Abstract
This study empirically investigates diffusion-based centralities as depictions of student role-based behavior in information exchange, uptake and argumentation, and as consistent indicators of student success in computer-supported collaborative learning. The analysis is based on a large dataset of 69 courses (n = 3,277 students) with 97,173 total interactions (of which 8,818 were manually coded). We examined the relationship between students’ diffusion-based centralities and a coded representation of their interactions in order to investigate the extent to which diffusion-based centralities are able to adequately capture information exchange and uptake processes. We performed a meta-analysis to pool the correlation coefficients between centralities and measures of academic achievement across all courses while considering the sample size of each course. Lastly, from a cluster analysis using students’ diffusion-based centralities aimed at discovering student role-taking within interactions, we investigated the validity of the discovered roles using the coded data. There was a statistically significant positive correlation that ranged from moderate to strong between diffusion-based centralities and the frequency of information sharing and argumentation utterances, confirming that diffusion-based centralities capture important aspects of information exchange and uptake. The results of the meta-analysis showed that diffusion-based centralities had the highest and most consistent combined correlation coefficients with academic achievement as well as the highest predictive intervals, thus demonstrating their advantage over traditional centrality measures. Characterizations of student roles based on diffusion centralities were validated using qualitative methods and were found to meaningfully relate to academic performance. Diffusion-based centralities are feasible to calculate, implement and interpret, while offering a viable solution that can be deployed at any scale to monitor students’ productive discussions and academic success.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Knowledge and behavior flow within social interactions which results in the adoption of innovations, endorsement of opinions, and spread of ideas, just to mention a few examples (Guilbeault et al., 2018) (Anderson et al., 2001; Fields & Kafai, 2009). These phenomena spread within the fabric of social networks through the process of diffusion (Anderson et al., 2001; Singh, 2018). Relationships between individuals are the joints in pathways through which information flows. Some have even compared the resulting pathways to ‘pipes’ that facilitate the flow. As emphasized by Siemens (2004), “the pipe is more important than the content within the pipe.” (Siemens, 2004). Consequently, the network structure, the roles played by collaborators within this structure, and the interaction dynamics at play in this structure all play significant roles in shaping knowledge diffusion.
Graph-based (network) representation of discourse has been established as a credible method and a foundation for visualizing, supporting, and enhancing argumentative knowledge construction in computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) (Baker et al., 2007; Lund et al., 2007; Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Pinkwart et al., 2006; Reed & Rowe, 2004). Therefore, researchers have harnessed the power of graph-based methods such as Social Network Analysis (SNA) to study the diffusion process using network measures to capture the overall network structure, the connectedness of users, and the relationship between collaborators. These methods are then used to further translate these properties into indicators, often referred to as centrality measures (Fields & Kafai, 2009; Saqr et al., 2019; Suthers, 2015). Centrality measures (computed over graph representations) have been successfully demonstrated to map conceptually to the diffusion processes associated with many phenomena such as knowledge transfer, the spread of viral memes, as well as the diffusion of behavior (Mochalova & Nanopoulos, 2013; Sumith et al., 2018). Such successful applications and the practical utility of the diffusion-based centrality measures noted in several fields have motivated this specific work investigating the possible value of these measures in capturing the flow, uptake, and diffusion of knowledge in CSCL settings.
We argue that an approach to characterizing knowledge diffusion that takes advantage of well-established graph-based centrality measures is able to capture knowledge co-construction, uptake, and argumentation in networked CSCL settings. Using network methods to understand the ways knowledge is exchanged, discussed or negotiated in collaborative learning (CL) scenarios aids in understanding students’ roles in collaboration, developing better monitoring mechanisms, and creating more consistent indicators of success (Cakir et al., 2005; Fields & Kafai, 2009; Lee & Tan, 2017a; Suthers & Desiato, 2012). A large volume of research has already sought to capture the essence of student interactions and further translate the representation of these interactions into indicators that can be used for modeling success (see Sect. 2.4). Yet, further research is needed on both fronts. Our work specifically builds on previous insights related to graph-based representation of argumentation and discourse elements in CSCL (Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Scheuer et al., 2010; Schwarz & Glassner, 2007), to the notion of uptake, the idea of worthiness of contributions and knowledge building in CSCL (Chen & Zhang, 2016; Lee & Tan, 2017a; Suthers, 2015; Suthers & Desiato, 2012), and finally to the work on diffusion of knowledge (Banerjee et al., 2013; Fields & Kafai, 2009). We bring these research strands together to provide practical and validated methods for quantifying and tracing interactions, uptake, and argumentation processes, identify relevant roles, and ultimately capture indicators of student success in CSCL.
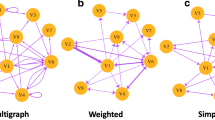
Previous studies in SNA have been mainly reported with small samples and/or for individual courses (see Fig. 2 for a full review), which suggests that a large-scale empirical investigation is needed. To overcome possible selection bias (i.e., reporting only on some interesting courses) or reporting bias (i.e., reporting only on positive findings), we report comprehensive findings from all courses with a collaborative learning design at Qassim University across several academic years (i.e., 69 course offerings in total). To address methodological concerns in pooling the results from the multiple courses, we draw from traditional statistical methods as well as meta-analytic approaches. Meta-analysis provides the means for assessing the consistency of results through estimation of heterogeneity (i.e., variability within results) as well as predictive intervals (i.e., the extent to which future results are expected to be similar) (Gurevitch et al., 2018). We examine the role of diffusion-based centralities in identifying student roles in collaboration and how these roles relate to performance. Most importantly, we validate our findings using a large dataset of manually coded interactions and report the results using the recommended effect sizes in order to rigorously evaluate the magnitude of the findings related to each step. Thus, this study aims to answer the following research questions:
-
RQ1: To which extent do diffusion-based centralities capture information exchange, uptake, and argumentation process?
-
RQ2: Can diffusion-based centralities be consistent indicators of study success in CSCL settings, and if so, which ones?
-
RQ3: Can diffusion-based centralities reveal students’ emergent roles and their possible correlation with learner performance?
Background
The optimal support of knowledge co-construction requires mechanisms that facilitate the mapping and tracing of student contributions. A large body of research in CSCL has demonstrated the worth of several tools and methods for visualizing argumentation processes and providing valuable insights both to students and teachers (Noroozi et al., 2012; Scheuer et al., 2010). This study builds on this immense body of research and offers a method based on graph-based diffusion centralities to help identify productive discussions as well as student roles in the discourse. Throughout this section, we cover graph-based representations of knowledge construction in CSCL. In particular, we build on the concepts of uptake, the spread of knowledge, and argumentation. Then, we provide a review of the literature explaining the concepts of diffusion and how diffusion is modeled. Later, we discuss diffusion metrics and how they are relevant to the dialogical interactions that occur in CSCL. We compare such operationalizations to other existing measures and highlight their advantages. We then review the previous literature on traditional SNA metrics, their use in CSCL, and how this study is meant to fill some of the existing gaps.
Graph-based representation and visualization of discourse in CSCL
The process of knowledge co-construction requires learners to engage in two dialogical spaces: cognitive and relational, both of which are essential elements for the success thereof (Janssen & Bodemer, 2013; Soller et al., 2005). The cognitive space encompasses both cognitive and metacognitive learning activities, such as discussing targeted concepts or learning strategies. The relational space is concerned with negotiations, communications and expressions of ideas (Janssen & Bodemer, 2013; Soller et al., 2005). Interaction in the relational space is aimed at reaching shared understanding about concepts under discussion in the cognitive space (Janssen & Bodemer, 2013). Both dimensions are intertwined since communication and speech acts—the building blocks thereof—incorporate both the cognitive and the relational dimensions. Such dialogical interactions “involve all dimensions of an individual –cognitive, communication, affective,” which make them valuable in educational settings (Mirza & Perret-Clermont, 2009). Therefore, capturing the process of dialogical interactions, uptake and diffusion can help us understand how knowledge is created, exchanged, debated, discussed, endorsed or refuted (Suthers et al., 2010; Wise et al., 2021).
The important elements of dialogical interactions in argumentative knowledge co-construction are participatory contributions related to the administration of participation; practices reflecting responsiveness and reciprocity (i.e., how a student responds, connects, and engages with others’ contributions), and representations of reasoning and argumentation strategies (Noroozi et al., 2012; Scheuer et al., 2010; Wise et al., 2021). According to Scheuer et al., (2010), argumentation may be visually represented in either of these forms: threaded, graph-based, matrix, linear, or hierarchically nested frames (containers). All such formats are types of graphs (or networks) in which the “elements of knowledge or discussions” are the nodes and the relations among such nodes are the edges (Bell, 2013; Pinkwart et al., 2006; Reed & Rowe, 2004). Representation in the form of graphs offers an intuitive method for visualizing the different types of knowledge production. Therefore, graph-based methods have been used extensively for analyzing and visualizing the threaded structure of argumentation transcripts (Baker et al., 2007; Lund et al., 2007; Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Pinkwart et al., 2006; Reed & Rowe, 2004). Examples of application include: supporting decision-making about the current state of debate (van Gelder, 2003), encouraging and helping scaffold discussions (Suthers & Hundhausen, 2003), or offering a medium for debate (Schwarz & Glassner, 2007). Several systems and tools exist to support argumentation and interaction visualization using different types of graphs (Scheuer et al., 2010). For instance, Digalo allows students to represent their argumentation as graphs within the tool (Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Schwarz & Glassner, 2007); Araucaria allows users to analyze the graphical representation of their arguments; DebateGraph allows the visualization of debates (Miller & Volz, 2013), and Metafora allows creating and visualizing plans as graphs (Schwarz et al., 2015).
Graph-based quantitative measures can also be used to capture the process of argumentation, debate, or knowledge construction. In CSCL, adding a post (i.e., a node) represents turn-taking. The advancement of argumentation may be visualized as adding another post (node) to a post (node) in an existing thread (Suthers, 2015; Wise et al., 2021). Aspects like depth, branching, and structure of interactions can then be captured and quantified in the form of graph-analytic measures. For instance, Clark & Sampson (2017) analyzed the quality of argumentation in threaded discussions using coded interactions. The authors measured the length and depth of threaded discussions and found that discussions with oppositional episodes are significantly longer, structurally more sophisticated, and tend to be grounded with reasons. (Clark & Sampson, 2017). The depth and branching of argumentation has been found to be malleable to intervention using collaborative scripts, which was found to be reflected in longer and deeper (more branched) forum threads (Weinberger et al., 2017). Similarly, the quality of argumentation has also been demonstrated to improve in response to providing appropriate visualization of the argumentation graphs (Lund et al., 2007; Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Nussbaum et al., 2007; Tsai et al., 2012).
Uptake and reply-worthiness
Further work on capturing the argumentation and knowledge construction process comes from research in learning analytics and SNA. Suthers et al., (2010) offered compelling evidence of how analytics can capture the process of knowledge construction or argumentation in what he referred to as the “uptake” process. Uptake—according to the authors—is a process that occurs when a learner “takes” a peer’s contribution and builds on it, advances the argument contained within it, or responds (Suthers et al., 2010). Such uptake is contingent on the relevance and the worthiness of the peer’s interaction. Their approach operationalizes the uptake concept in threaded discussions using graphs of relationships. Subsequently, Suthers (2015) suggested the Traces framework, which “identifies observable contingencies between events and uses these to build more abstract models of interaction and ties represented as graphs”. They used the Traces framework for the identification of central participants, significant interactions, as well as roles (Suthers, 2015). In the same vein, Lee & Tan (2017a) argued that learners respond to ideas or interactions in a knowledge-building setting based on their promisingness, i.e., relevance to the learning objectives or goals (Chen et al., 2015). Thus, the mining of uptake offers an indication of the promisingness and, more importantly, the learner’s contribution to the discourse (Lee et al., 2016; Lee & Tan, 2017a). The authors used a combination of SNA centrality measures (e.g., betweenness and degree centrality) to discover promising ideas and how the promising ideas influence the subsequent discourse (Lee et al., 2016). Further support for the concept of promising ideas was demonstrated using a combination of SNA metrics, which was able to discover more promising ideas. The tracing of uptake of promising ideas was also demonstrated using several methods, e.g., temporal analytics to demonstrate the evolution of uptake overtime (Lee & Tan, 2017a, b), using the “Idea Pipeline framework” which combines SNA and quality metrics (Lee et al., 2016).
Tracking the flow or diffusion of the argumentation process has also been demonstrated by several researchers using traditional methods. Anderson et al., (2001) studied the spread of arguments in children. Their main findings were that arguments “snowball”. For example, when a useful argument is used by a child, the tendency to spread and the probability of uptake or diffusion of this argument remains high (Anderson et al., 2001; Fields & Kafai, 2009) used ethnographic methods to track the diffusion of knowledge-sharing among school children. The authors were able to map the diversity of knoweldge-sharing situations and spaces that children use (Fields & Kafai, 2009). Similar work has been performed by Jeong et al., (2011) who used sequential analysis of coded discourse to study the transitions within and between argumentation episodes among children. The authors found that opposing arguments are more likely to elicit replies (be taken up) and trigger longer chains of discourse moves with rich argumentation.
This literature review shows that research in the learning sciences and in CSCL has investigated the potential of graph and related computational methods through use of different tools and taxonomies (e.g., flow, diffusion, uptake, spread, or evolution) for the purpose of studying the way students interact as well as the structure, quality, and content of such interactions. Our review of the literature offers credible empirical evidence of the value of tracing knowledge sharing, argumentation, and diffusion of knowledge using graph-based methods (or networks).
In this article, we build on previous research and use SNA to capture the process of argumentation, knowledge building, and uptake in threaded discussions represented as graphs. We do so by using diffusion centrality measures that were established in other fields to capture the diffusion of knowledge, behavior, and information related to the concept of uptake. The diffusion-based metrics (based on graph representations of threaded interactions) have been demonstrated to capture uptake process both in real-life settings and in simulation settings at least as well as more sophisticated diffusion modeling approaches and therefore provide a more practical alternative (Banerjee et al., 2013; Kitsak et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2016; Sumith et al., 2018).
Diffusion
The study of diffusion in graphs has been extensively investigated and modeled in a wide variety of phenomena across several domains, including the adoption of new fashion, the uptake of information, the ripple effect of stock market disturbances, the growth of political movements, the viral spread of Internet memes and, recently, in educational contexts (see e.g., Genlott et al., 2019; Guilbeault et al., 2018; Saqr & Viberg, 2020). According to Barabási (2013), a “key discovery of network science is that the architecture of networks emerging in various domains of science, nature, and technology are similar to each other.” Thus, models developed, e.g., for the examination of diffusion in social networks, were successfully employed for the study of the dynamics of e.g., the uptake of knowledge and diffusion of behavior (Cowan & Jonard, 2004; Kitsak et al., 2010; Singh, 2018). In fact, most of the trials at studying the uptake, diffusion or co-evolution of knowledge have harnessed the power of graph-based methods (e.g., networks) (Jalili & Perc, 2017; Scheuer et al., 2010; Suthers et al., 2010; Suthers & Desiato, 2012; Zhang et al., 2016). Yet, compared to other fields, diffusion-related research attempts in the area of education have hitherto been scarce (Burgess et al., 2018). In this study, we build on the previous work and extend such insights to the process of knowledge sharing, argumentation, and uptake in CSCL environments.
Diffusion modeling
Several models have been suggested to address the diffusion problem. These models include cascade-based models, such as the popular SIR (susceptible–infected–recovered) model, which proposes that an individual can spread an idea or opinion to one of his/her contacts with a certain probability (Singh, 2018; Zhang et al., 2016). The transmission rate (or uptake) depends mainly on the persuasiveness (related to promisingness discussed in Sect. 2.2) of the idea and the readiness of the contact to endorse it. Another type of such model is a homophily-based model, which proposes that similarities among individuals affect their adoption of knowledge or endorsement of behavior (Shakarian et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2016). Tipping models attempt to identify when an individual may adopt an idea, behavior, or technology. The models propose that there is a tipping point when a significant number of neighbors adopt such an idea. The diffusion in such models depends on the mass of adopters and their commitment and enthusiasm for the idea (Singh, 2018; Zhang et al., 2016).
The diffusion of knowledge, behavior or the uptake of information (e.g., in CSCL environment)—otherwise known as complex contagion—requires trust, multiple interactions and maybe even reinforcement from multiple sources to change an individual’s opinion (Centola, 2010; Guilbeault et al., 2018; Jalili & Perc, 2017; Lehmann & Ahn, 2018). As a possible solution to the complexity of modeling knowledge diffusion, researchers have capitalized on the wealth of information encoded in the individual position in a network to derive measures that can help identify the spreaders using simple metrics (Anderson et al., 2001; Banerjee et al., 2013; Kitsak et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2016; Sumith et al., 2018). Diffusion metrics use computational methods to identify the structural properties that facilitate the diffusion and uptake process, i.e., the process of uptake of information, or those who influence the way information is endorsed (Banerjee et al., 2013; Kitsak et al., 2010). These metrics aim to accurately reflect the uptake, the reply-worthy (promising) information to be endorsed and the actors’ roles (Banerjee et al., 2013; Kitsak et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2016; Sumith et al., 2018). A prime advantage of diffusion metrics is that they are easier to compute and require less technical knowledge compared to the more sophisticated diffusion models (Kitsak et al., 2010; Mochalova & Nanopoulos, 2013; Saqr & Viberg, 2020). Diffusion metrics encompass the traditional centrality measures and diffusion-specific measures, which have proven computationally efficient and to have good performance compared to more established complicated metrics (Guilbeault et al., 2018; Pei et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2016).
Diffusion metrics
Traditional centrality measures.
In CSCL, degree centralities, out-degree (number of contributed posts) and in-degree (received replies), quantify participatory contribution and externalization of a student as well as the reply-worthiness of the contributions he or she makes (Fig. 1). Higher degree centralities have been linked to the ability to spread information: a student with more contacts can—literally—spread information to a greater extent than another one with limited contacts. Nonetheless, the degree measures are local measures, i.e., they capture only the direct replies. As such, degree centralities offer no information about the uptake beyond the students’ immediate replies as they do not capture the connectedness of the contacts or how far information will be negotiated or endorsed (Saqr & Viberg, 2020; Sumith et al., 2018). Figure 1 shows four networks to illustrate the basic concepts of centrality measures. In all four networks, node A has higher values of the corresponding centrality than node B. In other words, Fig. 1(I) shows that node A receives more contributions than B (in-degree); Fig. 1(II) shows node A is closer to most other nodes than B (closeness); Fig. 1(III) shows node A lies in-between two groups of nodes (betweenness), and Fig. 1(IV) shows node A has the most outgoing connections (out-degree).
In addition to degree centralities, there are several other centrality measures that are often operationalized in CSCL settings. For instance, closeness centrality (inverse distance to others) reflects the reachability of a student by quantifying the closeness to all others in the network. Thus, a student with higher closeness centrality has a shorter distance to others and can possibly spread more information (Jalili & Perc, 2017; Mochalova & Nanopoulos, 2013). Betweenness centrality quantifies the extent to which a student is positioned in paths between two nodes within a network; that is, a student connecting two isolated groups may have access to resources from both, and therefore, has an advantage over the members of either group. Empirical research on networks has shown a limited correlation between betweenness centrality and the range of the spread of influence or diffusion (Kitsak et al., 2010; Mochalova & Nanopoulos, 2013).
Diffusion-based centralities.
An important finding in diffusion research is that the uptake probability—and consequently diffusion resulting from an interaction—is dependent on the position of the node that created it as well as the connectedness of the node and its embeddedness in the network (Anderson et al., 2001; Lee & Tan, 2017b; Suthers, 2015; Suthers & Desiato, 2012). Research has confirmed a positive correlation between such characteristics and diffusion capability. This work has resulted in a collection of diffusion-based centrality measures that have been proposed as a way to bring these characteristics together (position, connectedness and embeddedness) (Guilbeault et al., 2018; Saqr & Viberg, 2020; Singh, 2018; Zhang et al., 2016). In this study, based on the literature, we have selected the measures that have shown the potential for capturing the uptake process in online interactions. The selected measures represent the diffusion degree considering the cardinality of contacts, the connectedness of contacts, and the embeddedness of the node.
Nobel Laureate Abhijit Banerjee proposed the diffusion centrality in a seminal article in Science (Banerjee et al., 2013). Simply put, diffusion centrality measures how far a piece of information given to a user will be endorsed. Banerjee et al., (2013) empirically investigated if diffusion centrality captures the process of uptake of information about microfinance solutions among villagers in India. Villagers who had high diffusion centrality were more likely to spread the word and to encourage people to endorse (i.e., take up) their opinion. What is more, villagers were smart at identifying the key influencers and consequently, they were strategically selective from whom they got their information. The authors concluded that diffusion centrality performed better than traditional centrality measures in identifying spreaders of information (Banerjee et al., 2013). Subsequently, several researchers have applied diffusion centrality in several domains, e.g., spread rumors, politics and crime networks (Banerjee et al., 2019; Saqr & Viberg, 2020). This measure takes a practical approach by mapping the possibility of an interaction to generate replies (e.g., debate or an argument), and how these replies generate further replies. In doing so, diffusion centrality captures the uptake or the promisingness of interaction and consequently how other replies are contingent on such contributions.
Other important measures have similarly reflected the uptake and the diffusion probability of an individual to be related to the size and connectedness measured based on the nodes’ connections. In fact, research has consistently shown that there is a positive correlation between the extent of the connectedness of contacts and the uptake or diffusion potential of the node (Bae & Kim, 2014; Centola, 2010; Liu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017). A group of measures was proposed to compute the connectedness of the node.
In our study, the following measures were selected:
-
Maximum Neighborhood Component (MNC) is the cardinality of connected neighboring nodes excluding the target node. In a CSCL context, MNC reflects the breadth and length of the threads that the interaction is part of. A promising or reply-worthy interaction is expected to engage diverse participants and generate long threads of discussions resulting in sizable subnetworks and consequently higher values of MNC. The higher the MNC values are, the more the expected range of uptake (Liu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017).
-
Coreness (k-core property or linkage) is similar to H-index. The coreness of a network is defined as the maximum size subnetwork in which each node has at least degree k (Kitsak et al., 2010). The coreness of a vertex is the maximum k to which it belongs (Kitsak et al., 2010). A node that generates significant promising contributions attracts other participants with significant contributions and strong connections. Representing these relations as a graph places these nodes strategically towards the core of the network. Such strategic location enables the spread of information to a larger fraction of the network. Coreness has recently attracted attention following the key findings of the seminal work of Kitsak et al., (2010), who found that a user positioned in the core of a network has a significant influence on the information diffusion process to a larger sector of the community compared to degree centrality. Several other examples confirmed such findings, with empirical evidence on the spread of disease, rumors, economic crisis information and online information (Bae & Kim, 2014; Liu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017). In CSCL settings, users who are involved with highly interactive posts that attract active users (with high coreness values) are more likely to have their ideas spread, discussed and generate more interactions. Higher coreness values also reflect engagement in dense threads with highly interactive students.
-
Cross Clique Connectivity measures the number of cliques or triangles a node belongs to. A higher number of cliques reflects higher degrees of embeddedness, connectivity of the contacts, as well as strong ties. Cliques and variants have been studied extensively in different fields, including education. In CSCL, when interaction generates replies by two different participants, this creates a triangle with the initial post. Such triangles/cliques are a sign of the promisingness and reply-worthiness of the post. Research has shown that nodes embedded in more cliques are more likely to be spreaders. Cross-clique connectivity has been investigated and proven useful in several studies for the spread of online knowledge (Faghani & Nguyen, 2013; Saqr & Viberg, 2020).
To demonstrate the diffusion-based centrality measures—how they capture the process of uptake, and how they differ from traditional degree measures—a fictional CSCL scenario is demonstrated in Fig. 2. Although, in the sample network, node A started the conversation and received replies from B, C, D, E and F, said replies did not generate further discussions, debates or arguments. Conversely, the reply from G sparked a meaningful (promising) conversation that stimulated further productive discussion (uptake), which received other meaningful replies from H, I and J (Table 1). Those nodes had the highest diffusion values, as they were the nodes that stimulated the argumentation process, debates, and co-constructed knowledge. Node G has the highest value of diffusion centrality (followed by J, A), and it is embedded in more cliques than node A as well. Therefore, it is expected that node G—and also J—has a higher probability of uptake compared to node A (Table 1). Nodes G, H, I, and J have the highest coreness values (k = 3): they lie within the core of the network as well as have three connections to nodes with at least three connections (k = 3). Such strategic core positions resulted from their promising ideas that generated such intense engagement. While node A had six connections, these connections were mostly isolated (with just one connection each) so, although A had the highest degree centrality, it had the third-highest diffusion centrality. This example demonstrates how diffusion-based centrality measures were capable of accurately capturing the uptake and argumentation process compared to the traditional centrality measures.
SNA and academic achievement
CSCL provides students with an optimal medium for collaboration, productive interactions, and knowledge construction (Jeong & Hmelo-Silver, 2016). The relationship between productive students’ interactions in CSCL settings and improved academic achievement is widely accepted. In fact, several reviews and meta-analyses that synthesize a large number of other studies have provided firm empirical evidence of the positive association between the value of students’ interactions in collaborative learning settings and cognitive gain, as well as skill and knowledge acquisition (Borokhovski et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2018; Saqr & López-Pernas, 2021). Therefore, researchers have resorted to SNA to capture students’ interactions in CSCL settings and translate them into indicators of success, with inconclusive results. We believe that, since diffusion-based centralities are more concerned with knowledge construction, and uptake by collaborators they may offer better indicators for students’ success as well as indicators for productive discussions and reply-worthy arguments. Below is a review of previous research regarding centrality measures as indicators of success.
Most of the existing research investigating centrality measures as indicators of performance in CSCL settings has relied on individual courses with a limited number of students. The findings reported in such studies (Fig. 3) suggest that a positive relationship exists between centrality measures and academic achievement, however, with marked variability among indicators. For example, out-degree centrality was shown to correlate with student performance by some researchers (e.g., Hernández-García et al., 2015; Saqr & Alamro, 2019); yet, others did not identify any significant correlations (e.g., Liu et al., 2018a, b; Reychav et al., 2018). Similarly, in-degree centrality was found to be positively correlated with students’ performance by some scholars (e.g., (Z. Liu, Kang, Domanska, et al., 2018; Wise & Cui, 2018), whereas others have exhibited no significant correlations (e.g., Reychav et al., 2018; Saqr & Alamro, 2019). Such variable results and limited datasets have offered low potential for generalization. More recently, some studies have examined several courses, testing the value of centrality measures as indicators of student performance. For instance, four studies have used two courses (Cadima et al., 2012; Cho et al., 2007; Jiang et al., 2014; Joksimović et al., 2016), a study used four courses (Saqr et al., 2018), and another study used twelve courses (Saqr et al., 2020). All these studies have shown mixed results, where centrality measures were positively and significantly correlated with performance in some courses, while non-statistically significant in others, or even sometimes negatively significantly correlated. Such inconsistency was most noticeable in betweenness and closeness centralities.
After a thorough review of the literature (summarized in Fig. 3), we can conclude that there are several small studies with variable results and multiple course studies with mixed results. It becomes apparent that the most investigated centrality measures (betweenness and closeness centralities) have shown the most inconsistent results. These conclusions beg the need for large-scale studies with sufficient power to test the value of traditional centrality measures as indicators of student achievement, as well as for the search for new centrality measures that provide more consistent results.
We argue that diffusion-based centrality measures have the advantage of being more aligned with the collaborative process, as they capture the uptake of the argumentation process in CSCL, the extent of engagement of collaborators (i.e., the diffusion of argumentation), and the breadth of interactions among collaborators. In doing so, they capture considerable aspects of the process of knowledge construction. Therefore, diffusion-based centralities are able to fill the aforementioned gap, i.e., they may show more consistency compared to the traditional centrality measures and thus provide a valuable tool for educators who wish to monitor, optimize, or support students in CSCL.
Cadima et al., 2012; Cho et al., 2007; de-Marcos et al., 2016; Hernández-García et al., 2015; Jiang et al., 2014; Joksimović et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2018a, b, 2019; Liu et al., 2018a, b; Putnik et al., 2016; Reychav et al., 2018; Saqr et al., 2020; Saqr, Fors, & Nouri, Saqr et al., 2018a, b, c; Saqr, Fors, & Tedre, Saqr et al., 2018a, b, c; Saqr & Alamro, 2019; Wise & Cui, 2018.
SNA and students’ roles in CSCL
In CSCL settings, interactions among collaborators are facilitated or constrained by the dynamics of the collaborative learning process and the roles played by each actor (Saqr & Viberg, 2020). Roles can be defined as distinct patterns of behavioral engagement, contribution characteristics, and social orientation (Dowell et al., 2019; Strijbos & Weinberger, 2010). For instance, in online learning contexts, leaders show different social interaction patterns that distinguish them from non-leaders (Kim et al., 2020). There are two main types of roles: scripted roles which are defined by the educators to facilitate the collaborative process or trigger a certain interaction pattern. Scripted roles can specify duties, activities, or responsibilities of the learner and how the roles rotate or change (Strijbos & Weinberger, 2010). Emergent roles are spontaneously and dynamically assumed by learners as they structure the learning process. The emergent role perspective emphasizes learners’ autonomy and self-regulation. This study focuses on the emerging roles that students assume during the collaborative process.
Manually detecting the emergent roles can be an arduous process due to the large amount of online interaction data, the abundance of collaborative tasks, and the overtasked teachers (Dowell et al., 2019). Therefore, automatic approaches for detecting emergent roles are necessary. One empirical approach that has proved to be appropriate for the study of roles in CSCL settings is SNA (Haythornthwaite, 1996; Wasserman & Faust, 1994). Researchers have harnessed the power of SNA in ranking actors through quantification of their position, connectedness, and interactions to identify students’ roles in the collaborative process (Table 2). For instance, Temdee et al., (2006) suggested an approach for identifying the emergent leadership roles in a collaborative learning team based on the calculation of the leadership index, which was a combination of the degree, closeness and betweenness centralities. Their results indicated that the leadership index can be efficiently used to distinguish the leader role as verified by the students’ vote. Similarly, Stuetzer et al., (2013) used a combination of degree, betweenness, weighted degree and eigenvector centralities to identify brokering roles in a distance learning setting. They discovered that brokers have a central position on the network, lie in the shortest path between all other pairs of participants, and have the position to manage the information flow. In addition, they found that networks with brokers have much higher diffusion of information than networks without brokers. Other investigators have suggested other roles in different contexts and using a number of different SNA measures (C.-M. Chen & Chang 2014; Marcos-García et al., 2015; Ouyang & Chang, 2019; Saqr, Fors, Tedre, et al., 2018). The identification of roles in the previous studies has relied on profiling groups of learners with preset criteria for centrality measures, e.g., high values of degree centrality for the leader roles (active roles), and low centrality values for the isolated (or peripheral) roles.
In addition to profiling roles according to preset criteria, Kim & Ketenci (2019) used k-Means clustering to unveil groups of learners according to different centrality measures (in-degree, out-degree and betweenness), resulting in three different roles: full participants, inbound participants and peripheral participants. Their results showed that the classifications explained learner engagement level in three dimensions: cognition, behavior, and emotion. However, they also found that the profiled roles were more distinguishable than those formed by clustering. Table 2 lists the roles identified in the reviewed articles, the centralities used to characterize such roles, and the sample size of the studies.
Our review has highlighted some gaps in the literature, namely the reliance on traditional centrality measures that are hard to interpret in collaborative settings as well as not capturing the uptake process (see Sect. 2.1). Most of the reviewed articles based the role identification on preset centrality values, which lacks the rigor needed for identification and verification of the validity of such roles offered by robust statistical methods and modern machine learning. Lastly, most studies used single courses with a limited number of participants, which offer low potential for generalization. To fill the identified gaps, this study aims to investigate the possible role of diffusion-based centralities which we argue can accurately capture the argumentation process in the context of CSCL as a base for the identification of roles. We use modern machine learning methods for the discovery and verification of roles. We further use a large sample with several courses to overcome the limitations of convenience sampling.
Methods
Context
The present study is based on an integral dataset consisting of all the courses with a collaborative online module offered at the college of Qassim University between 2013 and 2019. To avoid selection or publication bias, all courses were included if they had at least 30 students. Courses with fewer than 30 students were excluded since they were considered unsuitable for the correlation meta-analysis as they violated the central limit theorem (Kwak & Kim, 2017). Overall, the study included 69 course offerings (15 different courses). Although each course covered different healthcare-related topics, they all had a common pedagogical underpinning based on Problem-Based Learning (PBL). The program is fairly homogenous, where all courses have been designed using similar principles to facilitate online PBL, have similar assessment strategies, and subject matter that integrates basic sciences and clinical sciences. Admission in the program is competitive and therefore, students’ admission grades are usually higher than those of other colleges. The courses integrate basic and clinical subjects in theme courses. For example, the course of Head and Neck: Structure and Function covers the subject of head and neck anatomy, physiology and pathology of the head and neck, as well as the common diseases of head and neck. The problems addressed in the course cover issues around head and neck. Other courses are structurally similar, e.g., Cell Structure and Function, Body Systems in Health and Diseases, Principles of Dental Sciences, Neuroscience, etc.
In each PBL course, students were divided into small groups with a tutor. The tutor role was relatively limited to face-to-face interactions. Students were assigned an open-ended problem on a weekly basis. They used an online forum to exchange ideas and perspectives, as well as argumentation about possible ways to understand, solve, or study the problem. Students’ performance was measured by the course grade, consisting of separate grades for: (1) the final exam, (2) the level of engagement in the online forums, and (3) students’ continuous assessment with the learning tasks and interaction during class. The final exam accounted for 80% of the overall grade, whereas the latter two components accounted for the remaining 20%; distributed as follows: 10% continuous assessment (e.g., practical assignments, seminar preparations, engagement in lectures and course duties), 5% for online forums, and 5% for face-to-face PBL group sessions.
Data collection
The data from the 69 course offerings were retrieved from the forum module of the Moodle learning management system for each post and included: the post author (the source), the replied-to (target), the post ID, the thread ID, the group ID, and the timestamp of each post.
Network Analysis
To capture the interaction processes, a post-reply directed network was constructed in which the author of each post was considered the source of the interaction, and the recipient replied-to was considered the target of the interaction (Saqr et al., 2020). An aggregate network was constructed for each PBL group (5–10 students) and prepared for analysis through the Igraph R package (Csardi & Nepusz, 2006). For each student, we report the calculated centrality measures according to (Poquet et al., 2021):
Degree centralities (Borgatti, 2005; Borgatti & Brass, 2019; Opsahl et al., 2010; Saqr et al., 2020).
-
Weighted out-degree centrality: Total number of posts contributed by a student. It is operationalized as a student’s contribution to the discourse, participation, and social positioning.
-
Weighted in-degree centrality: Total number of replies received by a student. It is operationalized as a student’s contribution to the discourse, number of reply-worthy contributions, and stimulation of others’ participation.
-
Weighted degree centrality: Sum of weighted in-degree and weighted out degree.
-
Out-degree centrality: Total number of students a student has interacted with. A high number indicates wide social capital, access to diverse opinions, and a larger network of connections.
-
In-degree centrality: Total number of students that a student has received replies from. A higher number indicates wide social capital, worthiness of contributions, as well as prestige.
-
Degree centrality: Sum of in-degree and out degree.
-
Closeness centrality: Inverse distance between the student and all others in the network. It is operationalized as the reachability of or access to other students (Bae & Kim, 2014; Borgatti & Brass, 2019).
-
Betweenness centrality: Total times a student node is found on the shortest path between two others. It is operationalized as bridging social capital, mediating between collaborators, and access to diverse groups (Bae & Kim, 2014; Borgatti & Brass, 2019).
-
Eigen centrality: In contrast to degree centrality, which counts all connections with equal weights, eigenvector centrality considers the connectedness of a student’s collaborators, i.e., connections to highly connected students are expected to be more important than connectedness to disconnected students (Bae & Kim, 2014; Borgatti & Brass, 2019).
Diffusion centralities.
-
Diffusion degree: Sum of collaborators’ diffusion probabilities, i.e., the probability that a student may spread an idea across the network. It is operationalized as the capability of the student to contribute posts that are reply-worthy and would stimulate uptake by others, i.e., the downstream uptake that a post has generated (Banerjee et al., 2013).
-
Coreness: Largest connected group of students in which all have degrees of at least k. It is operationalized as the strength of connectedness of the students’ collaborators. A student with high value has contributed reply-worthy ideas that engaged others. The result is the student being in a strategic position in the ‘core’ of the network, i.e., embedded in discussions that have attracted highly interactive students (who have high coreness values too) (Kitsak et al., 2010).
-
Cross clique connectivity: The number of cliques that a student is a part of. It is operationalized as the ability of students’ contributions to engage connected students who are also interacting with each other (forming triangles or cliques). Cliques are also a sign of strong connections (Faghani & Nguyen, 2013).
-
MNC: The cardinality of a student’s connections excluding the student, which reflects how connected student collaborators are and, thus, their ability to spread information or be engaged in discussions. A student who is engaged in longer threads with diverse participation from well-connected students has a high MNC (Liu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017).
For diffusion degree and coreness, we calculated the directed versions (the in and out): the in version considers only the incoming connections, and for the out version, we consider only the outgoing connections.
Discourse analysis
To investigate whether diffusion-based centrality measures are capable of capturing information exchange, uptake, and argumentation (RQ1), we (1) examined the relationship between these centralities and the frequency of coded interactions extracted from a dataset corresponding to five course offerings from the examined data. We did so by calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficient between each of the examined centralities and the frequency of the occurrence of relevant codes. We used Holm’s correction to account for multiple comparisons (Holm, 1979). We (2) performed analysis of variance between the identified emergent student roles, and the frequency of coded interactions was performed as well (see Sect. 3.6 for further details).
The coding scheme was based on the approach by Visschers-Pleijers et al., (2006) Verbal interactions in tutorial groups, which is a widely used coding scheme for PBL group interactions. Students’ interactions were classified into five categories: three of them learning-related (Questioning, Reasoning, Conflicts), as well as Procedural interactions and Off-task/Irrelevant interactions. We further took inspiration from (Aarnio et al., 2013; Yew & Schmidt, 2009) to expand the Reasoning category to include different types of information sharing (renamed the category to Information discussion), and the Conflicts episode to involve the argumentation types (renamed to Argument and debate). Two researchers coded 5% of the data separately. The initial inter-rater reliability (Cohen’s Kappa) was 0.6 to 0.8 for the different categories. Both researchers met and resolved disagreement and recoded the data separately, resulting in a final Cohen’s Kappa for all data of 0.91(McHugh, 2012). The final coding scheme is shown in Table S1.
Frequency analysis and meta-analysis
To investigate whether diffusion-based centralities serve as consistent indicators of study success in CSCL settings (RQ2), we first calculated Pearson’s correlation coefficient between each centrality measure and students’ final grades. To prepare the variables for Pearson’s correlation, we applied Box-Cox transformation to all variables so that they were closer to the normal distribution (Havlicek & Peterson, 1976; Nefzger & Drasgow, 1957; Peterson, 1977). In order to rigorously pool the correlation coefficients across all courses—while taking into account the sample size of each course—a correlation meta-analysis was performed (Hedges & Olkin, 1985). By doing so, we were able to calculate the heterogeneity within studies (course offerings in our case) (Gurevitch et al., 2018; Higgins & Thompson, 2002; Schwarzer et al., 2015). Therefore, we performed 17 meta-analyses (one for each centrality measure) to pool the correlations of all 69 course offerings. The combined correlation coefficient of the meta-analysis is a weighted average of all correlation coefficients in all courses. An inverse-variance pooling of Fisher’s z transformed correlations was performed to obtain an accurate weight for the sample size of each course offering. A random-effects model was selected for the reporting of the combined correlation coefficient since we expected the course offerings to be heterogeneous (which was confirmed by the moderate levels of heterogeneity indicators) (Schwarzer et al., 2015).
To measure the consistency of the results, we estimated the heterogeneity (between-study or course offering variance). Heterogeneity measures the extent to which effect sizes vary within a meta-analysis (Higgins & Thompson, 2002; Schwarzer et al., 2015). Heterogeneity was estimated using the Sidik-Jonkman method. Higher levels of heterogeneity indicate less consistent coefficients. In turn, low levels of heterogeneity are a sign of consistent findings that increase certainty that future applications of the centrality measure are expected to render comparable results. I2—a measure of heterogeneity—was selected because its insensitivity to changes in the number of studies and is easy to interpret (I2 of 25% or lower indicates very low heterogeneity; I2 from 25 to 50% indicates low heterogeneity; I2 from 50 to 75% indicates moderate heterogeneity, and I2 greater than 75% indicates substantial heterogeneity (Higgins & Thompson, 2002; Schwarzer et al., 2015). We also report the prediction interval, which has become the recommended measure of heterogeneity, that accurately establishes the future predictability of the indicator considering the heterogeneity, i.e., the expected range of values in which the future correlation would probably lie. The prediction interval can be interpreted in a similar way to confidence intervals. That is, if the lower and upper bounds are on the positive side or both on the negative side, we expect that future applications within similar contexts would have comparable results within the bounds of the predictive interval (IntHout et al., 2016).
Lastly, to compare with previously reported results in the literature, we computed the number of course offerings (frequency) in which each centrality measure had a positive and statistically significant correlation with grades (PSSG), positive and statistically insignificant correlations with grades (PSIG), negative and statistically significant correlation with grades (NSSG), as well as negative and statistically insignificant correlation with grades (NSIG).
Clustering
To investigate the possibility of using diffusion-based centralities to reveal students’ emergent roles (RQ3), we applied clustering following the methods of López-Pernas et al., (2021). In our case, clustering of students could help discover students with similar emergent roles based on their interaction patterns, operationalized as diffusion and traditional centrality measures. To limit the influence of extreme values, data was winsorized, i.e., values in the top and bottom 5% were replaced by their closest values. Since the value of distance measures could be heavily affected by the scale of each centrality measure, we standardized all the data (subtracted the mean and divided by standard deviation) before measuring the inter-observation dissimilarities (Likas et al., 2003; Steinley, 2006).
To estimate the optimum number of clusters, we used the NbClust R package which implements 30 indices for identifying the recommended number of clusters (Charrad et al., 2014). The majority (12/30) vote method suggested three clusters as the optimum number, which was selected for our study. The k-means algorithm was used to perform the clustering of students based on Euclidean distance. The clustering algorithm was evaluated using the silhouette coefficient method—a common internal validity measure—that estimates the extent to which an observation is assigned the right cluster by computing the average distance between clusters. A silhouette value of 1 means the observation is perfectly placed in the right cluster, while a value of -1 indicates wrong assignment (Steinley, 2006). To estimate the separation among the emergent roles identified, we performed a Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), comparing the mean values of the centrality measures among the three clusters (Ostertagova et al., 2014). To rigorously evaluate the magnitude of the obtained results, we calculated the epsilon-squared effect size (Tomczak & Tomczak, 2014). Post-hoc pairwise comparisons were performed through Dunn’s test to verify the magnitude and significance of the separation of clusters (emergent roles), using Holm’s correction for multiple testing (Holm, 1979).
To examine how the identified emergent roles relate to academic achievement, we performed a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA test to compare the final grades among the three clusters (Ostertagova et al., 2014). We computed the epsilon-squared effect size to evaluate the magnitude of the obtained results. We further used Dunn’s test to perform post-hoc pairwise comparisons using Holm’s correction. Lastly, to verify our hypothesis that diffusion centralities can capture the roles in information diffusion and argumentation (RQ1). We performed a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA test (using the same methods) to compare the identified roles with the frequencies against the coded dataset (Ostertagova et al., 2014).
Results
The study included 69 courses, 3,277 students, 97,173 interactions (of which 8,818 were manually coded). Table 3 shows the descriptive statistics of all the courses analyzed. The median number of students that completed each course was 48. The median frequency of interactions in a course was 1,065. Table 3 also reports the summary statistics of the centrality measures of each student (detailed per-course statistics are available in Table S2). As such, the dataset had medium-sized courses with relatively interactive students: each student had a median weighted degree of 37 and interacted with a median of 10 others. Table S3 shows the frequency of coded interactions.
There was a statistically significant positive correlation that ranged from moderate to strong magnitude between diffusion centralities and “Sharing info. and materials” (Fig. 4), which was highest in weighted degree centrality (r = 0.701, p < 0.01), coreness (r = 0.639, p < 0.01), diffusion degree (r = 0.578, p < 0.01), as well as in closeness (r = 0,473, p < 0.01); less so in betweenness centrality (r = 0.204, p = 0.004). A similar pattern is also noticed in “Sharing facts”, “Continuing argument”, “Argument” and less so in “Counter argument”. In general, the correlation coefficients were higher between diffusion-based centralities and the frequency of the codes that represent information sharing than with those related to task organizing, off-task activities and questions. In the “Questioning category”, the correlation was weak in the types of questions that stimulated more interactions (“Question open” and “Question critical”). Lastly, in the categories of “Off-tasks” and “Procedural Interactions”, the correlation was non-existing or very weak.
In summary, the reported results point to high selectivity of diffusion centralities for capturing information exchange, uptake, and argumentation, as well as other types of interactions that are reply-worthy (“Question open” and “Question critical”). The detailed correlation coefficients between each of the examined centralities and the frequency of the occurrence of relevant codes are shown in Fig. 4.
RQ2: Can diffusion-based centralities be consistent indicators of study success in CSCL settings, and if so, which?
We calculated Pearson’s correlation coefficient between students’ grades and centrality measures (traditional and diffusion ones) in each course offering. Compared to traditional centrality measures, diffusion-based centralities had a higher number of PSSG, and only one course offering with NSIG (coreness-in). The number of PSSG was generally higher in ‘out’ measures (e.g., coreness-out, diffusion degree out) and consequently in the total measures. Coreness out and coreness total had the highest frequency of PSSG (62 [89.9%]), followed by the diffusion degree out and cross clique centrality (61 [88.4%]). In summary, diffusion centralities were more likely to correlate positively and significantly with grades and, therefore, are expected to be better indicators of students’ success in CSCL settings. Among the traditional centrality measures, the results (Fig. 5) show that the weighted degree centralities were the most consistent indicators for a student. In most course offerings (62 [89.9%]), weighted degree and weighted out-degree were PSSG, closely followed by weighted in-degree (60 [87%]). The non-weighted degree centralities were slightly lower in terms of frequency of PSSG compared to the weighted variant (61 [88.4%] degree, 57 [82.6%] in-degree, 60 [87%] out-degree). However, there was a single course in which the correlation coefficient for non-weighted degree centrality was NSIG. The number of PSSG was the lowest in closeness centrality (54 of the course offerings [78.3%]), followed by betweenness centrality (46 [66.7%]), and Eigenvector centrality (50 [72.5%]). There were two instances of NSIG in betweenness centrality, three in closeness centrality, and one in eigenvector centrality.
Since the simple frequency of correlations is far from optimal for estimating our confidence and certainty in centrality measures, we proceed to report the results of the meta-analysis for more detailed and in-depth analysis (Table 4). The random-effects model of the combined correlation coefficients of the centrality measures of the 69 course offerings was highest for the coreness out centrality (r = 0.57 [CI 0.53:0.60]), with the narrowest range of CI (the difference between the low and high limits of CI), and the highest lower bounds of predictive intervals ([0.26;0.77]). The weighted degree showed close but slightly lower combined correlation coefficients (r = 0.56 [CI 0.52:0.60]) as well as predictive intervals ([0.25;0.77]). Total coreness followed with a combined correlation coefficient of (r = 0.55 [CI 0.51:0.59]) and a predictive interval of ([0.20;0.78]). In general, weighted degree and diffusion centralities had high combined correlation coefficients (ranging from 0.51 to 0.57) as well as statistically significant predictive intervals (with lower bounds within the range of 0.15 and 0.26 and upper bounds within the range of 0.75 and 0.78). These results are an indication of the robustness and remarkable value of diffusion and weighted degree centralities.
However, closeness centralities showed a statistically insignificant predictive interval ([-0.06;0.81]). Betweenness centralities exhibited the lowest combined correlation coefficient of all centralities of (r = 0.38 [CI 0.33:0.42]). Eigenvector centrality also showed a comparatively low combined correlation coefficient (r = 0.41 [CI 0.36:0.45]). The lower limit of the predictive interval of both betweenness centrality and eigenvector centrality was low (0.07). Figure 6 shows the forest plot of the combined correlation coefficients (of the 69 course offerings) of all centralities and their corresponding confidence intervals.
In summary, the results of frequency of correlation tests and the meta-analysis show that diffusion-based centralities, together with weighted degree centralities, have higher and consistent combined correlation coefficients with academic achievement (measured by grades).
*The vertical line in the center of the forest plot represents a correlation value of 0, whereas the horizontal lines represent the 95% confidence interval of the correlations for the corresponding course. The box in the middle represents the weight of each study (course offering in our case). The point inside the box represents the effect size. Course offerings with confidence intervals crossing the 0 line on either side are considered statistically insignificant. Course offerings with both confidence interval bounds on the right side of the 0 line are considered in favor of a statistically positive and significant correlation.
RQ3: Can diffusion-based centralities reveal students’ emergent roles and their possible correlation with learner performance?
Clustering of students’ centralities using k-means was performed to group similar patterns of students’ based on their interaction profiles. The examination of cluster centroids can give an idea about the ‘average’ or ‘typical’ profile of students that belong to each of the three identified groups (Fig. 7). The three identified emergent roles can be described as follows:
-
Influencers (n=675): Students in this cluster have higher diffusion centralities (coreness, diffusion degree and cross-clique centrality), indicating that their contributions were more likely to be influential, spread or attract other contributions (uptake). Influencers were close to more students (higher closeness centrality values) and posted information more frequently (higher weighted degree centrality). However, they had below average betweenness centralities, indicating that they were more likely to be starters of a discussion than followers who mediate or discuss others’ posts, or maybe they were more often engaged in interactions with the isolated students.
-
Mediators (n=1296): The mediators showed diffusion centralities that were slightly above average, and in-between the isolates and the influencers. Interestingly, mediators had the highest values of betweenness centrality, indicating that they acted as bridges between the influencers and the isolates. Mediators had eigenvector centrality close to the influencers, demonstrating that they had similar social capital, i.e., since the mediators follow the influencers, they are expected to show similar connectivity levels.
-
Isolates (n=1306): Isolates –as the name implies– have low centrality measures, lower diffusion centralities, smaller neighborhood sizes, as well as low eigenvector centralities. Yet, the isolates have values of betweenness centrality that are slightly below the influencers, as both groups have little role in bridging interactions.
The Kruskal-Wallis test showed that the roles identified were well separated (Table 5). All centrality measures differed significantly (p < 0.001) between clusters with an effect size that ranged from relatively strong (ε2 = 0.34) to strong (ε2 = 0.75). The post-hoc pairwise test showed significant differences between all pairs of clusters except for Eigenvector centrality between influencers and mediators. The complete pairwise comparisons with their corresponding statistics are detailed in Fig. S1. The average silhouette coefficient for the clusters was 0.33 (0.3 for the influencers, 0.47 for the isolates, and 0.2 for the mediators). Students who were identified as influencers had an average grade of 74.1 out of 100, compared to 63.52 for mediators and 44.87 for isolates (Fig. S2). The Kruskal-Wallis test showed that difference in grade was statistically significant with relatively strong effect size, (χ2(2) = 650, N = 3277, p < 0.001, ε2 = 0.2). The post-hoc pairwise test showed that grades were significantly different between clusters. Figure 7 shows the comparison between students’ centrality measures in each cluster.
Lastly, a comparison of the mean frequency of coded interactions among the three roles identified confirmed that each of the identified roles differed significantly on the parameters of information exchange, argumentation, and uptake (Table 6). The effect size was strong (ε2 = 0.462) for “Sharing info and materials” (ε2 = 0.46), relatively strong in “Sharing facts” (ε2 = 0.183), “Argument” (ε2 = 0.168), and “Continuing argument” (ε2 = 0.203); less so for “Evaluation” (ε2 = 0.132). Figure 8 shows the comparison between students’ coded interactions in each cluster. Questioning, Procedural and Off-task interactions either showed non-significant or very low effect sizes indicating the selectivity of the identified roles to the interactions related to information exchange, uptake, and argumentation.
Discussion
There are several constraints of time and effort that hinder the manual analysis of learners’ data. Therefore, computational methods are increasingly needed to help teachers in their efforts to support learners (Wise & Schwarz, 2017). Our study was motivated by the earlier encouraging research on uptake in CSCL (Chen & Zhang, 2016; Lee & Tan, 2017a; Suthers, 2015; Suthers & Desiato, 2012), emerging research on diffusion in other fields (Banerjee et al., 2013; Cowan & Jonard, 2004), and the need for better monitoring mechanisms for student collaboration. We aimed to examine the role that diffusion-based centrality measures—as a computational method—could play in capturing the uptake process and diffusion of argumentation. This may be particularly revealing of the ways students facilitate knowledge uptake or information flow, encourage others to participate, help endorse an opinion, embrace a plan in a project, or follow a collaboration script. While previous work has demonstrated the immense value of representing and visualizing interaction graphs (Baker et al., 2007; Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Reed & Rowe, 2004). The suitability of visualizations is limited by the number of interactions. That is, in large courses and thousands of messages, it becomes visually impossible to render usable insights (Scheuer et al., 2010). Therefore, computational methods that can make sense of big data are needed. Such computational methods should ideally build on the graph representations of threaded interactions and be able to capture metrics that are interpretable and understandable by teachers and students.
Modelling of diffusion or uptake of knowledge is subject to a number of conditions and difficulties, e.g., previous knowledge of the recipient, evaluation by the recipient (to accept or not) and need for reinforcement. These difficulties apply to CSCL as well, and have long been recognized (Suthers, 2015; Suthers & Desiato, 2012). The concepts of diffusion and uptake may vary by context, for instance, in PBL diffusion may mean the advancement of knowledge, in project-based learning it may mean the co-construction of new ideas (Suthers, 2015). However, computational methods can help infer the probability and the magnitude of uptake or diffusion based on the relational structure of the threaded interactions (Lee & Tan, 2017a; Suthers et al., 2010; Wise et al., 2021). With the availability of a significant corpus of data for each student, such inferences become more accurate, and the signal surpasses the noise. Suthers (2012) emphasized the importance of the practical applications of computational methods: “we should be more concerned with whether an automated method of analysis produces useful results in its applications rather than whether the specific intermediate representations are correlated with human analysis” (Suthers & Desiato, 2012). Our results have shown that diffusion-based centralities offer a practical solution for the inference of the uptake and argumentation within student’s interactions that has been moderately to strongly correlated with a human coded dataset and showed strong to relatively strong effect sizes in differentiating roles of students who share information or use argumentations (RQ1). Such high values of effect sizes point to the significance and importance of such methods bring to the inference of uptake and argumentation (Tomczak & Tomczak, 2014).
Regarding RQ2, we were especially interested in developing a better understanding of indicators of student success in CSCL settings. Our results have shown that compared to traditional centrality measures, diffusion-based centralities were more likely to be positively and significantly correlated with grades in almost all courses in all measures (except for one course for coreness-in). The results of the meta-analysis further confirmed these findings and showed that diffusion centralities had higher combined correlation coefficients, narrower confidence intervals, and higher predictive intervals, thus offering solid proof of the robustness and consistency of diffusion centrality measures as indicators of success as well as reflective of the relevance of diffusion-based centrality measures to collaborative context. This can be explained by the fact diffusion centralities capture the role of students in generating reply-worthy promising ideas that are more likely to be taken up as well as they generate longer threads and engagement of others (Chen & Zhang, 2016; Lee & Tan, 2017a; Poquet et al., 2020; Saqr & Montero, 2020; Suthers, 2015; Suthers & Desiato, 2012). Students who can generate such contributions are more likely to be more engaged, more participatory or high achievers (Anderson et al., 2001; de-Marcos et al., 2016; Reychav et al., 2018; Saqr & Montero, 2020). Diffusion-based centralities capture extra information (length of threads, the range of involvement of others and possibility of uptake), as such they are more likely to accurately reflect a realistic view of students’ efforts in the discourse. Diffusion-based centrality reflects how learners influence others’ contributions (e.g., encourage others to reply and participate) adding an aspect that traditional centrality measures do not reflect.
Another finding of our study was that degree centralities, which reflect the number of contributions and number of replies, showed good consistency and correlation coefficients. This is not surprising, since they reflect students’ efforts, participation in the discourse as well as the number of received replies (Joksimović et al., 2016; Romero & Ventura, 2020). However, as mentioned before, they do not reflect the breadth and range of uptake or the engagement of collaborators. The results of the most commonly used traditional measures (closeness and betweenness) regarding correlation coefficients with grades were the least consistent, which casts doubt on their value as indicators of student success. We believe that time has come for researchers to consider more relevant centrality measures such as diffusion centralities, as highlighted in the review of the literature (Table 2), these findings help fill such gaps and offer a credible alternative. A noteworthy finding is that the correlation of closeness centrality with argumentation and information sharing were moderate in most categories, pointing to the value thereof as a metric for information uptake. In other words, while caution should be exercised when using closeness centrality as indicator for success, it can be a reasonable indicator of participation in the discourse.
Diffusion-based centralities should be interpreted as proxy indicators for productive, stimulating discussions, longer threads, taken up by students or contributions that are reply worthy. This “proxy” indication offers a much-needed value compared to the ease of calculation and strong association with coded data. However, it is limited—as are all proxy indicators—in terms of accuracy, and specificity. In fact, this limitation applies to every tool and method that has been used to capture human discourse, ranging from natural language processing to even the more exhaustive methods of code and count. Natural language processing –although promising– has its challenges e.g., the need for large labeled datasets which are largely unavailable in education yet, and the difficulty in model interpretability (Li, 2018).
A remarkable challenge in collaborative learning networks relates to the accurate identification of students’ roles in a network. In this study, diffusion-based methods were used to identify emergent roles in the collaborative learning process. We relied on the aggregate values of diffusion and traditional centrality measures as well as machine learning to identify meaningful roles based on students’ interactions (RQ3). Compared to previous research, which has mainly used manual profiling based on preset roles (C.-M. Chen & Chang 2014; Marcos-García et al., 2015; Ouyang & Chang, 2019; Saqr, Fors, Tedre, et al., 2018; Stuetzer et al., 2013; Temdee et al., 2006), our approach relies on students’ contributions of ideas that are reply-worthy and more likely to be taken up and help engage others, in other words, ideas that help advance the argumentation process as well as contribute meaningfully to the discourse. Our method exhibited strong to relatively strong effect sizes when validated through comparison with coded interactions. We believe that this method offers easier interpretability of the roles and more relevance to collaborative knowledge construction. Our work builds on the work by Kim & Ketenci (2019), who used clustering for identifying roles, by adding the uptake aspect that is more relevant to discourse and argumentation. We have identified three roles: influencers who are able to generate more engaging and reply-worthy interactions, mediators who are more likely to engage and contribute to the argumentation rather than generate novel ideas, and an isolate type. The identified roles were significantly different regarding their diffusion centrality profiles with strong effect sizes, confirming the robustness of the technique. Similarly, the differences between the identified roles regarding performance showed relatively strong effect sizes. The comparison of the identified roles has revealed remarkable differences regarding performance with relatively strong effect size pointing to the significance of the findings.
Another noteworthy finding is the high number of emergent isolate students, while this is a frequent finding in the literature (Kim & Ketenci, 2019; Saqr & Viberg, 2020), diffusion centralities have shown that a large number of the seemingly active students are not contributing valuable ideas to the discourse. That is, they focus on sharing facts, and information rather than engaging in argumentation, debate, or contributing ideas that are worthy of discussion. A possible remedy could be through structuring the collaborative process with scripted roles, rotating the duties, and specifying how students approach the task. To identify such isolated roles, computational methods that take into account the content of the message and the depth of the thread, like diffusion centrality measures or specialized tools that support argumentation, are thus needed (Miller & Volz, 2013; Schwarz et al., 2015; Schwarz & Glassner, 2007).
Moodle –the learning platform used in this study– may have been not very efficient in helping students engage in deeper discussion, debate, or argumentation. In fact, compared to the specialized tools, Moodle lacks lots of the functionalities which support argumentation, e.g., visualization of arguments, visual editors or participation tracking (Anderson et al., 2001; Lund et al., 2007; Muller Mirza et al., 2007; Nussbaum et al., 2007; Tsai et al., 2012). The findings of this study could add an interesting dimension to these tools by offering quantitative indicators that help teachers get an idea about students’ interactions. Especially in large courses where visualization of a large number of messages may become difficult to understand.
PBL shares several similarities with CL but also differences. (1) Both PBL and CL have a common task or a learning activity, which is typically a real-life problem in PBL but not necessarily a problem in CL. (2) Both PBL and CL rely on small group interactions, in which students have to mutually collaborate to accomplish the task. (3) In Both PBL and CL, students are responsible and accountable for their learning. (4) Both PBL and CL have interdependence as a fundamental feature, however, both the approaches differ significantly in interdependence (Davidson & Major, 2014). In CL, teachers commonly use social and academic goals as a means to foster positive interdependence as well as structured tasks or assignments; seldom using roles, rewards or points. In PBL, teachers may use goals, structured tasks, roles and sometimes rewards (Davidson & Major, 2014). As such, information and problem-solving interdependence are key features of PBL as well as a motivating real-life problem with a structured interaction process where roles are commonly assigned (especially in face-to-face settings). These differences, and peculiarities of PBL would translate to structural graph differences, where groups are expected to have intense interactions, and dense information leading to connected and dense networks. Other essential features of PBL are that students do not essentially seek to solve the problem, but rather debate, discuss, and use argumentation which may result in more branching, deeper and longer threads.
The fact that PBL discussions are dense, with richer information exchange and debate make them likely to correlate with performance compared to other CL settings where discussions may be sparse, and far less correlated with performance. In some higher education settings, participation in CSCL may be below what educators aspire (Jeong & Hmelo-Silver, 2016). Similarly, MOOC forum discussions tend to be very sparse with infrequent participation and diverse students (Chen et al., 2021). Therefore, the scope of generalization for this study lies in similar PBL contexts, structured CL settings, and CL settings that involve rich information exchange. Generalizability to other contexts should be empirically confirmed before taking the results of this study at face value.
Our study has several strengths. We have demonstrated the results in 69 courses and thousands of students which is a proof of feasibility and scalability. We have also used a robust method—meta-analysis—for the calculation of the combined correlation coefficients as well as the predictive intervals, which offers a more realistic expectation of the performance of the predictor in the future and takes into account the heterogeneity and sample sizes. The discovered roles in our study have been verified with a coded dataset and showed high values of effect sizes regarding the separation of roles or grades. We believe that using the data of all the courses in the institution presents solid evidence as well as excludes possible bias. Our approach offers a verified computational method which is feasible to implement due to the availability of different software applications that can compute such diffusion-based centrality measures. Educators can use such metrics as robust indicators of success for students in collaborative settings or monitoring their productive interactions and how they contribute as well as encourage others to contribute. We wish that researchers build on our approach, investigate other methods of analysis and other metrics, and compare results to ours. Although we have used a large sample, the generalizability of results is subject to investigation and further confirmation.
Limitations
Our study is not without limitations. The inclusion of online PBL grades within the final grades may have added some noise or confounding to the correlation analysis. Since these grades were only 5% of the total grade students earned, we believe this effect is minimal and had no effect on the conclusions of the article. Since most of the studies have performed correlational analyses, we opted for using correlation analysis as well to be able to compare our results to those of previous works, and to establish the value and worth of the indicators. Accounting and investigating the different factors that influence the obtained results warrants further investigations, which we aim to pursue in our future studies. We studied the indicators separately to facilitate easy interpretability and estimation of magnitude of effect size so that educators can have an idea about what they can expect from an indicator. Several other analytical techniques could help understand the complexities of the interaction process e.g., Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM). HLM could account for the role of tutors, the composition of the group and other factors such as nestedness. Lastly, we have used a large number of students to derive our conclusions. Such inference using a large dataset may result in statistically significance results, even with small or negligible effect sizes. Therefore, we have relied on the effect size as a more accurate measure for the magnitude of results as well as predictive intervals. We encourage the readers to rely on the effect sizes as a more reliable measure of magnitude and expected impact of the findings (Suthers & Hundhausen, 2003).
Appendix

Figure S1. Box plot comparing students’ centrality measures within the three identified clusters through Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn pairwise test.

Figure S2. Box plot comparing students’ grades within the three identified clusters through Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn pairwise test.
Table S1. Coding scheme for the PBL forum data used in the study
Category | Code | Code Description |
|---|---|---|
Information discussion | Sharing info and materials | Sharing share information or learning resources related to the discussion. |
Sharing facts | Providing objective information (no reasoning), which does not represent the student’s words (e.g., definitions or facts). | |
Conclusion | Closing a discussion or stating the outcome of the conversation. | |
Comparison | Contrasting different issues and ideas or concepts by comparing them without reasoning. | |
Argument and debate | Evaluation | Assessing other students’ work or ideas and giving opinions or judgments for their or others’ work with reasoning. |
Argument | Reasoning, justifying, or rationally trying to resolve differences of perspectives and issues in critical discussion. | |
Continuing argument | Continuing an argument given by other students. | |
Counter argument | Providing a contradicting view for a given argument with reasoning and rationally disproving. | |
Disagreement | Disagreeing with other students’ opinions or statements. | |
Questioning | Question open | Raising a question that demands for new information and elaborated explanations of a specific contribution. |
Question critical | Raising a question to challenge another person’s contribution. | |
Question verification | Asking for clarification of a proposed idea or shared knowledge. | |
Question alternative | Making a logical extension of a previous question that has already been answered proposing an alternative explanation. | |
Procedural interactions | Team building | Talking about the group and related issues. |
Problem handling | Addressing about a specific team issue and way to solve that issue. | |
Task management | Discussing about how to divide the work and about the progress of the assigned tasks. | |
Off-task / Irrelevant interactions | Sharing feelings | Sharing their feelings about others’ work or comments. |
Sharing experience | Sharing experiences related to the discussion. |
Table S2. Courses, student numbers, and median values of all parameters of each course
Cours | Students | Edges | Degree | In-Degree | Out-Degree | Weighted Degree | Weighted In-Degree | Weighted Out-Degree | Betweenness | Closeness | Eigenvector | Neighborhood | Coreness Total | Coreness In | Coreness Out | Cross Clique Connectivity | Diffusion Degree Total | Diffusion Degree In | Diffusion Degree Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | 43 | 1103.5 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 46.0 | 23.0 | 21.0 | 1.27 | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 40.0 | 21.0 | 17.0 | 48.0 | 384.0 | 176.0 | 175.0 |
2 | 48 | 477.5 | 9.0 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 18.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 2.48 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 13.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 35.0 | 121.0 | 45.5 | 54.0 |
3 | 64 | 2052.0 | 11.0 | 6.0 | 5.5 | 55.5 | 29.0 | 24.5 | 1.42 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 49.0 | 25.5 | 23.5 | 58.0 | 514.0 | 205.0 | 223.0 |
4 | 50 | 1632.0 | 14.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 64.0 | 32.0 | 32.5 | 1.06 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.89 | 51.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 128.0 | 554.0 | 234.0 | 252.5 |
5 | 49 | 1512.5 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 51.0 | 27.0 | 25.0 | 1.03 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 45.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 46.0 | 411.0 | 182.0 | 170.0 |
6 | 42 | 2190.5 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 93.0 | 47.5 | 44.0 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.79 | 76.0 | 42.0 | 35.5 | 44.0 | 656.5 | 297.5 | 306.5 |
7 | 56 | 809.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 17.0 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 14.0 | 166.5 | 41.5 | 40.0 |
8 | 42 | 484.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 17.0 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 15.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 122.0 | 36.0 | 39.5 |
9 | 48 | 1679.0 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 64.0 | 33.5 | 31.5 | 1.53 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.56 | 57.5 | 30.5 | 28.0 | 30.0 | 511.5 | 189.5 | 137.5 |
10 | 58 | 1314.0 | 12.5 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 39.5 | 21.5 | 18.5 | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.64 | 31.0 | 16.0 | 14.0 | 116.0 | 411.0 | 163.5 | 142.5 |
11 | 49 | 808.0 | 7.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 29.0 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 26.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 16.0 | 285.0 | 113.0 | 109.0 |
12 | 54 | 1156.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 33.0 | 17.0 | 14.0 | 1.32 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 27.0 | 13.0 | 12.5 | 32.0 | 295.5 | 117.5 | 110.5 |
13 | 47 | 801.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 26.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.33 | 26.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 12.0 | 327.0 | 166.0 | 119.0 |
14 | 31 | 1244.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 69.0 | 36.0 | 34.0 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 53.0 | 32.0 | 26.0 | 18.0 | 490.0 | 224.0 | 215.0 |
15 | 31 | 1871.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 89.0 | 46.0 | 43.0 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.62 | 76.0 | 37.0 | 38.0 | 16.0 | 636.0 | 303.0 | 219.0 |
16 | 50 | 945.5 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 24.0 | 13.5 | 12.0 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 21.0 | 9.5 | 10.5 | 13.0 | 151.5 | 61.0 | 66.0 |
17 | 36 | 840.5 | 6.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 33.5 | 14.5 | 16.0 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 32.0 | 12.5 | 15.5 | 19.0 | 382.5 | 115.0 | 98.0 |
18 | 41 | 1730.5 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 73.0 | 38.0 | 35.0 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 67.0 | 34.0 | 33.0 | 20.0 | 482.0 | 210.0 | 191.0 |
19 | 50 | 782.5 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 19.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.21 | 17.0 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 98.5 | 33.5 | 41.0 |
20 | 48 | 1304.5 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 40.5 | 19.0 | 16.5 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 32.0 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 12.0 | 247.5 | 77.5 | 107.0 |
21 | 56 | 1429.5 | 11.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 35.5 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 0.91 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 30.0 | 15.0 | 13.0 | 68.0 | 305.0 | 125.5 | 98.0 |
22 | 53 | 1888.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 63.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 47.0 | 24.0 | 23.0 | 76.0 | 503.0 | 202.0 | 235.0 |
23 | 42 | 2045.0 | 10.0 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 87.5 | 45.0 | 43.0 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.81 | 87.0 | 43.0 | 41.0 | 40.0 | 704.5 | 300.0 | 312.0 |
24 | 31 | 1220.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 57.0 | 30.0 | 24.0 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.50 | 49.0 | 25.0 | 24.0 | 8.0 | 356.0 | 145.0 | 136.0 |
25 | 53 | 1609.0 | 15.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 50.0 | 26.0 | 24.0 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.44 | 0.73 | 39.0 | 19.0 | 17.0 | 74.0 | 403.0 | 174.0 | 189.0 |
26 | 42 | 2111.0 | 9.5 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 95.0 | 47.5 | 47.5 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.88 | 80.0 | 36.5 | 41.5 | 24.0 | 617.0 | 190.5 | 311.5 |
27 | 49 | 616.5 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 14.0 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 13.0 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 | 52.0 | 19.0 | 31.0 |
28 | 47 | 741.5 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 20.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 4.0 | 80.0 | 34.0 | 31.0 |
29 | 54 | 1321.0 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 41.0 | 20.5 | 20.0 | 0.69 | 0.07 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 30.0 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 48.0 | 356.5 | 136.5 | 149.5 |
30 | 50 | 1118.0 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 48.5 | 24.0 | 22.5 | 1.60 | 0.08 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 38.5 | 20.5 | 18.0 | 334.0 | 548.5 | 244.5 | 222.0 |
31 | 48 | 596.5 | 10.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 25.0 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 2.70 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 20.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 56.0 | 206.0 | 66.0 | 76.5 |
32 | 47 | 573.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 25.0 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 2.68 | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.75 | 22.0 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 48.0 | 258.0 | 88.0 | 94.0 |
33 | 48 | 867.0 | 14.5 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 34.5 | 17.5 | 18.5 | 3.15 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 30.0 | 12.0 | 17.0 | 195.0 | 366.5 | 148.5 | 151.0 |
34 | 54 | 1127.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 37.0 | 22.0 | 15.0 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.54 | 34.0 | 14.0 | 13.5 | 65.0 | 422.0 | 159.5 | 162.0 |
35 | 53 | 976.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 37.0 | 18.0 | 15.0 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 31.0 | 17.0 | 13.0 | 128.0 | 371.0 | 152.0 | 107.0 |
36 | 54 | 1072.5 | 13.5 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 38.5 | 18.5 | 17.5 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 0.43 | 0.81 | 29.5 | 15.0 | 13.5 | 172.0 | 349.0 | 138.0 | 158.0 |
37 | 54 | 2960.0 | 18.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 113.0 | 57.5 | 56.5 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 1.00 | 87.0 | 46.0 | 41.5 | 512.0 | 1185.5 | 478.0 | 523.0 |
38 | 44 | 1293.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 32.5 | 17.0 | 15.0 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 29.0 | 15.0 | 13.5 | 5.0 | 143.0 | 56.0 | 68.0 |
39 | 44 | 1065.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 35.5 | 19.0 | 15.5 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 30.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 8.0 | 163.5 | 64.0 | 74.5 |
40 | 42 | 602.5 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 30.0 | 14.5 | 14.5 | 0.88 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 27.5 | 14.0 | 13.5 | 13.5 | 131.0 | 50.5 | 42.0 |
41 | 42 | 737.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 33.0 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 30.5 | 15.5 | 15.0 | 12.0 | 156.0 | 56.5 | 64.5 |
42 | 42 | 1560.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 68.5 | 35.0 | 33.5 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.62 | 58.5 | 26.5 | 30.0 | 22.5 | 443.0 | 161.0 | 187.5 |
43 | 46 | 769.5 | 14.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 34.0 | 16.0 | 17.0 | 2.75 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 26.0 | 12.0 | 15.0 | 76.0 | 329.5 | 117.5 | 141.0 |
44 | 46 | 718.0 | 12.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 26.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 2.74 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.73 | 21.5 | 10.5 | 11.5 | 61.0 | 271.0 | 90.5 | 117.0 |
45 | 46 | 527.5 | 9.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 19.5 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 5.64 | 0.06 | 0.44 | 0.58 | 14.0 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 34.0 | 178.5 | 62.5 | 60.0 |
46 | 47 | 1083.0 | 16.0 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 39.0 | 20.0 | 19.0 | 4.71 | 0.07 | 0.56 | 0.83 | 32.0 | 13.0 | 17.0 | 328.0 | 518.0 | 211.0 | 196.0 |
47 | 44 | 1309.5 | 17.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 66.5 | 33.5 | 33.0 | 0.64 | 0.09 | 0.79 | 0.91 | 53.0 | 26.0 | 24.5 | 400.0 | 670.0 | 252.5 | 296.0 |
48 | 44 | 805.0 | 11.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 35.5 | 19.0 | 17.0 | 1.61 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 0.80 | 29.0 | 14.0 | 16.0 | 80.0 | 313.5 | 107.5 | 117.5 |
49 | 55 | 2307.0 | 17.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 78.0 | 45.0 | 36.0 | 0.51 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 0.83 | 66.0 | 39.0 | 28.0 | 388.0 | 1033.0 | 423.0 | 460.0 |
50 | 55 | 2846.0 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 81.0 | 44.0 | 43.0 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.90 | 66.0 | 35.0 | 31.0 | 384.0 | 1219.0 | 521.0 | 476.0 |
51 | 42 | 1109.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 31.5 | 16.5 | 14.5 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 27.5 | 14.0 | 12.5 | 8.0 | 129.5 | 56.5 | 57.5 |
52 | 42 | 608.5 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 18.0 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 17.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 38.5 | 16.0 | 14.5 |
53 | 46 | 1497.0 | 14.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 55.5 | 29.5 | 29.0 | 2.50 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 46.0 | 23.0 | 23.5 | 128.5 | 663.5 | 252.5 | 269.5 |
54 | 49 | 744.0 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 27.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 3.23 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 24.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 44.0 | 274.0 | 96.0 | 103.0 |
55 | 48 | 712.5 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 26.0 | 13.5 | 13.0 | 2.28 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 0.73 | 21.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 93.0 | 242.0 | 99.0 | 101.0 |
56 | 48 | 1953.5 | 16.5 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 80.0 | 41.0 | 39.0 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 50.0 | 24.0 | 23.0 | 384.0 | 648.0 | 290.0 | 324.0 |
57 | 41 | 938.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 45.0 | 24.0 | 22.0 | 1.56 | 0.09 | 0.68 | 0.82 | 37.0 | 18.0 | 19.0 | 120.0 | 447.0 | 152.0 | 174.0 |
58 | 41 | 659.0 | 9.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 31.0 | 18.0 | 15.0 | 1.54 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.70 | 28.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | 48.0 | 304.0 | 103.0 | 106.0 |
59 | 54 | 1056.5 | 7.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 37.0 | 19.5 | 17.5 | 0.36 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 32.5 | 13.0 | 15.0 | 67.0 | 284.5 | 67.0 | 89.0 |
60 | 56 | 1726.0 | 12.5 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 56.5 | 28.5 | 30.5 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 19.0 | 53.0 | 443.0 | 158.0 | 215.0 |
61 | 56 | 786.0 | 8.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 23.5 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 0.61 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 22.0 | 156.0 | 43.5 | 54.5 |
62 | 48 | 957.5 | 12.5 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 35.5 | 16.0 | 17.0 | 1.03 | 0.07 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 24.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 50.0 | 227.5 | 98.5 | 93.0 |
63 | 50 | 557.5 | 8.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 20.5 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 1.79 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 18.5 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 38.0 | 202.5 | 67.5 | 67.0 |
64 | 48 | 768.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 29.5 | 16.0 | 15.5 | 3.13 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 25.0 | 12.0 | 10.0 | 45.0 | 267.0 | 101.0 | 113.5 |
65 | 48 | 698.5 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 30.5 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 2.18 | 0.07 | 0.56 | 0.65 | 23.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 41.0 | 260.0 | 93.5 | 94.5 |
66 | 50 | 599.5 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 13.5 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 0.97 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 6.5 | 71.0 | 26.0 | 30.0 |
67 | 50 | 486.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 11.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 48.5 | 21.0 | 9.0 |
68 | 45 | 1067.5 | 9.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 39.0 | 22.0 | 17.0 | 1.15 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 32.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 32.0 | 251.0 | 89.0 | 94.0 |
69 | 46 | 536.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 19.0 | 10.5 | 8.0 | 0.77 | 0.07 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 13.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 74.0 | 27.0 | 46.0 |
Table S3. Frequency of coded interactions
Code | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
Sharing info and materials | 4030 | 45,70% |
Sharing facts | 1172 | 13,29% |
Evaluation | 865 | 9,81% |
Argument | 1043 | 11,83% |
Continuing Argument | 567 | 6,43% |
Counter Argument | 115 | 1,30% |
Sharing experience | 47 | 0,53% |
Disagreement | 37 | 0,42% |
Conclusion | 9 | 0,10% |
Question open | 179 | 2,03% |
Question critical | 203 | 2,30% |
Question verification | 91 | 1,03% |
Question alternative | 18 | 0,20% |
Team building | 130 | 1,47% |
Problem handling | 77 | 0,87% |
Task management | 235 | 2,67% |
References
Aarnio, M., Lindblom-Ylänne, S., Nieminen, J., & Pyörälä, E. (2013). Dealing with conflicts on knowledge in tutorial groups. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 18(2), 215–230
Agélii Genlott, A., Grönlund, Ã., & Viberg, O. (2019). Disseminating digital innovation in school—leading second-order educational change. Education and Information Technologies, 24(5), 3021–3039
Anderson, R. C., Nguyen-Jahiel, K., McNurlen, B., Archodidou, A., Kim, S. Y., Reznitskaya, A. … Gilbert, L. (2001). The snowball phenomenon: Spread of ways of talking and ways of thinking across groups of children. Cognition and Instruction, 19(1), 1–46
Bae, J., & Kim, S. (2014). Identifying and ranking influential spreaders in complex networks by neighborhood coreness. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 395, 549–559
Baker, M., Andriessen, J., Lund, K., Van Amelsvoort, M., & Quignard, M. (2007). Rainbow: A framework for analysing computer-mediated pedagogical debates. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 2(2–3), 315–357
Banerjee, A., Chandrasekhar, A. G., Duflo, E., & Jackson, M. O. (2013). The Diffusion of Microfinance. Science, 341(6144), 1236498–1236498
Banerjee, A., Chandrasekhar, A. G., Duflo, E., & Jackson, M. O. (2019). Using Gossips to Spread Information: Theory and Evidence from Two Randomized Controlled Trials. Review of Economic Studies, 86(6), 2453–2490
Barabási, A. L. (2013). Network science. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 371(1987), 20120375. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2012.0375
Bell, P. (2013). Using Argument Map Representations to Make Thinking Visible for Individuals and Groups. In Cscl 2 (pp. 471–528). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410601544-24
Borgatti, S. P. (2005). Centrality and network flow. Social Networks, 27(1), 55–71
Borgatti, S. P., & Brass, D. J. (2019). Centrality: Concepts and Measures. In Social Networks at Work (pp. 9–22)
Borokhovski, E., Bernard, R. M., Tamim, R. M., Schmid, R. F., & Sokolovskaya, A. (2016). Technology-supported student interaction in post-secondary education: A meta-analysis of designed versus contextual treatments. Computers & Education, 96, 15–28
Burgess, L. G., Riddell, P. M., Fancourt, A., & Murayama, K. (2018). The Influence of Social Contagion Within Education: A Motivational Perspective. Mind, Brain, and Education, 12(4), 164–174
Cadima, R., Ojeda, J., & Monguet, J. M. (2012). Social Networks and Performance in Distributed Learning Communities. Educational Technology & Society, 15(4), 296–304
Cakir, M., Xhafa, F., Zhou, N., & Stahl, G. (2005). Thread-based analysis of patterns of collaborative interaction in chat. Proceedings of the 2005 Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education: Supporting Learning through Intelligent and Socially Informed Technology, June 2014, 120–127
Centola, D. (2010). The Spread of Behavior in an Online Social Network Experiment. Science, 329(5996), 1194–1197
Charrad, M., Ghazzali, N., Boiteau, V., Niknafs, A., & Charrad, M. M. (2014). Package ‘nbclust.’. Journal of Statistical Software, 61(6), 1–36
Chen, B., Håklev, S., & Rosé, C. P. (2021). Collaborative Learning at Scale. In International handbook of computer-supported collaborative learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65291-3
Chen, B., Scardamalia, M., & Bereiter, C. (2015). Advancing knowledge-building discourse through judgments of promising ideas. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 10(4), 345–366
Chen, B., & Zhang, J. (2016). Analytics for Knowledge Creation: Towards Epistemic Agency and Design-Mode Thinking. Journal of Learning Analytics, 3(2), 139–163
Chen, C. M., & Chang, C. C. (2014). Mining learning social networks for cooperative learning with appropriate learning partners in a problem-based learning environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 22(1), 97–124
Chen, J., Wang, M., Kirschner, P. A., & Tsai, C. C. (2018). The Role of Collaboration, Computer Use, Learning Environments, and Supporting Strategies in CSCL: A Meta-Analysis. Review of Educational Research, 88(6), 799–843
Cho, H., Gay, G., Davidson, B., & Ingraffea, A. (2007). Social networks, communication styles, and learning performance in a CSCL community. Computers & Education, 49(2), 309–329
Clark, D. B., & Sampson, V. D. (2017). Analyzing the quality of argumentation supported by personally-seeded discussions. In Computer Supported Collaborative Learning 2005: The Next 10 Years! (pp. 76–85). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781351226905-11/analyzing-quality-argumentation-supported-personally-seeded-discussions-douglas-clark-victor-sampson
Cowan, R., & Jonard, N. (2004). Network structure and the diffusion of knowledge. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 28(8), 1557–1575
Csardi, G., & Nepusz, T. (2006). The Igraph software package for complex network research.InterJournal, Complex Sy,1695
Davidson, N., & Major, C. H. (2014). Boundary Crossings: Cooperative Learning, Collaborative Learning, and Problem-Based Learning. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25(3&4), 7–55
de-Marcos, L., García-López, E., García-Cabot, A., Medina-Merodio, J. A., Domínguez, A., Martínez-Herráiz, J. J., & Diez-Folledo, T. (2016). Social network analysis of a gamified e-learning course: Small-world phenomenon and network metrics as predictors of academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 60(PG-312-321), 312–321
Dowell, N. M. M., Nixon, T. M., & Graesser, A. C. (2019). Group communication analysis: A computational linguistics approach for detecting sociocognitive roles in multiparty interactions. Behavior Research Methods, 51(3), 1007–1041
Faghani, M. R., & Nguyen, U. T. (2013). A Study of XSS Worm Propagation and Detection Mechanisms in Online Social Networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 8(11), 1815–1826
Fields, D. A., & Kafai, Y. B. (2009). A connective ethnography of peer knowledge sharing and diffusion in a tween virtual world. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 4(1), 47–68
Guilbeault, D., Becker, J., & Centola, D. (2018). Complex Contagions: A Decade in Review (pp. 3–25). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77332-2_1
Gurevitch, J., Koricheva, J., Nakagawa, S., & Stewart, G. (2018). Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature, 555(7695), 175–182
Havlicek, L. L., & Peterson, N. L. (1976). Robustness of the Pearson Correlation against Violations of Assumptions. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 43(3_suppl), 1319–1334
Haythornthwaite, C. (1996). Social network analysis: An approach and technique for the study of information exchange. Library & Information Science Research, 18(4), 323–342
Hedges, L. V., & Olkin, I. (1985). Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. Elsevier
Hernández-García, Ã., González-González, I., Jiménez-Zarco, A. I., & Chaparro-Peláez, J. (2015). Applying social learning analytics to message boards in online distance learning: A case study. Computers in Human Behavior, 47(PG-68-80), 68–80
Higgins, J. P. T., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21(11), 1539–1558
Holm, S. (1979). A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 6(2), 65–70
IntHout, J., Ioannidis, J. P. A., Rovers, M. M., & Goeman, J. J. (2016). Plea for routinely presenting prediction intervals in meta-analysis.BMJ Open, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010247
Jalili, M., & Perc, M. (2017). Information cascades in complex networks. Journal of Complex Networks, 5(5), 665–693
Janssen, J., & Bodemer, D. (2013). Coordinated Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning: Awareness and Awareness Tools. Educational Psychologist, 48(1), 40–55
Jeong, A., Clark, D. B., Sampson, V. D., & Menekse, M. (2011). Sequential Analysis of Scientific Argumentation in Asynchronous Online Discussion Environments. Analyzing Interactions in CSCL (pp. 207–233). Springer US
Jeong, H., & Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2016). Seven Affordances of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning: How to Support Collaborative Learning? How Can Technologies Help? Educational Psychologist, 51(2), 247–265
Jiang, S., Fitzhugh, S. M., & Warschauer, M. (2014). Social positioning and performance in MOOCs. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 1183, 55–58
Joksimović, S., Manataki, A., Gašević, D., Dawson, S., Kovanović, V., & de Kereki, I. F. (2016). Translating network position into performance. Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Learning Analytics & Knowledge - LAK ’16, 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1145/2883851.2883928
Kim, M. K., & Ketenci, T. (2019). Learner participation profiles in an asynchronous online collaboration context. The Internet and Higher Education, 41, 62–76
Kim, M. K., Wang, Y., & Ketenci, T. (2020). Who are online learning leaders? Piloting a leader identification method (LIM). Computers in Human Behavior, 105, 106205
Kitsak, M., Gallos, L. K., Havlin, S., Liljeros, F., Muchnik, L., Stanley, H. E., & Makse, H. A. (2010). Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks. Nature Physics, 6(11), 888–893
Kwak, S. G., & Kim, J. H. (2017). Central limit theorem: the cornerstone of modern statistics. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology, 70(2), 144
Lee, A. V. Y., & Tan, S. C. (2017a). Promising Ideas for Collective Advancement of Communal Knowledge Using Temporal Analytics and Cluster Analysis. Journal of Learning Analytics, 4(3), 76–101
Lee, A. V. Y., & Tan, S. C. (2017b). Temporal analytics with discourse analysis: Tracing ideas and impact on communal discourse. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, 120–127. https://doi.org/10.1145/3027385.3027386
Lee, A. V. Y., Tan, S. C., & Chee, J. K. K. (2016). Idea identification and analysis (I2A): A search for sustainable promising ideas within knowledge-building discourse. Proceedings of International Conference of the Learning Sciences (ICLS), 1, 90–97
Lehmann, S., & Ahn, Y. Y. (2018). Complex Spreading Phenomena in Social Systems Influence and Contagion in Real-World Social Networks
Li, H. (2018). Deep learning for natural language processing: advantages and challenges. National Science Review, 5(1), 24–26
Likas, A., Vlassis, N., & Verbeek, J., J. (2003). The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognition, 36(2), 451–461
Liu, S., Chai, H., Liu, Z., Pinkwart, N., Han, X., & Hu, T. (2019). Effects of Proactive Personality and Social Centrality on Learning Performance in SPOCs. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, 2(PG-481-487), 481–487. https://doi.org/10.5220/0007756604810487
Liu, Y., Tang, M., Zhou, T., & Do, Y. (2016). Identify influential spreaders in complex networks, the role of neighborhood. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 452, 289–298
Liu, Z., Kang, L., Domanska, M., Liu, S., Sun, J., & Fang, C. (2018a). Social network characteristics of learners in a course forum and their relationship to learning outcomes. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, 1(PG-15-21), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006647600150021
Liu, Z., Kang, L., Su, Z., Liu, S., & Sun, J. (2018b). Investigate the relationship between learners’ social characteristics and academic achievements. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1113(1), 012021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1113/1/012021
López-Pernas, S., Saqr, M., & Viberg, O. (2021). Putting It All Together: Combining Learning Analytics Methods and Data Sources to Understand Students’ Approaches to Learning Programming.Sustainability, 13(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094825
Lund, K., Molinari, G., Séjourné, A., & Baker, M. (2007). How do argumentation diagrams compare when student pairs use them as a means for debate or as a tool for representing debate? International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 2(2–3), 273–295
Marcos-García, J. A., Martínez-Monés, A., & Dimitriadis, Y. (2015). DESPRO: A method based on roles to provide collaboration analysis support adapted to the participants in CSCL situations. Computers & Education, 82, 335–353
McHugh, M. L. (2012). Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica, 22(3), 276–282
Miller, J. K., & Volz, M. (2013). Composing Arguments: An Argumentation and Debate Textbook for the Digital Age. CreateSpace
Mirza, N. M., & Perret-Clermont, A. N. (2009). Argumentation and Education. In Muller, N., Mirza, & Perret-Clermont, A. N. (Eds.), Argumentation and Education: Theoretical Foundations and Practices. Springer US
Mochalova, A., & Nanopoulos, A. (2013). On the role of centrality in information diffusion in social networks. ECIS 2013 - Proceedings of the 21st European Conference on Information Systems
Muller Mirza, N., Tartas, V., Perret-Clermont, A. N., & De Pietro, J. F. (2007). Using graphical tools in a phased activity for enhancing dialogical skills: An example with Digalo. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 2(2–3), 247–272
Nefzger, M. D., & Drasgow, J. (1957). The needless assumption of normality in Pearson’s r. American Psychologist, 12(10), 623
Noroozi, O., Weinberger, A., Biemans, H. J. A. A., Mulder, M., & Chizari, M. (2012). Argumentation-Based Computer Supported Collaborative Learning (ABCSCL): A synthesis of 15 years of research. Educational Research Review, 7(2), 79–106
Nussbaum, E. M., Winsor, D. L., Aqui, Y. M., & Poliquin, A. M. (2007). Putting the pieces together: Online argumentation vee diagrams enhance thinking during discussions. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 2(4), 479–500
Opsahl, T., Agneessens, F., & Skvoretz, J. (2010). Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Social Networks, 32(3), 245–251
Ostertagova, E., Ostertag, O., & Kováč, J. (2014). Methodology and application of the Kruskal-Wallis test. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 611, 115–120
Ouyang, F., & Chang, Y. H. (2019). The relationships between social participatory roles and cognitive engagement levels in online discussions. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(3), 1396–1414
Pei, S., Morone, F., & Makse, H. A. (2018). Theories for Influencer Identification in Complex Networks. In Complex spreading phenomena in social systems (pp. 125–148). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77332-2_8
Peterson, N. L. (1977). Effect of the violation of assumptions upon significance levels of the Pearson r. Psychological Bulletin, 84(2), 373–377
Pinkwart, N., Aleven, V., Ashley, K., & Lynch, C. (2006). Toward Legal Argument Instruction with Graph Grammars and Collaborative Filtering Techniques. Intelligent Tutoring Systems (pp. 227–236). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer
Poquet, O., Saqr, M., & Chen, B. (2021). Recommendations for Network Research in Learning Analytics: To Open a Conversation. In O. Poquet, B. Chen, M. Saqr, & T. Hecking (Eds.), Proceedings of the NetSciLA2021 Workshop “Using Network Science in Learning Analytics: Building Bridges towards a Common Agenda” (NetSciLA2021) (Issue 2868, pp. 34–41). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2868/
Poquet, O., Tupikina, L., & Santolini, M. (2020). Are forum networks social networks? Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Analytics & Knowledge, 366–375. https://doi.org/10.1145/3375462.3375531
Putnik, G., Costa, E., Alves, C., Castro, H., Varela, L., & Shah, V. (2016). Analysing the correlation between social network analysis measures and performance of students in social network-based engineering education. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 26(3), 413–437
Reed, C., & Rowe, G. (2004). Araucaris: Software for Argument Analysis, Diagramming and Representation. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 13(04), 961–979
Reychav, I., Raban, D. R., & McHaney, R. (2018). Centrality Measures and Academic Achievement in Computerized Classroom Social Networks. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 56(4), 589–618
Romero, C., & Ventura, S. (2020). Educational data mining and learning analytics: An updated survey. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 10(3), e1355
Saqr, M., & Alamro, A. (2019). The role of social network analysis as a learning analytics tool in online problem based learning. BMC Medical Education, 19(1), 160
Saqr, M., Fors, U., & Nouri, J. (2018a). Using social network analysis to understand online Problem-Based Learning and predict performance.PLOS ONE, 13(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203590
Saqr, M., Fors, U., & Tedre, M. (2018b). How the study of online collaborative learning can guide teachers and predict students’ performance in a medical course. BMC Medical Education, 18(1), 24
Saqr, M., Fors, U., Tedre, M., & Nouri, J. (2018c). How social network analysis can be used to monitor online collaborative learning and guide an informed intervention.PLOS ONE, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194777
Saqr, M., & López-Pernas, S. (2021). The curious case of centrality measures: a large-scale empirical investigation. Journal of Learning Analytics, 8(3), in-press
Saqr, M., & Montero, C. S. (2020). Learning and Social Networks -Similarities, Differences and Impact. IEEE 20th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT)
Saqr, M., Nouri, J., & Jormanainen, I. (2019). A Learning Analytics Study of the Effect of Group Size on Social Dynamics and Performance in Online Collaborative Learning. In Scheffel, M., Broisin, J., Pammer-Schindler, V., Ioannou, A., & Schneider, J. (Eds.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (11722 vol., pp. 466–479). Cham: Springer
Saqr, M., & Viberg, O. (2020). Using Diffusion Network Analytics to Examine and Support Knowledge Construction in CSCL Settings. In C. Alario-Hoyos, M. J. Rodríguez-Triana, l M. Scheffe, I. Arnedillo-Sánchez, & D. S.M. (Eds.), Proceedings of EC-TEL 2020: Addressing Global Challenges and Quality Education (Vol. 12315, Issue 1, pp. 158–172). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57717-9_12
Saqr, M., Viberg, O., & Vartiainen, H. (2020). Capturing the participation and social dimensions of computer-supported collaborative learning through social network analysis: which method and measures matter? International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 15(2), 227–248
Scheuer, O., Loll, F., Pinkwart, N., & McLaren, B. M. (2010). Computer-supported argumentation: A review of the state of the art. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 5(1), 43–102
Schwarz, B. B., de Groot, R., Mavrikis, M., & Dragon, T. (2015). Learning to learn together with CSCL tools. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 10(3), 239–271
Schwarz, B. B., & Glassner, A. (2007). The role of floor control and of ontology in argumentative activities with discussion-based tools. In International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning (Vol, 2(4), 449–478
Schwarzer, G., Carpenter, J. R., & Rücker, G. (2015). Meta-Analysis with R.Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21416-0
Shakarian, P., Bhatnagar, A., Aleali, A., Shaabani, E., & Guo, R. (2015). The Independent Cascade and Linear Threshold Models. In SpringerBriefs in Computer Science (Issue 9783319231044, pp. 35–48). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23105-1_4
Siemens, G. (2004). Connectivism: A Learning Theory for the Digital Age. International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning, 2
Singh, S. S. (2018). A Survey on Information Diffusion Models in Social Networks. In International Conference on Advanced Informatics for Computing Research (Vol. 956). Springer Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3143-5
Soller, A., Monés, A. M., Jermann, P., & Muehlenbrock, M. (2005). From Mirroring to Guiding: A Review of State of the Art Technology for Supporting Collaborative Learning. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 15(4), 261–290
Steinley, D. (2006). K-means clustering: a half‐century synthesis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 59(1), 1–34
Strijbos, J. W., & Weinberger, A. (2010). Emerging and scripted roles in computer-supported collaborative learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(4), 491–494
Stuetzer, C. M., Koehler, T., Carley, K. M., & Thiem, G. (2013). “Brokering” Behavior in Collaborative Learning Systems. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 100, 94–107
Sumith, N., Annappa, B., & Bhattacharya, S. (2018). Influence maximization in large social networks: Heuristics, models and parameters. Future Generation Computer Systems, 89, 777–790
Suthers, D. D. (2015). From contingencies to network-level phenomena. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Learning Analytics And Knowledge, 16-20-Marc, 368–377. https://doi.org/10.1145/2723576.2723626
Suthers, D. D., & Desiato, C. (2012). Exposing Chat Features through Analysis of Uptake between Contributions. Proceedings of the 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 3368–3377. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2012.274
Suthers, D. D., Dwyer, N., Medina, R., & Vatrapu, R. (2010). A framework for conceptualizing, representing, and analyzing distributed interaction. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 5, 5–42
Suthers, D. D., & Hundhausen, C. D. (2003). An Experimental Study of the Effects of Representational Guidance on Collaborative Learning Processes. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 12(2), 183–218
Temdee, P., Thipakorn, B., Sirinaovakul, B., & Schelhowe, H. (2006). Of Collaborative Learning Team: An Approach for Emergent Leadership Roles Identification by Using Social Network Analysis. In Pan, Z., Aylett, R., Diener, H., Jin, X., Göbel, S., & Li, L. (Eds.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (3942 vol., pp. 745–754). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer
Tomczak, M., & Tomczak, E. (2014). The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends in Sport Sciences, 1(21), 19–25
Tsai, C. Y., Jack, B. M., Huang, T. C., & Yang, J. T. (2012). Using the Cognitive Apprenticeship Web-based Argumentation System to Improve Argumentation Instruction. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 21(4), 476–486
van Gelder, T. (2003). Enhancing Deliberation Through Computer Supported Argument Visualization. In Visualizing Argumentation (pp. 97–115). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-0037-9_5
Visschers-Pleijers, A. J. S. F., Dolmans, D. H. J. M., De Leng, B. A., Wolfhagen, I. H., A., P., & Van Der Vleuten, C. P. M. (2006). Analysis of verbal interactions in tutorial groups: A process study. Medical Education, 40(2), 129–137
Wang, J., Hou, X., Li, K., & Ding, Y. (2017). A novel weight neighborhood centrality algorithm for identifying influential spreaders in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 475, 88–105
Wasserman, S., & Faust, K. (1994). Social network analysis: Methods and applications. In Social network analysis: Methods and applications. (pp. xxxi, 825–xxxi, 825). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511815478
Weinberger, A., Fischer, F., & Stegmann, K. (2017). Computer-supported collaborative learning in higher education: Scripts for argumentative knowledge construction in distributed groups. Computer supported collaborative learning 2005: The next 10 years! (pp. 717–726). Routledge
Wise, A. F., & Cui, Y. (2018). Unpacking the relationship between discussion forum participation and learning in MOOCs. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge, PG-330-339, 330–339. https://doi.org/10.1145/3170358.3170403
Wise, A. F., Knight, S., & Shum, B. (2021). S. Collaborative Learning Analytics. International Handbook of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 1–19
Wise, A. F., & Schwarz, B. B. (2017). Visions of CSCL: eight provocations for the future of the field. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 12(4), 423–467
Yew, E. H. J., & Schmidt, H. G. (2009). Evidence for constructive, self-regulatory, and collaborative processes in problem-based learning. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 14(2), 251–273
Zhang, Z. K., Liu, C., Zhan, X. X., Lu, X., Zhang, C. X., & Zhang, Y. C. (2016). Dynamics of information diffusion and its applications on complex networks. Physics Reports, 651, 1–34
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mahmud Khan for coding the qualitative data and Ramy Elmoazen for his technical support.
Funding
Open access funding provided by University of Eastern Finland (UEF) including Kuopio University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS has contributed to the idea conceptualization, research design, and planning. MS has performed data collection. MS and SLP have contributed to the methods, data analysis and reporting of results and visualization. All graphics and illustrations have been created by SLP. MS has contributed to coding of the data. MS, SLP have contributed to manuscript writing and revision. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Saqr, M., López-Pernas, S. Modelling diffusion in computer-supported collaborative learning: a large scale learning analytics study. Intern. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn 16, 441–483 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09356-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09356-4