Abstract
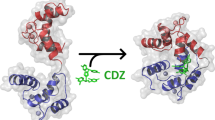
Calmodulin (CaM) is a multifunctional Ca2+-binding protein regulating the activity of many enzymes in response to fluctuation of the intracellular Ca2+ level. It has been shown that a CaM Q41C/K75C mutant (CaMSS) with a disulfide bond in the N-terminal domain exhibits greatly reduced affinity to Ca2+. In the present study, the experimental results revealed a unique metal binding pattern in CaMSS towards La3+ and Ca2+ separately: the mutant protein binds Ca2+ at site I, III and IV; however, it binds La3+ at site I, II and IV. A putative mechanism was proposed which is the conformation of site II (or site III) of CaMSS could be altered and thus loses its metal ion affinity in response to metal binding in the opposite terminal domain possibly through the long range domain interaction. The present work may offer new perspectives for understanding the mechanisms of specific metal ion affinity in CaM and for CaM-based protein design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang MJ, Toshiyuki T, Mitsuhiko I. Calcium-induced conformational transition revealed by the solution structure of apo calmodulin. Nat Struct Biol, 1995, 2: 758–767
Kuboniwa H, Tjandra N, Grzesiek S, Ren H, Klee CB, Bax A. Solution structure of calcium-free calmodulin. Nat Struct Biol, 1995, 2: 768–776
Haiech J, Klee CB, Demaille JG, Haiech J. Effects of cations on affinity of calmodulin for calcium: ordered binding of calcium ions allows the specific activation of calmodulin-stimulated enzymes. Theoretical approach to study of multiple ligand binding to a macromolecule. Biochemistry, 1981, 20: 3890–3897
Wang C-LA, Aquaron RR, Leavis PC, Gergely J. Metal-binding properties of calmodulin. Eur J Biochem, 1982, 124: 7–12
Ye Y, Lee HW, Yang W, Shealy S, Yang JJ. Probing site-specific calmodulin calcium and lanthanide affinity by grafting. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127: 3743–3750
Maune JF, Beckingham K, Martin SR, Bayley PM. Circular dichroism studies on calcium binding to two series of calcium binding site mutants of drosophila melanogaster calmodulin. Biochemistry, 1992, 31: 7779–7786
Martin SR, Maune JF, Beckingham K, Bayley PM. Stopped-flow studies of calcium dissociation for calcium-binding-site mutants of drosophila melanogaster calmodulin. Eur J Biochem, 1992, 205: 1107–1114
Starovasnik M, Su DR, Beckingham K, Klevit RE. A series of point mutations reveal interactions between the calcium-binding sites of calmodulin. Protein Sci, 1992, 1: 245–253
Yang Q, Hu J, Yang X, Wang K. Mastoparan/mastoparan x altered binding behavior of La3+ to calmodulin in ternary complexes. J Inorg Biochem, 2008, 102: 278–284
Tan RY, Mabuchi Y, Grabarek Z. Blocking the Ca2+-induced conformational transitions in calmodulin with disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem, 1996, 271: 7479–7483
Grabarek Z. Structure of a trapped intermediate of calmodulin: calcium regulation of EF-hand proteins from a new perspective. J Mol Biol, 2005, 346: 1351–1366
Hu J, Jia X, Li Q, Yang X, Wang K. Binding of La3+ to calmodulin and its effects on the interaction between calmodulin and calmodulin binding peptide, polistes mastoparan. Biochemistry, 2004, 43: 2688–2698
Bowers WF, Fluton S, Thompson J. Clin Pharmacokinet, 1984, 9: 49–60
Chang W, Li ka. Concise Handbook of Analytical Chemistry. Beijing: Peking University publishing company, 1981
Sun YS. The Physical and Chemical Constants of Rare Earth Elements. Beijing: Metallurgy Press, 1978
Xu K, Yang XD, Wang K. La3+ induced binding of calmodulin (CaM) to CaM-binding proteins in rat brain homogenate. Chem J Chin Univ, 2008, 29: 2525–2530
Tiandra N, Kuboniwa H, Ren H, Bax A. Rotational dynamics of calcium-free calmodulin studied by NMR relaxation measurements. Eur Jof Biochem, 1995, 230: 1014–1024
Urbauer JL, Short JH, Dow LK, Wand AJ. Structural analysis of a novel interaction by calmodulin: high-affinity binding of a peptide in the absence of calcium. Biochemistry, 1995, 34: 8099–8109
Mitsuhiko I, Marion D, Kay LE, Shih H, Krinks M, Klee CB, Bax A. Heteronuclear 3D NMR and isotopic labeling of calmodulin: towards the complete assignment of the 1h NMR spectrum. Biochem Pharm, 1990, 40: 153–160
Wendy SV, Brenda RS, Elena R, William RL. Calcium binding to calmodulin mutants monitored by domain-specific intrinsic phenylalanine and tyrosine fluorescence. Biophys J, 2002, 83: 2767
Ohki Sy, Ikura M, Zhang M. Identification of Mg2+-binding sites and the role of Mg2+ on target recognition by calmodulin. Biochemistry, 1997, 36: 4309–4316
Ouyang H, Vogel HJ. Metal ion binding to calmodulin: NMR and fluorescence studies. BioMetals, 1998, 11: 213–222
Dean JA. Lang’s handbook of chemistry, 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2003
Elad P, Ran F, Esther N, Menachem G. A molecular dynamics study of the effect of Ca2+ removal on calmodulin structure. Biophys J, 2006, 90: 3842
Ababou A, Shenvi RA, Desjarlais JR. Long-range effects on calcium binding and conformational change in the N-domain of calmodulin. Biochemistry, 2001, 40: 12719–12726
Ikura M, Hasegawa N, Aimoto S, Yazawa M, Yagi K, Hikichi K. 113Cd-NMR evidence for cooperative interaction between amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains of calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1989, 161: 1233–1238
Pedigo S, Shea MA. Quantitative endoproteinase gluc footprinting of cooperative Ca2+ binding to calmodulin: Proteolytic susceptibility of E31 and E87 indicates interdomain interactions. Biochemistry, 1995, 34: 1179–1196
Medvedeva MV, Polyakova OV, Watterson DM, Gusev NB. Mutation of Lys-75 affects calmodulin conformation. FEBS Letters, 1999, 450: 139–143
Nelson MR, Chazin WJ. Structures of EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins: diversity in the organization, packing and response to Ca2+ binding. BioMetals, 1998, 11: 297–318
Grabarek Z. Structural basis for diversity of the EF-hand calcium-binding proteins. J Mol Biol, 2006, 359: 509–525
Yiming Y, Hsiau-Wei L, Wei Y, Sarah JS, Anna LW, Zhi-ren L, Ivan T, Robert H, Robert W, Jenny JY. Metal binding affinity and structural properties of an isolated EF-loop in a scaffold protein. Protein Eng, 2001, 14: 1001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20671008 & 20637010) and the Key Construction Program of the National “985” Project. Dr. Changwen Jin, Dr. Xianrong Guo and Dr. You Li at Beijing NMR Center, Peking University, are gratefully acknowledged for their assistance in data collection and analysis of Bruker DRX 600 NMR spectrometer. We also thank Dr. T. Squier at University of Kansas for the generous gift of the plasmid encoding gene of chicken calmodulin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Yang, X. & Wang, K. Metal binding discrimination of the calmodulin Q41C/K75C mutant on Ca2+ and La3+ . Sci. China Chem. 53, 797–806 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-0059-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-0059-2