Abstract
Purpose
Estimating the joint probability of occurrence and joint return period of suspended sediment load (SSL) is necessary for the design and operation of hydraulic structures. The amount of SSL is closely related to the amount of runoff, which is highly dependent on the amount of rainfall. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to estimate the joint probability of occurrence and the joint return period of SSL values given rainfall and river discharge values.
Methods
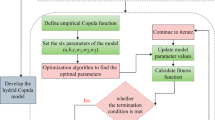
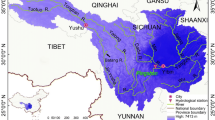
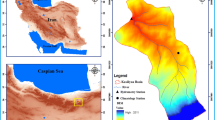
The vine copula family was used in this study to trivariate frequency analyses of SSL associated with rainfall and stream flow in Allah Basin, Iran. We used daily data of 140 events recorded at Jokanak station during 1975–2020. To create the probabilistic model, the structures of D-vine, C-vine, and R-vine copula functions, as well as rotational, Gaussian, and independent modes, were examined based on log-likelihood, AIC, and BIC criteria.
Results
The results of examining the marginal distributions showed that the generalized Pareto (RMSE=3.91, NSE=0.98, MAPE=3.91), log-normal (RMSE=2.69, NSE=0.99, MAPE=7.69), and GEV (RMSE=2.16, NSE=0.99, MAPE=5.43) are the best-fitted distributions on rainfall, river flow, and SSL data, respectively. By examining the various vine structures, the D-vine was chosen as a suitable copula (AIC=−727.8, BIC=−714.3, and log-likelihood=366.9) for modeling the dependency structure among rainfall (R), river flow (Q), and SSL. Examining the tree structure of considered copulas revealed that the D-vine copula maintains the dependency of the pairs of variables by selecting the best edges until the last tree. Frank and Clayton’s 180-degree copulas were chosen as the best internal copula functions. The conditional return period of suspended sediment load in the study area was calculated and presented as contour curves based on rainfall and corresponding discharge. The return period provided is given by the occurrence of runoff and rainfall values. Compared to the univariate method, the presented return period includes a range of data. For example, in the 2-year return period, changes in SSL values provide a range of 0.46 to 1,395,579 tons per day, given the corresponding rainfall and runoff values with probabilities of 0.0031 to 0.50.
Conclusions
Using this model, SSL values can be estimated by having the amounts of rainfall and river flow at different probability levels. The results showed that using the rotated copulas can describe the correlation in all directions, and therefore provide more reliable results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data used in this research will be available (by the corresponding author), upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes written and used in this research will be available (by the corresponding author), upon reasonable request.
References
Adamson PT, Metcalfe AV, Parmentier B (1999) Bivariate extreme value distributions: an application of the Gibbs sampler to the analysis of floods. Water Resour Res 35(9):2825–2832. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999WR900152
Agarwal AH, Mishra SK, Singh JK (2006) Simulation of runoff and sediment yield using artificial neural networks. Biosyst Eng 97(4):597–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.02.014
Asselman NEM (2000) Fitting and interpretation of sediment rating curves. J Hydrol 234(3–4):228–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00253-5
Bajirao TS, Kumar P, Kumar M, Elbeltagi A, Kuriqi A (2021) Superiority of hybrid soft computing models in daily suspended sediment estimation in highly dynamic rivers. Sustainability 13:542. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020542
Bedford T, Cooke R (2001) Probabilistic risk analysis: foundations and methods. Cambridge University Press. https://www.amazon.com/Probabilistic-Risk-Analysis-Foundations-Methods/dp/0521773202
Bezak N, Mikoš M, Šraj M (2014) Trivariate frequency analyses of peak discharge, hydrograph volume and suspended sediment concentration data using copulas. Water Resour Manag 28:2195–2212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0606-2
Bezak N, Rusjan S, Fijavž MK, Mikoš M, Šraj M (2017) Estimation of suspended sediment loads using copula functions. Water 9:628. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080628
Buyukyildiz M, Kumcu SY (2017) An estimation of the suspended sediment load using adaptive network based fuzzy inference system, support vector machine and artificial neural network models. Water Resour Manag 31(4):1343–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1581-1
Cigizoglu HK, Alp M (2006) Generalized regression neural network in modeling river sediment yield. Adv Eng Softw 37:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2005.05.002
Czado C (2019) Analyzing dependent data with vine copulas. Lecture Notes in Statistics, Springer, 222. https://link.springer.com/book/. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13785-4
Fan J, Liu X, Li W (2023) Daily suspended sediment concentration forecast in the upper reach of Yellow River using a comprehensive integrated deep learning model. J Hydrol 129732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129732
Favre AC, El Adlouni S, Perreault L, Thiémonge N, Bobée B (2004) Multivariate hydrological frequency analysis using copulas. Water Resour Res 40(1). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002456
Favre AC, Musy A, Morgenthaler S (2002) Two-site modeling of rainfall based on the Neyman-Scott process. Water Resour Res 38(12):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002WR001343
Joe H (1997) Multivariate models and multivariate dependence concepts. Springer New York, NY. https://link.springer.com/book/9781489931061
Kaveh K, Bui MD, Rutschmann P (2017) A comparative study of three different learning algorithms applied to ANFIS for predicting daily suspended sediment concentration. Int J Sediment Res 32(3):340–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2017.03.007
Khalili K, Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Mirabbasi R, Ahmadi F (2016) Investigation of spatial and temporal variability of precipitation in Iran over the last half century. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30(4):1205–1221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1095-4
Khozeymehnezhad H, Nazeri Tahroudi M (2019) Annual and seasonal distribution pattern of rainfall in Iran and neighboring regions. Arab J Geosci 12:1–11
Kurowicka D, Cooke RM (2007) Sampling algorithms for generating joint uniform distributions using the vine-copula method. Comput Stat Data Anal 51(6):2889–2906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2006.11.043
Lafdani EK, Nia AM, Ahmadi A (2013) Daily suspended sediment load prediction using artificial neural networks and support vector machines. J Hydrol 478:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.048
Li F, Zheng Q (2016) Probabilistic modelling of flood events using the entropy copula. Adv Water Resour 97:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.09.016
Li S, Xie Q, Yang J (2022) Daily suspended sediment forecast by an integrated dynamic neural network. J Hydrol 604:127258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127258
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Pourreza-Bilondi M, Ramezani Y (2019) Toward coupling hydrological and meteorological drought characteristics in Lake Urmia Basin, Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 138(3):1511–1523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02919-4
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, De Michele C, Mirabbasi R (2021) Flood routing via a copula-based approach. Hydrol Res 52(6):1294–1308. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2021.008
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, De Michele C, Mirabbasi R (2022a) Application of copula functions for bivariate analysis of rainfall and river flow deficiencies in the Siminehrood River Basin, Iran. J Hydrol Eng 27(11):05022015. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0002207
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, De Michele C, Mirabbasi R (2022b) Application of copula‐based approach as a new data‐driven model for downscaling the mean daily temperature. Int J Climatol 43(12). https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7752
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, De Michele C, Mirabbasi R (2022c) Trivariate joint frequency analysis of water resources deficiency signatures using vine copulas. Appl Water Sci 12(4):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01589-4
Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, De Michele C, Mirabbasi R (2022d) Multivariate analysis of rainfall and its deficiency signatures using vine copulas. Int J Climatol 42(4):2005–2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7349
Nelsen RB (2006) An introduction to copulas, ser. Lecture Notes in Statistics. Springer, New York. https://link.springer.com/book/. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-28678-0
Peng Y, Shi Y, Yan H, Zhang J (2020) Multivariate frequency analysis of annual maxima suspended sediment concentrations and floods in the Jinsha River, China. J Hydrol Eng 25(9):05020029. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001977
Phillips RW, Spence C, Pomeroy JW (2011) Connectivity and runoff dynamics in heterogeneous basins. Hydrol Process 25:3061–3075. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8123
Pronoos Sedighi M, Ramezani Y, Nazeri-Tahroudi M, Taghian M (2023) Joint frequency analysis of river flow rate and suspended sediment load using conditional density of copula functions. Acta Geophys 71(1):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00894-5
Rahul AK, Shivhare N, Kumar S, Dwivedi SB, Dikshit PKS (2022) Modelling suspended sediment concentration and discharge relationship using neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Arab J Geosci 15:493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09744-6
Salih SQ, Sharafati A, Khosravi K, Faris H, Kisi O, Tao H, Yaseen ZM (2020) River suspended sediment load prediction based on river discharge information: application of newly developed data mining models. Hydrol Sci J 65:624–637. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1703186
Salvadori G, De Michele C (2007) On the use of copulas in hydrology: theory and practice. J Hydrol Eng 12(4):369–380. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2007)12:4(369)
Samadianfard S, Kargar K, Shadkani S, Hashemi S, Abbaspour A, Safari MJS (2022) Hybrid models for suspended sediment prediction: optimized random forest and multi-layer perceptron through genetic algorithm and stochastic gradient descent methods. Neural Comput Appl 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06550-1
Seyedian SM, Rouhani H (2015) Assessing ANFIS accuracy in estimation of suspended sediments. Gradevinar 67(12):1225–1236. https://doi.org/10.14256/JCE.1210.2015
Shadkani S, Abbaspour A, Samadianfard S, Hashemi S, Mosavi A, Band SS (2021) Comparative study of multilayer perceptron-stochastic gradient descent and gradient boosted trees for predicting daily suspended sediment load: the case study of the Mississippi River, US. Int J Sediment Res 36(4):512–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2020.10.001
Shamaei E, Kaedi M (2016) Suspended sediment concentration estimation by stacking the genetic programming and neuro-fuzzy predictions. Appl Soft Comput 45:187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.03.009
Sklar M (1959) Fonctions de repartition a n dimensions et leurs marges. Publications De L’institut Statistique De L’université De Paris 8:229–231
Sproles EA, Leibowitz SG, Reager JT, Wigington PJ, Famiglietti JS (2015) GRACE storage-runoff hysteresis reveal the dynamics of regional watersheds. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:3253–3272. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-3253-2015
Tabatabaei SM, Dastourani M, Eslamian S, Nazeri-Tahroudi M (2022) Ranking and optimizing the rain-gauge networks using the entropy–copula approach (case study of the Siminehrood Basin, Iran). Appl Water Sci 12(9):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01735-y
Vahidi MJ (2022) Bivariate analysis of river flow and suspended sediment load in Aharchai Basin, Iran. Arab J Geosci 15(14):1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10526-3
Walling DE (1977) Assessing the accuracy of suspended sediment rating curves for a small basin. Water Resour Res 13(3):531–538. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR013i003p00531
Wolfs V, Willems P (2014) Development of discharge-stage curves affected by hysteresis using time varying models, model trees and neural networks. Environ Model Softw 55:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.01.021
Xiao Y, Guo S, Liu P, Fang B (2008) A new design flood hydrograph method based on bivariate joint distribution. Int Assoc Hydrol Sci 319:75–82. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20093172552
Yang C, Lee KY (2018) Analysis of flow-sediment rating curve hysteresis based on flow and sediment travel time estimations. Int J Sediment Res 33:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2017.10.003
Yilmaz B, Aras E, Kankal M, Nacar S (2019) Prediction of suspended sediment loading by means of hybrid artificial intelligence approaches. Acta Geophys 67:1693–1705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00374-3
Yu K, Hehuizi Z, Zhang X, Li P, Zhanbin L, Zhang X, Zhao Y (2020) Probability prediction of the suspended sediment concentration using copulas. Authorea. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.159108314.43203315.
Yue S, Ouarda TBMJ, Bobée B (2001) A review of bivariate gamma distributions for hydrological application. J Hydrol 246(1–4):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00374-2
Zeyneb T, Nadir M, Boualem R (2022) Modeling of suspended sediment concentrations by artificial neural network and adaptive neuro fuzzy interference system method–study of five largest basins in Eastern Algeria. Water Pract Technol 17(5):1058. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2022.050
Zhang L, Singh V (2006) Bivariate flood frequency analysis using the copula method. J Hydrol Eng 11(2):150–164. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2006)11:2(150)
Zounemat-Kermani M, Kişi Ö, Adamowski J, Ramezani-Charmahineh A (2016) Evaluation of data driven models for river suspended sediment concentration modeling. J Hydrol 535:457–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.012
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Iran Water Resources Management Company for providing the data needed in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The participation of A. Khashei-Siuki, M. Nazeri Tahroudi, and A. M. Jafari includes the data collection, running the model, and writing the original draft, and the participation of M. J. Vahidi and Rasoul Mirabbasi includes running the model, analyzing the results, and writing - editing the revised article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hugh Smith
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vahidi, M.J., Mirabbasi, R., Khashei-Siuki, A. et al. Modeling of daily suspended sediment load by trivariate probabilistic model (case study, Allah River Basin, Iran). J Soils Sediments 24, 473–484 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03629-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03629-1