. Preparation of gold dispersions of varying particle size: Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature-Phys Sci, 1973, 241: 20–22
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley, New York, 1980
Calvo EJ, Etchenique R, Danilwicz C, Diaz L. Electrical communication between electrodes and enzymes mediated by redox hydrogels. Anal Chem, 1996, 68: 4186–4193
Shan D, Yao WJ, Xue HG. Electrochemical study of ferrocenemethanol modified layered double hydroxides composite matrix: Potential application in the development of amperometric biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron, 2007, 23: 432–437
Cass AEG, Davis G, Francis GD, Hill HAO, Aston WJ, Higgins IJ, Plotkin EV, Scott LDL, Turner APF. Ferrocene-mediated enzyme electrode for amperometric determination of glucose. Anal Chem, 1984, 56: 667–671
Wang JF, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Yin B, Xu Y, Guan S. An amperometric immunosensor based on layer-by-layer assembly of L-cysteine and nanosized Prussian blue on gold electrode for determination of human chorionic gonadotrophin. Electroanalysis, 2009, 21: 707–714
Doron A, Katz E, Willner I. Organization of Au colloids as monolayer films onto ITO glass surfaces: application of the metal colloid films as base interfaces to construct redox-active monolayers. Langmuir, 1995, 11: 1313–1317
Zhang TT, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Liu KG, Ling SJ. Study on an immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles and a nano-calcium carbonate/Prussian blue modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta, 2009, 165: 53–58
Liu ZY, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Zhuo Y, Hong CL, Yang Xia. Highly sensitive, reagentless amperometric immunosensor based on a novel redox-active organic-inorganic composite film. Sens Actuators B, 2008, 134: 625–631
Tang DY, Xia BY. Electrochemical immunosensor and biochemical analysis for carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical diagnosis. Microchim Acta, 2008, 163: 41–48
Pan J, Yang Q. Antibody-functionalized magnetic nano-particles for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen using a flow-injection electrochemical device. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2007, 388: 279–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Yuan, R., Chai, Y. et al. Glucose oxidase as a blocking agent-based signal amplification strategy for the fabrication of label-free amperometric immunosensors. Sci. China Chem. 54, 536–544 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4124-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4124-7