Abstract
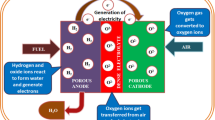
Two types of lanthanum doped strontium manganite (LSM)-yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) composite cathodes were prepared, one with the finger-like straight open pores by the phase inversion tape casting, and the other with the randomly distributed tortuous pores by the conventional tape casting. A gas permeation flux of 42.5 × 105 Lm−2 h−1 was measured under a trans-membrane pressure of 0.6 bar for the former while only 10.6 × 105 Lm−2 h−1 for the latter. Fuel cells supported on the as-prepared LSM-YSZ composite cathodes were fabricated, comprising a 15 μm thick YSZ electrolyte layer and a 20 μm thick NiO-YSZ anode. The electrochemical performance of the fuel cells was measured using H2 as fuels and air as oxidants. The cell supported on the phase-inversion derived cathode showed a maximum power density of 362 mWcm−2 at 850 °C, while only 149 mWcm−2 for the cell supported on the cathode formed by the conventional method. The difference in the electrochemical performance between the two cells can be attributed to the pore structure of the cathode supports. It is concluded that the phase inversion tape casting provides a simple and effective approach for tailoring the pore structure of the cathode support and thus enhancing the electrochemical performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. Steele, A. Heinzel, Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 414(6861), 345–352 (2001)
S.C. Singhal, Science and Technology of Solid-Oxide Fuel Cells. MRS Bull. 25(03), 16–21 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2000.13
X. Li, N. Xu, X. Zhao, K. Huang, Performance of a commercial cathode-supported solid oxide fuel cells prepared by single-step infiltration of an ion-conducting electrocatalyst. J. Power Sources 199, 132–137 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.10.079
T.X. Ho, P. Kosinski, A.C. Hoffmann, A. Vik, Modeling of transport, chemical and electrochemical phenomena in a cathode-supported SOFC. Chem. Eng. Sci. 64(12), 3000–3009 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2009.03.043
K. Yamahara, C. Jacobson, S. Visco, X. Zhang, L. Dejonghe, Thin film SOFCs with cobalt-infiltrated cathodes. Solid State Ionics 176(3–4), 275–279 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2004.08.017
K. Huang, A. Zampieri, M. Ise, Cathode polarizations of a cathode-supported solid oxide fuel cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(10), B1471 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3478145
Y. Liu, S. Hashimoto, H. Nishino, K. Takei, M. Mori, Fabrication and characterization of a co-fired La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ cathode-supported Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 thin-film for IT-SOFCs. J. Power Sources 164(1), 56–64 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.10.093
G. Miao, C. Yuan, T. Chen, Y. Zhou, W. Zhan, S. Wang, Sr2Fe1+xMo1−xO6−δ as anode material of cathode–supported solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41(2), 1104–1111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.12.045
K. Yamahara, C. Jacobson, S. Visco, L. Dejonghe, Catalyst-infiltrated supporting cathode for thin-film SOFCs. Solid State Ionics 176(5–6), 451–456 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2004.09.023
M. Liu, D. Dong, F. Zhao, J. Gao, D. Ding, X. Liu, G. Meng, High-performance cathode-supported SOFCs prepared by a single-step co-firing process. J. Power Sources 182(2), 585–588 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.04.039
T. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Fang, L. Lei, C. Ren, F. Chen, Steam electrolysis in a solid oxide electrolysis cell fabricated by the phase-inversion tape casting method. Electrochem. Commun. 61, 106–109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2015.10.015
C. Jin, C. Yang, F. Chen, Effects on microstructure of NiO–YSZ anode support fabricated by phase-inversion method. J. Membr. Sci. 363(1–2), 250–255 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.07.044
C. Ren, T. Liu, P. Maturavongsadit, J.A. Luckanagul, F. Chen, Effect of PEG additive on anode microstructure and cell performance of anode-supported MT-SOFCs fabricated by phase inversion method. J. Power Sources 279, 774–780 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.140
W. He, H. Huang, G. J-f, L. Winnubst, C. C-s, Phase-inversion tape casting and oxygen permeation properties of supported ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 452, 294–299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.09.063
H. Huang, J. Lin, Y. Wang, S. Wang, C. Xia, C. Chen, Facile one-step forming of NiO and yttrium-stabilized zirconia composite anodes with straight open pores for planar solid oxide fuel cell using phase-inversion tape casting method. J. Power Sources 274, 1114–1117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.10.190
M. Marinšek, K. Zupan, J. Maeek, Ni–YSZ cermet anodes prepared by citrate/nitrate combustion synthesis. J. Power Sources 106(1), 178–188 (2002)
S.U. Rehman, R.-H. Song, J.-W. Lee, T.-H. Lim, S.-J. Park, S.-B. Lee, Effect of GDC addition method on the properties of LSM–YSZ composite cathode support for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Int. 42(10), 11772–11779 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.098
T. Liu, C. Ren, S. Fang, Y. Wang, F. Chen, Microstructure tailoring of the nickel oxide-Yttria-stabilized zirconia hollow fibers toward high-performance microtubular solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(21), 18853–18860 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am5046907
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NOs.51572255, 51602228).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Lin, J., Liu, T. et al. Tailoring the pore structure of cathode supports for improving the electrochemical performance of solid oxide fuel cells. J Electroceram 40, 138–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-018-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-018-0112-7