Abstract
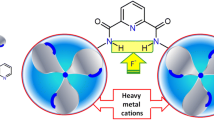
As a powerful macrocyclic host molecule with unique conformation and cavity structure that are fine-tuned by the bridging nitrogen atoms, methylazacalix[4]pyridine (MACP-4) has been shown to selectively recognize Zn2+ and form stable Zn(II)-MACP-4 complexes both in solid state and solution with an association constant up to 5.97 (logK s). The molecular recognition of Zn(II)-MACP-4 complexes towards various amino acids and anions with different geometry was investigated by using the spectral titration methods and X-ray analysis. The Zn(II)-MACP-4 complex was found to recognize the 17 amino acids tested with the association constant up to 3.97 (logK s). On the other hand, the Zn(II)-MACP-4 complex selectively interacted with anions and the maximum association constant of 3.9 (logK s) was obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuroda Y, Kato Y, Higashioji, T, Hasegawa J, Kawanami S, Takahashi M, Shiraishi N, Tanabe K, Ogoshi H. Chiral amino acid recognition by a porphyrin-based artificial receptor. J Am Chem Soc, 1995, 117: 10950–10958, and cited references herein
Imai H, Munakata H, Uemori Y, Sakura N. Chiral recognition of amino acids and dipeptides by a water-soluble zinc porphyrin. Inorg Chem, 2004, 43: 1211–1213
Angelini N, Micali N, Mineo P, Scamporrino E, Villari V, Vitalini D. Uncharged water-soluble Co(II)-porphyrin: A receptor for aromatic α-amino acids. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109: 18645–18651
Schmuck C, Machon U. Amino acid binding by 2-(guanidiniocarbonyl) pyridines in aqueous solvents: A comparative binding study correlating complex stability with stereoelectronic factors. Chem Eur J, 2005, 11: 1109–1118
Ballistreri F P, Notti A, Pappalardo S, Parisi M F, Pisagatte. Multipoint molecular recognition of amino acids and biogenic amines by ureidocalix[5]arene receptors. Org Lett, 2003, 5: 1071–1074
Kim H J, Asif R, Chung D S, Hong J I. Amino acid recognition of pyridine bis(oxazoline)-copper(II) complex in aqueous solvent. Tetrahedron Lett, 2003, 44: 4335–4338
Pascal R A, Spergel J, Engbersen D V. Synthesis and X-ray crystallographic characterization of a (1,3,5)cyclophane with three amide N-H groups surrounding a central cavity: A neutral host for anion complexation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27: 4099–4102
Valiyaveettil S, Engbersen J F J, Verboom W, Reinhoudt D N. Synthesis and complexation studies of neutral anion receptors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1993, 32: 900–901
Bisson A P, Lynch V M, Monahan M K C, Anslyn E V. Recognition of anions through NH-π hydrogen bonds in a bicyclic cyclophane-selectivity for nitrate. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1997, 36: 2340–2342
Kelley T R, Kim M G. Relative binding affinity of carboxylate and its isosteres: Nitro, phosphate, phosphonate, sulfonate, and δ-lactone. J Am Chem Soc, 1994, 116: 7072–7080
Gale P A, Sessler J L, Král V, Lynch V. Calix[4]pyrroles: Old yet new anion-binding agents. J Am Chem Soc, 1996, 118: 5140–5141
Schmidtchen F P. Inclusion of anions in macrotricyclic quaternary ammonium salts. Angew. Chem Int Ed Engl, 1977, 16: 720–721
Schmidtchen F P. Synthese macrotricyclischer amine. Chem. Ber, 1980, 113: 864–874
Worm K, Schmidtchen F P. Molecular recognition of anions by zwitterionic host molecules in water. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1995, 34: 65–66
Yang X, Knobler C B, Hawthorne M F. [12]Mercuracarborand-4, the first representative of a new class of rigid macrocyclic electrophiles: The chloride ion complex of a charge-reversed analogue of [12]crown-4. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1991, 304: 1507–1508
Inoue Y, Hakushi T, Liu Y, Tong L H, Shen B J, Jin D S. Thermodynamics of molecular recognition by cyclodextrins. 1. Calo-rimetric titration of inclusion complexation of naphthalenesulfonates with α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrins: enthalpy-entropy compensation. J Am Chem Soc, 1993, 115: 475–481
Mascal M, Armstrong A, Bartberger M D. Anion-aromatic bonding: A case for anion recognition by π-acidic rings. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124: 6274–6276
Quiñonero D, Garau C, Rotger C, Frontera A, Ballester P, Costa A, Deyà P M. Anion-π interactions: Do they exist? Angew Chem Int Ed, 2002, 41: 3389–3392
Rosokha Y S, Lindeman S V, Rosokha S V, Kochi J K. Halide recognition through diagnostic “anion-π” interactions: Molecular complexes of Cl−, Br−, and I− with olefinic and aromatic π receptors. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2004, 43: 4650–4652
Berryman O B, Bryantsev V S, Stay D P, Johnson D W, Hay B P. Solution phase measurement of both weak σ and C-H⋯X− hydrogen bonding interactions in synthetic anion receptors. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 48–58
Wang D X, Zheng Q Y, Wang Q Q, Wang M X. Halide recogniton by tetraoxacalix[2]arene[2]triazine receptors: Concurrent noncovalent halide-π and lone-pair-π interactions in host-halide-water ternary complex. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 7485–7488
Wang M X, Yang H B. A general and high yielding fragment coupling synthesis of heteroatom-bridged calixarenes and the unprecedented examples of calixarene cavity fine-tuned by bridging heteroatoms. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126: 15412–15422
Katz J L, Feldman M B, Conry R R. Synthesis of functionalized oxacalix[4]arenas. Org Lett, 2005, 7: 91–94
Katz J L, Selby K J, Conry R R. Single-step synthesis of D 3h-symmetric bicyclooxacalixarenes. Org Lett, 2005, 7: 3505–3507
Katz J L, Geller B J, Conry R R. Synthesis of oxacalixarenes incorporating nitrogen heterocycles: Evidence for thermodynamic control. Org Lett, 2006, 8: 2755–2758
Maes W, Van Rossom W, Van Hecke K, Van Meervelt L, Dehaen W. Selective synthesis of functionalized thia- and oxacalix[2]arene[2]-pyrimidines. Org Lett, 2006, 8: 4161–4164
Hao E, Fronczek F R, Vicente M G H. Synthesis of oxacalixarene-locked bisporphyrins and higher oligomers. J Org Chem, 2006, 71: 1233–1236
Chambers R D, Hoskin P R, Kenwright A R, Khalil A, Richmond P, Sandford G, Yufit D S, Howard J A K. Polyhalogenated heterocyclic compounds. Macrocycles from perfluoro-4-isopropylpyridine. Org Biomol Chem, 2003: 2137–2147
Chambers R D, Hoskin P R, Khalil A, Richmond P, Sandford G, Yufit D S, Howard J A K. Macrocycles from polyfluoro-pyridine derivatives. J Fluorine Chem, 2002, 116: 19–22
Li X H, Upton T G, Gibb C L D, Gibb B C. Resorcinarenes as templates: A general strategy for the synthesis of large macrocycles. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125: 650–651
Yang F, Yan L W, Ma K Y, Yang L, Li J H, Chen L J, You J S. Efficient synthesis of a variety of new functionalized oxacalixarenes by Ullmann coupling reactions. Eur J Org Chem, 2006: 1109–1112
Wang Q Q, Wang D X, Ma H W, Wang M X. Synthesis of tetraazacalix[2]arene[2]triazines: Tuning the cavity by the substituents on the bridging nitrogen atoms. Org Lett, 2006, 8: 5967–5970
Wang Q Q, Wang D X, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Formation and conformational conversion of flattened partial cone oxygen bridged calix[2]arene[2]triazines. Org Lett, 2007, 9: 2847–2850
Hou B Y, Zheng Q Y, Wang D X, Huang Z T, Wang M X. Highly efficient construction of large molecular cavity using 1,3-alternate tetraoxzcalix[2]arene[2]triazine as a platform. Chem Commun, 2008, 3864–3866
Ito A, Ono Y, Tanaka K. Tetraaza[1.1.1.1]metacyclophane. New J Chem, 1998, 779–781
Ito A, Ono Y, Tanaka K. N-methyl-substituted aza[1n]metacyclophane: Preparation, structure, and properties. J Org Chem, 1999, 64: 8236–8241
Miyazaki Y, Kanbara T, Yamamoto T. Preparation of new type of azacalixarene, azacalix[n](2,6)pyridine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43: 7945–7948
Wang M X, Zhang X H, Zheng Q Y. Synthesis, structure, and [60]fullerene complexation properties of azacalix[m]arene[n]pyridines. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2004, 43: 838–842
Gong H Y, Zhang X H, Wang D X, Ma H W, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Methylazacalixpyridines: Remarkable bridging nitrogen-tuned conformations and cavities with unique recognition properties. Chem Eur J, 2006, 12: 9262–9275
Gong H Y, Zheng Q Y, Zhang X H, Wang D X, Wang M X. Methylazacalix[4]pyridine: En route to Zn2+-specific fluorescence sensors. Org Lett, 2006, 8: 4895–4898
Gong H Y, Wang D X, Xiang J F, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Highly selective recognition of diols by a self-regulating fine-tunable methylazacalix[4]pyridine cavity: Guest-dependent formation of molecular-sandwich and molecular-capsule complexes in solution and the solid state. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13: 7791–7802
Liu S Q, Wang D X, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Synthesis and structure of nitrogen bridged calix[5]- and [10]-pyridines and their complexation with fullerenes. Chem Commun, 2007, 3856–3858
Zhang E X, Wang D X, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Synthesis of large macrocyclic azacalix[n]pyridines (n = 6–9) and their complexation with fullerenes C60 and C70. Org Lett, 2008, 10: 2565–2568
Tsue H, Ishibashi K, Takahashi H, Tamura R. Exhaustively methylated azacalix[4]arene: Preparation, conformation, and crystal structure with exclusively CH/π-controlled crystal architecture. Org Lett, 2005, 7: 2165–2168
Fukushima W, Kanbara T, Yamamoto T. Azacalix[n]arenas with NH-amino group: NH⋯OCH3 interaction-assisted synthesis, structure, and reactivity. Synlett, 2005, 2931–2934
Selby T D, Blackstock S C. Macrocyclic poly arylamines for rigid connection of poly radical cation spins. Org Lett, 1999, 1, 2053–2055
Suzuki Y, Yanagi T, Kanbara T, Yamamoto T. Preparation of N-(p-tolyl)azacalix[n](2,6)pyridines constructed of various numbers of the recurring unit. Synlett, 2005, 263–266
Gong H Y, Wang D X, Zheng Q Y, Wang M X. Highly selective complexation of metal ions by the self-tuning tetraazacalixpyridine macrocycles. Tetrahedron, 2009, 87–92
Crystallographic data for MACP-4·1.5ZnI2·I2·H2O (C24H24I5N8-OZn1.5′): Mr = 1173.07, Triclinic, space group P21/m, a = 14.781(3), b = 14.358(3), c = 15.814(3) Å, α = 90.00°, β = 107.87°(3), γ = 90.00°, V = 3194.2(11) Å3, T = 293(2) K, full-matrix least-squares refinement on F 2 converged to R F = 0.1456 [I > 2σ(I)], 0.2065 (all data) and Rw(F 2) = 0.4221 [I > 2σ(I)], 0.4636 (all data), goodness of fit 1.724
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20672115, 20875094 & 20532030), Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2007CB808005), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, H., Wang, D., Huang, Z. et al. Recognition of amino acids and anions by a Zn(II)-methylazacalix[4]pyridine complex. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 52, 1639–1645 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0186-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0186-9