Abstract
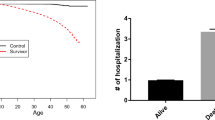
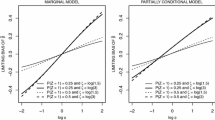
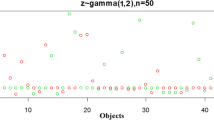
Multivariate recurrent event data arises when study subjects may experience more than one type of recurrent events. In some situations, however, although event times are always observed, event categories may be partially missing. In this paper, an additive-multiplicative rates model is proposed for the analysis of multivariate recurrent event data when event categories are missing at random. A weighted estimating equations approach is developed for parameter estimation, and the resulting estimators are shown to be consistent and asymptotically normal. In addition, a model-checking technique is presented to assess the adequacy of the model. Simulation studies are conducted to evaluate the finite sample behavior of the proposed estimators, and an application to a platelet transfusion reaction study is provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P K, Gill R D. Cox’s regression model for counting processes: A large sample study. Ann Statist, 1982, 10: 1100–1120
Cai J, Schaubel D E. Marginal mean/rates models for multiple type recurrent event data. Lifetime Data Anal, 2004, 10: 121–138
Chen B E, Cook R J. The analysis of multivariate recurrent events with partially missing event types. Lifetime Data Anal, 2009, 15: 41–58
Chen X, Wang Q, Cai J, et al. Semiparametric additive marginal regression models for multiple type recurrent events. Lifetime Data Anal, 2012, 18: 504–527
Gao G, Tsiatis A A. Semiparametric estimators for the regression coefficients in the linear transformation competing risks model with missing cause of failure. Biometrika, 2005, 92: 875–891
Kalbfleisch J D, Prentice R L. The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data, 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2002
Liang K Y, Zeger S L. Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika, 1986, 73: 13–22
Lin D Y, Wei L J, Yang I, et al. Semiparametric regression for the mean and rate functions of recurrent events. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 2000, 62: 711–730
Lin D Y, Wei L J, Ying Z. Checking the Cox model with cumulative sums of martingale-based residuals. Biometrika, 1993, 80: 557–572
Lin F, Cai J, Fine J P, et al. Nonparametric estimation of the mean function for recurrent event data with missing event category. Biometrika, 2013, 100: 727–740
Little R J A, Rubin D B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data. New Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2002
Liu Y, Wu Y, Cai J, et al. Additive-multiplicative rates model for recurrent events. Lifetime Data Anal, 2010, 16: 353–373
Lu K, Tsiatis A A. Multiple imputation methods for estimating regression coefficients in the competing risk model with missing cause of failure. Biometrics, 2001, 57: 1191–1197
Lu W, Liang Y. Analysis of competing risks data with missing cause of failure under additive hazards model. Statist Sinica, 2008, 18: 219–234
Patterson B J, Freedman J, Blanchette V, et al. Effect of premedication guidelines and leukoreduction on the rate of febrile nonhaemolytic platelet transfusion reactions. Transfusion Medicine, 2000, 10: 199–206
Pepe M S, Cai J. Some graphical displays and marginal regression analyses for recurrent failure times and time dependent covariates. J Amer Statist Assoc, 1993, 88: 811–820
Pollard D. Empirical Processes: Theory and Applications. Hayward, CA: Institute of Mathematical Statistics, 1990
Rudin W B. Principles of Mathematical Analysis, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math, 1976
Schaubel D E, Cai J. Rate/mean regression for multiple-sequence recurrent event data with missing event category. Scand J Statist, 2006, 33: 191–207
Schaubel D E, Cai J. Multiple imputation methods for recurrent event data with missing event category. Canad J Statist, 2006, 34: 677–692
Schaubel D E, Zeng D, Cai J. A semiparametric additive rates model for recurrent event data. Lifetime Data Anal, 2006, 12: 389–406
Song X, Sun L, Mu X, et al. Additive hazards regression with censoring indicators missing at random. Canad J Statist, 2010, 38: 333–351
Sun L, Kang F. An additive-multiplicative rates model for recurrent event data with informative terminal event. Lifetime Data Anal, 2013, 19: 117–137
Sun L, Zhu L, Sun J. Regression analysis of multivariate recurrent event data with time-varying covariate effects. J Multivariate Anal, 2009, 100: 2214–2223
van der Vaart A W, Wellner J A. Weak Convergence and Empirical Processes. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1996
Zeng D, Lin D Y. Efficient estimation of semiparametric transformation models for counting processes. Biometrika, 2006, 93: 627–640
Zhao X, Liu L, Liu Y, et al. Analysis of multivariate recurrent event data with time-dependent covariates and informative censoring. Biom J, 2012, 54: 585–599
Zhu L, Sun J, Tong X, et al. Regression analysis of multivariate recurrent event data with a dependent terminal event. Lifetime Data Anal, 2010, 16: 478–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, P., Sun, L., Zhao, X. et al. An additive-multiplicative rates model for multivariate recurrent events with event categories missing at random. Sci. China Math. 58, 1163–1178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-015-5000-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-015-5000-x
Keywords
- additive-multiplicative rates model
- missing data
- multivariate recurrent events
- semiparametric model
- weighted estimating equation