Abstract
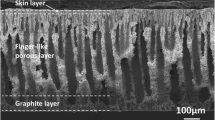
Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) micro tubular electrolyte membranes for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) were prepared via the combined wet phase inversion and sintering technique. The as-derived YSZ micro tubes consist of a thin dense skin layer and a thick porous layer that can serve as the electrode of fuel cells. The dense and the porous electrolyte layers have the thickness of 3–5 μm and 70–90 μm, respectively, while the inner surface porosity of the porous layer is higher than 28.1%. The two layers are perfectly integrated together to preclude the crack or flake of electrolyte film from the electrode. The presented method possesses distinct advantages such as technological simplicity, low cost and high reliability, and thus provides a new route for the preparation of micro tubular SOFCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele B C H, Heinzel A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature, 2001, 414(15): 345–352
Hibino T, Hashimoto A, Inoue T, Tokuno J, Yoshida S, Sano M. Low-operating-temperature solid oxide fuel cell in hydrocarbon-air mixtures. Science, 2000, 288(16): 2031–2033
Shao Z P, Haile S M. A high-performance cathode for the next generation of solid-oxide fuel. Nature, 2004, 431(9): 170–173
Zhan Z L, Barnett S A. An octane-fueled solid oxide fuel cell. Science, 2005, 308: 844–847
Will J, Mitterdorfer A, Kleinlogel C, Perednis D, Gauckler L J. Fabrication of thin electrolytes for second-generation solid oxide fuel cells. Sol St Ion, 2000, 131: 79–96
Basu R N, Blass G, Buchkremer H P, Stover D, Tietz F, Wessel E, Vinke I C. Simplified processing of anode-supported thin film planar solid oxide fuel cells. J Eur Ceram, 2005, 25(4): 463–471
Mineshige A, Fukushima K, Tsukada K, Kobune M, Yazawa T, Kikuchi K, Inaba M, Ogumi Z. Preparation of dense electrolyte layer using dissociated oxygen electrochemical vapor deposition technique. Sol St Ion, 2004, 175: 483–485
Zhou L, Chen M J, Yi B L. Technology progress in tubular solid oxide fuel cell. Battery Bimontly (in Chinese), 2005, 35(1): 63–65
Ota T, Kayama M, Wen C J, Yamada K, Takahashi H. Object-based modeling of SOFC system: Dynamic behavior of micro-tube SOFC. J Power Sou, 2003, 118: 430–439
Sammes N M, Du Y, Bove R. Design and fabrication of a 100 W anode supported micro-tubular SOFC stack. J Power Sou, 2005, 145: 428–434
Suzuki T, Funahashi Y, Yamaguchi T, Fujishiro Y, Awano M. Fabrication and characterization of micro tubular SOFCs for advanced ceramic reactors. J Alloy Com, 2008, 451: 632–635
Liu Y, Mori M, Funahashi Y, Fujishiro Y, Hirano A. Development of micro-tubular SOFCs with an improved performance via nano-Ag impregnation for intermediate temperature operation. Electrochem Comm, 2007, 9: 1918–1923
Tan X, Liu Y, Li K. Mixed conducting ceramic hollow-fiber membranes for air separation. AIChE J, 2005, 51(7): 1991–2000
Young T-H, Chen L-W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination, 1995, 103: 233–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2006AA03Z464), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20676073) and National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2007CB209700)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, X., Yin, W., Meng, B. et al. Preparation of electrolyte membranes for micro tubular solid oxide fuel cells. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 51, 808–812 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0068-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0068-6