Abstract
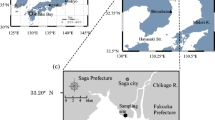
Sediment denitrification rates at six Yangtze River estuary tidal flat locations (mudflats and salt marshes) were measured from July 2003 to October 2004. In winter and summer, spatial distribution of denitrification rates was not great in the Yangtze estuary, while in spring and autumn, denitrification rates had a great spatial distribution because of the human activity effect. The temporal change of denitrification rates was greater. They ranged from 0.2 to 36.4 μmolN·m−2·h−1, and were higher in the summertime. The annual average of sediment denitrification rate was 18.2±12.3 μmolN·m−2·h−1 in the middle tidal flat and 15.1±9.45 μmolN·m−2·h−1 in the low tidal flat in the Yangtze estuary. Data analysis indicated that the temperature was the primary factor controlling the process of denitrification (significant positive correlation, P<0.01); at the same time, the content of sediment total nitrogen (TN) and the molar ratio of sediment carbon and nitrogen (C/N) had significant positive correlation (P<0.05) and negative correlation (P<0.05) with denitrification rates, respectively. In the Yangtze estuary, increasing of water salinity had no significant inhibition of denitrification because of the wide change range of water salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galloway J N, Schlesinger W H, Levy H H, Michaels A, Schnoor J L. Nitrogen fixation: anthropogenic enhancement-environmental response. Global Biogeochem Cy, 1995, 9(2): 235–252
Fields S. Global nitrogen cycling out of control. Environ Health Persp, 2004, 112(4): A556–A563
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis. Washington DC: Island Press, 2005, 34
Stevens C J, Dise N B, Mountford J O, Gowing D J. Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science, 2004, 303: 1876–1879
Thomas J A, Telfer M G, Roy D B, Preston C D, Greenwood J J D, Asher J, Fox R, Clarke R T, Lawton J H. Comparative losses of British butterflies, birds, and plants and the global extinction crisis. Science, 2004, 303: 1879–1881
Martin T L, Kaushik N K, Trevors J T, Whiteley H R. Review: Denitrification in temperate climate riparian zones. Water Air Soil Poll, 1999, 111: 171–186
Hopkins T S, Kinder C A. LOICZ land and ocean interactions in the coast zone. IGBP Core Project Report, N C USA. 1993
Nedwell D B. Estuaries and saltmashes: Interface between land and sea. Environ Manage Health, 1996, 7(2): 20–23
Trimmer M, Nedwell D B, Sivyer D B, Malcolm S J. Nitrogen fluxes through the lower estuary of the Great Ouse, England: the role of the bottom sediments. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser, 1998, 163: 109–124
Chen Z, Wang D, Xu S, Zhang X, Liu J. Inorganic nitrogen fluxes at the sediment-water interface in tidal flat of the Yangtze Estuary. Act Geo S (in Chinese), 2005, 60(2): 328–336
Wang D, Chen Z, Xu S, Hu L, Wang J. Denitrification in Chongming east tidal flat sediment, Yangtze Estuary, China. Sci China Ser D-Earth, 2006, 49(10): 1090–1097
Gu H, Xiong X, Liu M, Li Y. Geochemistry of nitrogen in Changjiang estuary I. nitrate in Changjiang estuary sea water. Shand Mar College Act (in Chinese), 1981, 11(4): 37–46
Fu R, Shen H. The fluxes of the dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus at fresh water end member in the Changjiang Estuary. Act Oceanol S (in Chinese), 2002, 24(4): 34–43
Shen Z, Liu Q, Zhang S, Miao H, Zhang P. A nitrogen budget of the Changjiang River catchment. Ambio, 2003, 32: 65–69
Shen Z, Liu Q, Zhang S, Miao H, Zhang P. The dominant controlling factors of high content inorganic N in the Changjiang River and its mouth. Oceanol Limnol S (in Chinese), 2001, 33(5): 465–473
Duan S, Zhang S, Chen B, Zhang X, Wang L, Yan W. Concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus and nutrient transport to estuary of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2000, 21(1): 53–56
Hou L, Liu M, Jiang H, Xu S, Ou D, Liu Q, Zhang B. Ammonium adsorption by tidal flat surface sediments in the Yangtze Estuary. Environ Geol, 2003, 45: 72–78
Wang D, Chen Z, Qian C, Xu S. Effect of salinity on NH +4 exchange behavior at the sediment-water interface in east Chongming tidal flat. Mar Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2002, 21(3): 5–9
Chen Z, Liu J, Xu S, Wang D, Zheng X. Impact of macrofaunal activities on the DIN exchange at the sediment-water interface along the tidal flat of Yangtze River estuary. Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2005, 26(6): 43–50
Qian C, Chen Z, Hu L, Deng H. Effects of sediment resuspension on nitrogen and phosphate exchange at the sediment-water interface in east Chongming tidal flat. Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2003, 24(5): 114–119
Ou D, Liu M, Hou L, Liu Q, Zhang B, Yang Y. Effect of reclamation on the distribution of inorganic nitrogen in sediments from Donghai beach. Mar Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2002, 21(8): 18–22
Xu J, Wang Y, Wang Q, Yin J. Nitrous oxide concentration and nitrification and denitrification in Zhujiang River Estuary, China. Act Oceanol S, 2005, 24(3): 122–130
Yin S, Cheng L, Shen Q. Denitrification and nitrate reduction to ammonium in Taihu lake and Yellow sea inter-tidal marine sediment. Pedosphere, 1999, 9(4): 305–309
Wang D, Chen Z, Wang J, Xu S, Yang H, Chen H, Yang L, Hu L. Dentrification, nitrous oxide emission and adsorption in intertidal flat, Yangtze Estuary, in summer. Geochimica (in Chinese), 2006, 35(3): 221–226
Deng H, Chen Z, Xu S, Wang D, Liu J, Liu W. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in landfill leachate in summer by the tideland near Laogang Landfill in Shanghai. Environ Pollut Prot (in Chinese), 2005, 27(6): 401–406
Rudolph J, Frenzel P, Pfennig N. Acetylene inhibition technique underestimates in situ denitrification rates in intact cores of freshwater sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 1985: 101–106
Knowles R. Acetylene inhibition technique: development, advantage, and potential problem. In: Revsbech N P, Sorensen J (Eds.), Denitrification in Soil and Sediment. New York: Plenum Press, 1990, 151–166 (FEMS Symposium No. 56)
Teissier S and Torre M. Simultaneous assessment of nitrification and denitrification on freshwater epilithic biofilms by acetylene block method. Water Res, 2002, 36: 3903–3811
Han W Y. The Investigation Manual On Chemical Elements in Sea Water (in Chinese). Beijing: Ocean Press, 1986. 121–148
Bao S. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis (in Chinese). Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. 30–34
Nedwell D B, Jickells T D, Trimmer M, Sanders R. Nutrients in estuaries. Adv Ecol Res, 1999, 29: 43–92
Hamersley M R, Howes B L. Control of denitrification in a septage-treating artificial wetland: The dual role of particulate organic carbon. Water Res, 2002, 36: 4415–4427
Barnes J, Owens N J P. Denitrification and nitrous oxide concentrations in the Humber estuary, UK, and adjacent coastal zones. Mar Pollut Bull, 1998, 37: 247–260
Livingstone M W, Smith R V, Laughlin R J. A spatial study of denitrification potential of sediment in Belfast and Strangford Loughs and its significance. Sci Total Environ, 2000, 251/252: 369–380
Casey R E, Taylor M D, Klaine S J. Localization of denitrification activity in macropores of a riparian wetland. Soil Biol Biochem, 2004, 36: 563–569
Ogilvie B, Nedwell D B, Harrison R M, Robinson A, Sage A. High nitrate, muddy estuaries as nitrogen sinks: The nitrogen budget of the River Colne Estuary (United Kingdom). Mar Ecol-Prog Ser, 1997, 150: 217–228
Pattinson S N, Garcia Ruiz R, Whitton B A. Spatial and seasonal variation in denitrification in the Swale-Ouse system, a river continuum. Sci Total Environ, 1998, 210: 289–305
Herbert R A. Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 1999, 23: 563–590
Zimmerman A R, Benner R. Denitrification, nutrient regeneration and carbon mineralization in sediments of Galveston Bay, Texas, USA. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser, 1994, 114(3): 275–288
Nowicki, B. L. The effect of temperature, oxygen, salinity, and nutrient enrichment on estuarine denitrification rates measured with a modified nitrogen gas flux technique. Estuar Coast Shelf S, 1994, 38: 137–156
Conley D J, Johnstone R W. Biogeochemistry of N, P and Si in Baltic Sea sediments: Response to a stimulated deposition of a spring diatom bloom. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser, 1995, 122(1–3): 265–276
Rysgaard S, Thastum P, Dalsgaard T, Christensen P B, Sloth N P. Effects of salinity on adsorption capacity, nitrification and denitification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries, 1999, 22(1): 21–30
Magalhães C M, Joye S B, Moreira R M, Wiebe W J, Bordalo A A. Effect of salinity and inorganic nitrogen concentrations on nitrification and denitrification rates in intertidal sediments and rocky biofilms of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Water Res, 2005, 39: 1783–1794
Saunders D L, Kalff J. Denitrification rate in the sediment of Lake Memphremagog, Canada-USA. Water Res, 2001, 35(8): 1897–1904
Nedwell D B. Distribution and pool sizes of microbially available carbon in sediment measured by a microbiological assay. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 1987, 45: 47–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40173030, 40571006 and 40131020), the Science & Technology Department of Shanghai (Grant Nos. 05DZ120007 and 05JC14059) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Chen, Z., Xu, S. et al. Denitrification in tidal flat sediment, Yangtze estuary. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 50, 812–820 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0109-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0109-6