Abstract
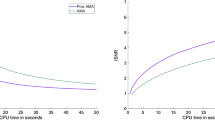
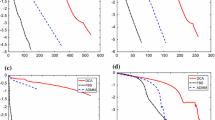
In this paper, we develop a novel alternating linearization method for solving convex minimization whose objective function is the sum of two separable functions. The motivation of the paper is to extend the recent work Goldfarb et al. (2013) to cope with more generic convex minimization. For the proposed method, both the separable objective functions and the auxiliary penalty terms are linearized. Provided that the separable objective functions belong to C 1,1(ℝn), we prove the O(1/∈) arithmetical complexity of the new method. Some preliminary numerical simulations involving image processing and compressive sensing are conducted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attouch H, Bolte J. On the convergence of the proximal algorithm for nonsmooth functions involving analytic features. Math Program, 2009, 116: 5–16
Attouch H, Czarnecki M-O, Peypouquet J. Coupling forward-backward with penalty schemes and parallel splitting for constrained variational inequalities. SIAM J Optim, 2011, 21: 1251–1274
Beck A, Teboulle M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2009, 2: 183–202
Bertsekas D P. Convex Analysis and Optimization. Nashua, NH: Athena Scientific, 2003
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends Mach Learn, 2011, 3: 1–122
Candès E J, Recht B. Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Found Comput Math, 2009, 9: 717–772
Chang T H, Hong M Y, Wang X F. Multi-agent distributed optimization via inexact consensus ADMM. ArXiv: 1402.6065, 2014
Chen G, Teboulle M. A proximal-based decomposition method for convex minimization problems. Math Program, 1994, 64: 81–101
Chen S, Donoho D, Saunders M. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J Sci Comput, 1998, 20: 33–61
Eckstein J. Augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for convex optimization: A tutorial and some illustrative computational results. RUTCOR Research Report, 2012, 34 pages
Figueiredo M A T, Nowak R D. An EM algorithm for wavelet-based image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2003, 12: 906–916
Fukushima M. Application of the alternating direction method of multipliers to separable convex programming problems. Comput Optim Appl, 1992, 1: 93–111
Gabay D, Mercier B. A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximations. Comput Math Appl, 1976, 2: 17–40
Glowinski R. On alternating directon methods of multipliers: A historical perspective. In: Modeling, Simulation and Optimization for Science and Technology. Dordrecht: Springer, 2014, 59–82
Glowinski R, Marroco A. Sur l’approximation, paréléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes de Dirichlet non linéaires. ESAIM Math Model Numer Anal, 1975, 9: 41–76
Goldfarb D, Ma S Q, Scheinberg K. Fast alternating linearization methods for minimizing the sum of two convex functions. Math Program, 2013, 141: 349–382
Golub G H, Van Loan C F. Matrix Computations. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996
Han D R, He H J, Yang H, et al. A customized Douglas-Rachford splitting algorithm for separable convex minimization with linear constraints. Numer Math, 2014, 127: 167–200
Han D R, Yuan X M, Zhang W X. An augmented Lagrangian based parallel splitting method for separable convex minimization with applications to image processing. Math Comp, 2014, 83: 2263–2291
Hansen P, Nagy J, O’Leary D. Deblurring Images: Matrices, Spectra, and Filtering. Philadelphia: SIAM, 2006
He B S, Liao L Z, Han D R, et al. A new inexact alternating directions method for monotone variational inequalities. Math Program, 2002, 92: 103–118
He B S, Tao M, Yuan X M. Alternating direction method with Gaussian back substitution for separable convex programming. SIAM J Optim, 2012, 22: 313–340
He B S, Yuan X M. On the O(1/n) convergence rate of the Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J Numer Anal, 2012, 50: 700–709
Hestenes M R. Multiplier and gradient methods. J Optim Theory Appl, 1969, 4: 303–320
Hong M Y, Luo Z Q. On the linear convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers. ArXiv:1208.3922, 2012
Kiwiel K C, Rosa C H, Ruszczynski A. Proximal decomposition via alternating linearization. SIAM J Optim, 1999, 9: 668–689
Ma S Q. Alternating proximal gradient method for convex minimization. http://www.optimization-online.org/DBHTML/2012/09/3608.html, 2012
Nesterov Y. Introductory Lectures on Convex Optimization: A Basic Course. New York: Springer, 2004
Nesterov Y. Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Math Program, 2005, 103: 127–152
Powell M J D. A method for nonlinear constraints in minimization problems. In: Optimization. New York: Academic Press, 1969, 283–298
Recht B, Fazel M, Parrilo P. Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization. SIAM Rev, 2010, 52: 471–501
Rockafellar R T. Convex Analysis. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1970
Rockafellar R T. Augmented Lagrangians and applications of the proximal point algorithm in convex programming. Math Oper Res, 1976, 1: 97–116
Tao M, Yuan X M. Recovering low-rank and sparse components of matrices from incomplete and noisy observations. SIAM J Optim, 2011, 21: 57–81
Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 1996, 58: 267–288
Tseng P. Further applications of a splitting algorithm to decomposition in variational inequalities and convex programming. Math Program, 1990, 48: 249–263
Wang X F, Yuan X M. The linearized alternating direction method of multipliers for Dantzig selector. SIAM J Sci Comput, 34: 2792–2811
Yang J F, Zhang Y. Alternating direction algorithms for l1-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM J Sci Comput, 2011, 33: 250–278
Yuan X M. Alternating direction method for covariance selection models. J Sci Comput, 2012, 51: 261–273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Cai, X. & Jia, Z. A proximal alternating linearization method for minimizing the sum of two convex functions. Sci. China Math. 58, 1–20 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-015-4986-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-015-4986-4