Abstract
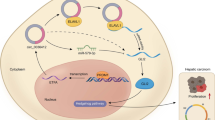
The link of proto-oncogenic protein Wnt-1 production with NF-κB activation has been functionally demonstrated in PC12 cells, a rat pheochromocytoma cell line of neural crest lineage, while it is not yet verified in human cells. The link can be indirectly supported in our previous report that functional proteomics identifies enhanced expression of NF-κB-associated Wnt-1 production in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. This study aimed to further validate this link in human cells using anti-sense strategy. The effects of sequence-specific anti-sense morpholino oligonucleotides (ONs) targeting against pre-mRNA sequences of human p50 and p65 subunits of NF-κB as well as Wnt-1 genes were investigated. It revealed that all the three morpholino ONs inhibited NF-κB activation in human hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2 cells along with decreased Wnt-1 production. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay ascertained the direct binding of NF-κB-p50 to the Wnt-1 promoter. Additionally, anti-P50 and anti-P65 morpholino ONs also repressed the phosphorylation of Iκ Bα which temporarily correlated with the inhibition of NF-κB activation accompanied by decreased Wnt-1 production by HepG2 cells. In summary, NF-κB activation is critically involved in the production of Wnt-1 by HepG2 cells. These results may have important oncology implications in treating patients with NF-κB-associated Wnt-1-producing cancers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- Iκ Bs:
-
Inhibitors of NF-κB
- IKK:
-
IκB kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear transcription factor-κB
- ONs:
-
Oligonucleotides
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- Wnt-1 :
-
Wingless-type MMTV integration site gene family, member 1
- Wnts:
-
Wnt proteins
References
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW (2002) NF-κB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2:301–310
Santoro MG, Rossi A, Amici C (2003) NF-κB and virus infection: who controls whom. EMBO J 22:2552–2560
Baeuerie PA, Baltimore D (1996) NF-κB: ten years after. Cell 57:13–20
Didonato JA, Hayakawa M, Rothwart DM, Zandi E, Karin M (1997) A cytokine-responsive IκB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-κB. Nature 388:548–554
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Mayo MW, Baldwin AS (2000) The transcription factor NF-κB: control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1470:M55–M62
Nusse R, Varmus HE (1992) Wnt genes. Cell 69:1073–1087
Miller JR (2002) The Wints Genome. Biol 3:30011–30015
Kusserow A, Pang K, Sturm C, Hrouda M, Lentfer J, Schmidt HA, Technau U, von Haeseler A, Hobmayer B, Martindale MQ, Holstein TW (2005) Unexpected complexity of the Wnt gene family in a sea anemone. Nature 433:156–160
Cardigan KM, Nusse R (1997) Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development genes. Dev 11:3286–3305
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 14:1837–1841
Nusse R, Varmus HE (1982) Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 31:99–109
Nelson WJ, Nusse R (2004) Convergence of Wnt, β-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science 303:1483–1487
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signaling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434:5843–5450
Staal FJT, Clevers HC (2005) Wnt signaling and haematopoiesis: a Wnt-Wnt situation. Nat Rev Immunol 5:21–30
Goldring SR, Goldring MB (2007) Eating bone or adding it: the Wnt pathway decides. Nat Med 13:133–134
Seifert JRK, Modzik M (2007) Frizzled/PCP signaling: a conserved mechanism regulating cell polarity and directed motility. Nat Rev Genet 8:126–138
Bournat JC, Brown AMC, Soler P (2000) Wnt-1 dependent activation of the survival factor NF-κB in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res 61:21–32
Lee TH, Tai DI, Cheng CJ, Sun CS, Lin CY, Sheu MJ, Lee WP, Peng CY, Wang AHJ, Tsai SL (2006) Enhanced nuclear factor-kappa B-associated Wnt-1 expression in hepatitis B- and C-related hepatocarcinogenesis: identification by functional proteomics. J Biomed Sci 13:27–39
Novina CD, Sharp PA (2004) The RNAi revolution. Nature 430:161–164
Kurreck J (2003) Antisense techonologies: Improvement through novel chemical modifications. Eur J Biochem 270:1628–1644
Kim DK, Rossi JJ (2007) Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet 8:173–184
Alter J, Lou F, Rabinowitz A, Yin H, Rosenfeld J, Wilton SD, Patridge TA, Lu QL (2006) Systemic delivery of morpholino oligonucleotide restores dystrophin expression bodywide and improves dystrophic pathology. Nat Med 12:175–177
Tyson-Capper AJ, Europe-Finner GN (2006) Novel targeting of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) pre-mRNA using antisense morpholino oligonucleotides directed to the 3’acceptor and 5’ donor splicing sites of exon 4: suppression of COX-2 activity in human amnion-derived WISH and myometric cells. Mol Pharmacol 69:796–804
Smith RA, Miller TM, Yamanaka K, Monia BP, Condon TP, Hung G, Lobsiger CS, Ward CM, McAlonis-Downes M, Wei H, Wancewicz EV, Bennett F, Cleveland DW (2006) Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for neurodegenerative disease. J Clin Invest 116:2290–2296
Abmayr SM, Workman JL (1991) Preparation of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts from mammalian cells. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 12.1.1–12.1.9
Tai DI, Tsai SL, Chen YM, Chuang YL, Peng CY, Sheen IS, Yeh CT, Chang KSS, Huang SN, Kuo GC, Liaw YF (2000) Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in hepatitis C virus infection: implications for pathogenesis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 31:656–664
Katschinski DM, Robins HI, Schad M, Frede S, Fandrey J (1999) Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in hyperthermia-induced apoptosis of human leukemia cells. Cancer Res 59:3404–3410
Rüegg C, Yilmaz A, Bieler G, Barnat J, Chaubert P, Lejeune FJ (1998) Evidence for the involvement of endothelial cell integrin αVβ3in the destruction of the tumor vasculature induced by TNF and IFN-γ. Nat Med 4:408–414
Kawai M, Nishikomori R, Jung EY, Tai G, Yamanaka C, Mayumi M, Heike T (1995) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits intercellular adhesion molecule-1 biosynthesis induced by cytokines in human fibroblasts. J Immunol 154:2333–2341
van Ooyen A, Kwee V, Nusse R (1985) The nucleotide sequence of human int-1 mammary oncogene: evolutionary conservation of coding and non-coding sequences. EMBO J 4:2905–2909
Luo JL, Tan W, Korchynskyi O, Zhang M, Gonias SL, Cheresh DA, Karin M (2007) Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKα controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 446:690–694
Theodorou V, Kimm MA, Boer M, Wessels L, Theelen W, Jonkers J, Hilkens J (2007) MMTV insertional mutagenesis identifies genes, gene families and pathways involved mammary cancer. Nat Genet 39:759–769
Arheden K, Mandahl N, Strombeck B, lsaksson M, Mitelman F (1988) Chromosome localization of the human oncogene INT1 to 12q 13 by in situ hybridization Cytogenet. Cell Genet 47:86–87
Nusse R, Ooyen A, van Cox D, Fung YK, Varmus H (1984) Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature 307:131–136
Echelard Y, Vassileva G, McMahon AP (1994) C is-acting regulatory sequences governing Wnt-1 expression in the developing mouse CNS. Development 120:2213–2224
Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, Qian BZ, Zhu ZD, Yan Q, Cai T, Zhang X, Xiao HS, Qu J, Liu F, Huang QH, Cheng ZH, Li NG, Du JJ, Hu W, Shen KT, Lu G, Fu G, Zhong M, Xu SH, Gu WY, Huang W, Zhao XT, Chen Z, Han ZG (2001) Insight into hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of corresponding noncancerous liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15089–15094
Fukutomi T, Zhou Y, Kawai S, Eguchi H, Wands JR, Li J (2005) Hepatitis C virus core protein stimulates hepatocyte growth: correlation with upregulation of wnt-1 expression. Hepatology 41:1096–1105
Doria M, Klein N, Lucito R, Schneider RJ (1995) The hepatitis B virus HBx protein is a dual specificity cytoplasmic activator of Ras and nuclear activator of transcription factors. EMBO J 14:4747–4757
Su F, Schneider RJ (1996) Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates transcription factor NF-κB by acting on multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors of rel-related proteins. J Virol 70:558–4566
Yoshida H, Kato N, Shiratori Y, Otsuka M, Maeda S, Kato J, Omata M (2001) Hepatitis C virus core protein activates nuclear factor kappa B-dependent signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor. J Biol Chem 276:16399–163405
Boya P, Larrea E, Sola I, Majano P-L, Jiménez C, Civeira M-P, Prieto J (2001) Nuclear factor-κB in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis C: decreased RelA expression is associated with enhanced fibrosis progression. Hepatology 34:1041–1048
Gong G, Waris G, Tanveer R, Siddiqui A (2001) Human hepatitis C virus NS5A protein alters intracellular calcium levels, induces oxidative stress, and activates STAT-3 and NF-κB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9599–9604
Marusawa H, Hijikata M, Chiba T, abd Shimotohno K (1999) Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits fas- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis via NF-κB activation. J Virol 73:4713–4720
Cha MY, Kim CM, Park YM, Ryu WS (2004) Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential for the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatoma cells. Hepatology 39:1683–1693
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W (1996) Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382:638–642
Peifer M (1997) Beta-catenin as oncogene: the smoking gun. Science 275:1752–1753
Morin PI (1999) Beta-catenin signaling and cancer. Bioessays 21:1021–1030
Merle P, Kim M, Herrmann M, Gupte A, Lefrançois L, Califano S, Trépo C, Tanaka S, Vitvitski L, de la Monte S, Wands JR (2005) Oncogenic role of frizzled-7/ β- catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 43:854–862
Schroeder JA, Adriance MC, McConnell EJ, Thompson MC, Pockaj B, Gendlers SJ (2002) ErbB-β-catenin complexes are associated with human infiltrating ductal breast and murine mammary tumor virus (MMTV)-Wnt-1 and MMTV-c-neu transgenic carcinomas. J Biol Chem 277:22692–22698
Ruiz i Altaba A, Sánchez P, Dahmane N (2002) Gli and Hedgehog in cancer: tumors, embryos, and stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2:361–370
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H (2003) Caught up a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1653:1–24
Yokota N, Nishizawa S, Ohta S, Date H, Sugimura H, Namba H, Maekawa M (2002) Role of WNT pathway in medulloblastoma oncogenesis. Int J Cancer 101:198–201
Gilbertson RJ (2004) Medulloblastoma: signaling a change in treatment. Lancet Oncol 5:209–218
Rhee CS, Sen M, Lu D, Wu C, Leoni L, Rubin J, Carson CM (2002) Wnt and frizzled receptors as potential targets for immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncogene 21:6598–6605
Wang CY, Cusack JC, Liu R, Baldwin AS (1999) Control of inducible chemoresistance: enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis through inhibition of NF-kappa B. Nat Med 5:421–427
Hong WK, Sporn MB (1997) Recent advances in chemoprevention of cancer. Science 278:1073–1077
Nakanishi C, Toi M (2005) Nuclear factor-κB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 5:297–309
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Chi Mei Foundation CMFHT9102, CMFHT9322 and CMFHT 9401, Tainan, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, CS., Wu, KT., Lee, HH. et al. Anti-sense morpholino oligonucleotide assay shows critical involvement for NF-κB activation in the production of Wnt-1 protein by HepG2 cells: oncology implications. J Biomed Sci 15, 633–643 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-008-9251-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-008-9251-1