Abstract
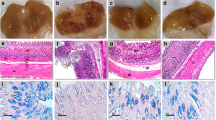
The aim of this study was to elucidate the gastroprotective activity and possible mechanism of involvement of araloside A (ARA) against ethanol- and aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice. The experimental mice were randomly divided into control, model, omeprazole (20 mg/kg, orally) and ARA (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg, orally). Gastric ulcer in mice was induced by intragastric administration of 80% ethanol (10 mL/kg) containing 15 mg/mL aspirin 4 h after drug administration on day 7. The results indicated that ARA could significantly raise gastric juice volume and acidity; ameliorate gastric mucosal blood flow, gastric binding mucus volume, ulcer index and ulcer inhibition rate; suppress H+/K+-ATPase activity, which was confirmed by computer-aided docking simulations; inhibit the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c into the cytoplasm; inhibit caspase-9 and caspase-3 activities and down-regulate mRNA expression levels; down-regulate the mRNA and protein expressions of apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 and protein expression of cleaved poly(ADP ribose) polymerase-1; and up-regulate Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expressions and down-regulate Bax mRNA and protein expressions, thus elevating the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in a dose-dependent manner. Histopathological observations further provided supportive evidence for the aforementioned results. The results demonstrated that ARA exerted beneficial gastroprotective effects on alcohol- and aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice, which was related to suppressing H+/K+-ATPase activity as well as pro-apoptotic protein expression, and promoting anti-apoptotic protein expression, thus alleviating gastric mucosal injury and cell death.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang QY, Huang NY, Wang JZ, Luo HJ, He HB, Ding MR, Deng WQ, Zou K (2013) The H+/K+-ATPase inhibitory activities of Trametenolic acid B from Trametes lactinea (Berk.) Pat, and its effects on gastric cancer cells. Fitoterapia 89:210–217
Shin JM, Vagin O, Munson K, Kidd M, Modlin IM, Sachs G (2008) Molecular mechanisms in therapy of acid-related diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:264–281
Shin JM, Munson K, Vagin O, Sachs G (2009) The gastric H+/K+-ATPase: structure, function, and inhibition. Pflugers Arch 457:609–622
Weidemüller C, Hauser K (2009) Ion transport and energy transduction of P-type ATPases: implications from electrostatic calculations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:721–729
Chakraborty S, Stalin S, Das N, Choudhury ST, Ghosh S, Swarnakar S (2012) The use of nano-quercetin to arrest mitochondrial damage and MMP-9 upregulation during prevention of gastric inflammation induced by ethanol in rat. Biomaterials 33:2991–3001
Lee GJ, Chae SJ, Jeong JH, Lee SR, Ha SJ, Pak YK, Kim W, Park HK (2011) Characterization of mitochondria isolated from normal and ischemic hearts in rats utilizing atomic force microscopy. Micron 42:299–304
Lee MJ, Chen HM, Tzang BS, Lin CW, Wang CJ, Liu JY, Kao SH (2011) Ocimum gratissimum aqueous extract protects H9c2 myocardiac cells from H(2)O(2)-induced cell apoptosis through Akt signalling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/578060
Orsucci D, Mancuso M, Siciliano G (2008) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and PARP-1 network: a new target for neuroprotective effects of tetracyclines? J Physiol 586:2427–2428
Tjandrawinata RR, Nailufar F, Arifin PF (2013) Hydrogen potassium adenosine triphosphatase activity inhibition and downregulation of its expression by bioactive fraction DLBS2411 from Cinnamomum burmannii in gastric parietal cells. Int J Gen Med 6:807–815
Yang ZF, Tang HF, Jia YY, Xi MM, Wen AD (2008) The effect of total saponin of Aralia Taibaiensison Glycemia Lipidan antioxidation in hyperglyce mice. Pharm J Chin PLA 24:110–113
Yook CS (1981) Medicinal plants of Korea. Jinmyung Publishing Co., Ltd, Seoul
Namba T (1980) The encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with color pictures, vol Vol II. Hoikusha Publishing Co., Ltd, Osaka
Munwha Broadcast Corporation (ed.) (1987) Korean folk medicinal therapeutics. Keumbak Publishing. Co., Ltd, Seoul
Lee EB, Kim OJ, Kang SS, Jeong C (2005) Araloside A, an antiulcer constituent from the root bark of Aralia elata. Biol Pharm Bull 28:523–526
He HB, Zhang YF, Li XM, Li XQ, Qin HL, Liu CX, Tang HB, Wang JZ, Zou K (2017) Effect of triterpene from Chaenomeles speciose (Sweet) Nakai on gastric acid secretion and gastric mucosal barrier function in indomethacin induced mice. Biotic Resour 39:211–216
Martín MJ, Marhuenda E, Pérez-Guerrero C, Franco JM (1994) Antiulcer effect of naringin on gastric lesions induced by ethanol in rats. Pharmacology 49:144–150
Shinoda T, Ogawa H, Cornelius F, Toyoshima C (2009) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4 A resolution. Nature 459:446–450
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z (2000) The protein data bank. Anhui Med Pharma J 28:235–242
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Sali A, Blundell TL (1993) Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815
Schrödinger LLC (2010) www.schrodinger.com (New York). Accessed 30 Dec 2017
Vaguine AA, Richelle J, Wodak SJ (1999) SFCHECK: a unified set of procedures for evaluating the quality of macromolecular structure-factor data and their agreement with the atomic model. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 55:191–205
DeLano WL (2004) The PyMOL molecular graphics system. DeLano Scientific, San Carlos
Wang S, He HB, Xiao SZ, Wang JZ, Bai CH, Wei N, Zou K (2014) Comparison of cardioprotective effects of labeled and unlabeled oleanoic acids with new BOPIM dye on primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes following hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Pharmacol Rep 66:677–685
Sohn YA, Hwang SA, Lee SY, Hwang IY, Kim SW, Kim SY, Moon A, Lee YS, Kim YH, Kang KJ, Jeong CS (2015) Protective effect of liriodendrin isolated from Kalopanax pictus against gastric injury. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 23:53–59
Bhattacharya S, Banerjee D, Bauri AK, Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay SK (2007) Healing property of the Piper betel phenol, allylpyrocatechol against indomethacin-induced stomach ulceration and mechanism of action. World J Gastroenterol 13:3705–3713
Lv RX, Du LL, Lu CW, Wu JH, Ding MC, Wang C, Mao NF, Shi ZC (2017) Allicin protects against H2O2- induced apoptosis of PC12 cells via the mitochondrial pathway. Exp Ther Med 14:2053–2059
Huang SL, He HB, Zou K, Bai CH, Xue YH, Wang JZ, Chen JF (2014) Protective effect of tomatine against hydrogen peroxide-induced neurotoxicity in neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 66:844–854
Zhao HG, Zhou SL, Lin YY, Dai HF, Huang FY (2017) Toxicarioside N induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell by activating the p38MAPK pathway. Arch Pharm Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0956-4
Namulema J, Nansunga M, Kato CD, Kalange M, Olaleye SB (2018) Thyroid hormones increase stomach goblet cell numbers and mucin expression during indomethacin induced ulcer healing in Wistar rats. Thyroid Res 11:1–8
Lamers CB, Biemond I, Masclee AA, Veenendaal RA (1996) Therapy and prevention of gastric ulcer. Yale J Biol Med 69:265–270
Higuchi K, Watanabe T, Tanigawa T, Tominaga K, Fujiwara Y, Arakawa T (2010) Sofalcone, a gastroprotective drug, promotes gastric ulcer healing following eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori: a randomized controlled comparative trial with cimetidine, an H2-receptor antagonist. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Suppl 1:S155–S160
Walker J, Hell J, Liszt KI, Dresel M, Pignitter M, Hofmann T, Somoza V (2012) Identification of beer bitter acids regulating mechanisms of gastric acid secretion. J Agric Food Chem 60:1405–1412
Lewin MJ (1999) Cellular mechanisms and inhibitors of gastric acid secretion. Drugs Today (Barc) 35:743–752
Bienia A, Sodolski W, Luchowska E (2002) The effect of chronic alcohol abuse on gastric and duodenal mucosa. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 57:570–582
O’Connor HJ, Dixon MF, Wyatt JI, Axon AT, Dewar EP, Johnston D (1987) Campylobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2:633–634
Tsai HF, Hsu PN (2017) Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori in immune pathogenesis of gastric mucosal damage. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 50:4–9
Luo X, Kraus WL (2012) On PAR with PARP: cellular stress signaling through poly (ADP-ribose) and PARP-1. Genes Dev 26:417–432
Krishnakumar R, Kraus WL (2010) The PARP side of the nucleus: molecular actions, physiological outcomes, and clinical targets. Mol Cell 39:8–24
Cregan SP, Dawson VL, Slack RS (2004) Role of AIF in caspase-dependent and caspase- independent cell death. Oncogene 23:2785–2796
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 81202905, 31370373).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Li, X., Yu, H. et al. Gastroprotective effect of araloside A on ethanol- and aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice: involvement of H+/K+-ATPase and mitochondrial-mediated signaling pathway. J Nat Med 73, 339–352 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1256-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1256-0