Abstract
Purpose
Dendrocalamus brandisii has a long planting history in Yunnan Province, China. Practical experience has proven that a long planting duration will affect the soil bacterial community. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of the planting duration on soil environmental factors and the soil bacterial community of D. brandisii to provide a scientific basis and theoretical support for the efficient and sustainable management of D. brandisii and the improvement of soil quality.
Materials and methods
Soil samples were collected from D. brandisii with similar habitats, consistent management measures, and different planting durations (5, 10, 20, and 40 years). The differences in the soil bacterial community structure, diversity, and functional groups under different planting durations were analyzed using high-throughput sequencing technology and the FAPROTAX function prediction tool to reveal the main soil environmental factors influencing the variations in the soil bacterial community.
Results and discussion
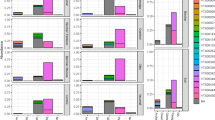
Soil organic carbon (SOC), total potassium (TK), and available phosphorus (AP) increased and then decreased with increasing planting durations, while pH, total phosphorus (TP), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) showed the opposite change trend, indicating that not all environmental factors changed regularly with increasing planting durations. The relative abundance of Verrucomicrobia gradually increased and that of Chloroflexi gradually decreased with increasing planting duration, indicating that different successional patterns existed in the soil bacterial community. Different planting durations affected the changes of soil bacterial community diversity, and the Richness index and Shannon index at 10 years was the highest under all planting durations. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) and analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) showed that there were significant differences in soil bacterial community structure with different planting durations. Chemoheterotrophy, aerobic chemoheterotrophy, and cellulolysis were the main functional groups in the soil of D. brandisii, and there were significant differences between different planting durations. Correlation analysis showed that pH, NO3−-N, the C/N ratio, and the C/P ratio were the dominant factors affecting the soil bacterial community.
Conclusions
The planting durations of D. brandisii changed the structure, diversity, and functional groups of the soil bacterial community primarily by affecting soil environmental factors.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Sequencing raw data is available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, PRJNA850842.
References
Andreote FD, Jiménez DJ, Chaves D, Dias AC, Luvizotto DM, Dini-Andreote F, Fasanella CC, Lopez MV, Baena S, Taketani RG, de Melo IS (2012) The microbiome of Brazilian mangrove sediments as revealed by metagenomics. PLoS ONE 7(6):e38600
Averill C, Hawkes CV (2016) Ectomycorrhizal fungi slow soil carbon cycling. Ecol Lett 19(8):937–947
Bahru T, Ding YL (2020) Effects of thinning intensity and growth parameters on Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz shoot production in Simao District, Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Glob Ecol Conserv 22:e00954
Banning NC, Gleeson DB, Grigg AH, Grant CD, Andersen GL, Brodie EL, Murphy DV (2011) Soil microbial community successional patterns during forest ecosystem restoration. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(17):6158–6164
Bisht SS, Sethy AK, Pandey A (2017) Histo-anatomical and bio-chemical study of Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz before, during and after flowering. J Indian Acad Wood Sci 14:122–126
Callahan BJ, Mcmurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson A, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583
Cardinale BJ, Srivastava DS, Duffy JE, Wright JP, Downing AL, Sankaran M, Jouseau C (2006) Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature 443(7114):989–992
Che RX, Liu D, Qin JL, Wang F, Wang WJ, Xu ZH, Li LF, Hu JM, Tahmasbian I, Cui XY (2020) Increased litter input significantly changed the total and active microbial communities in degraded grassland soils. J Soils Sediments 20:2804–2816
Chen H, Boutros PC (2011) VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics 12:35
Chen FL, Zheng H, Zhang K, Ouyang ZY, Lan J, Li HL, Shi Q (2013) Changes in soil microbial community structure and metabolic activity following conversion from native Pinus massoniana plantations to exotic Eucalyptus plantations. For Ecol Manage 291:65–72
Deng Q, Cheng XL, Hui DF, Zhang Q, Li M, Zhang QF (2016) Soil microbial community and its interaction with soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics following afforestation in central China. Sci Total Environ 541:230–237
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(3):626–631
Fierer N, Craine JM, McLauchlan K, Schimel JP (2005) Litter quality and the temperature sensitivity of decomposition. Ecology 86:320–326
Galicia L, Garcia-Oliva F (2004) The effects of C, N and P additions on soil microbial activity under two remnant tree species in a tropical seasonal pasture. Appl Soil Ecol 26(1):31–39
Guo MJ, Wu FH, Hao GG, Qi Q, Li R, Li N, Wei LM, Chai TJ (2017) Bacillus subtilis improves immunity and disease resistance in rabbits. Front Immunol 8:354
He D, Shen W, Eberwein J, Zhao Q, Ren L, Wu Q (2017) Diversity and co-occurrence network of soil fungi are more responsive than those of bacteria to shifts in precipitation seasonality in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 115:499–510
Jiang S, Xing YJ, Liu GC, Hu CY, Wang XC, Yan GY, Wang QG (2021) Changes in soil bacterial and fungal community composition and functional groups during the succession of boreal forests. Soil Biol Biochem 161(3):108393
Jing ZB, Cheng JM, Su JS, Bai Y, Jin JW (2014) Changes in plant community composition and soil properties under 3-decade grazing exclusion in semiarid grassland. Ecol Eng 64:171–178
Jošić D, Ćirić A, Soković M, Stanojković-Sebić A, Pivic R, Lepšanović Z, Glamočlija JM (2015) Antifungal activities of indigenous plant growth promoting Pseudomonas spp. from alfalfa and clover rhizosphere. Front Life Sci 8(2):1–8
Kelkar BU, Sharma SK, Shukla SR (2020) Optimization of pressing parameters of PF-bonded laminated bamboo lumber from Dendrocalamus brandisii. J Indian Acad Wood Sci 17:149–157
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(15):5111–5120
Li B, Chen YP, Liu Q, Hu SN, Chen XH (2011) Complete genome analysis of Sulfobacillus acidophilus strain TPY, isolated from a hydrothermal vent in the Pacifc Ocean. J Bacteriol 193(19):5555–5556
Liu M, Liu J, Jiang CY, Wu M, Song RS, Gui RY, Jia JX, Li ZP (2017) Improved nutrient status affects soil microbial biomass, respiration, and functional diversity in a Lei bamboo plantation under intensive management. J Soils Sediments 17(4):917–926
Liu D, Huang Y, Sun H, An S (2018) The restoration age of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation impacts soil microbial biomass and microbial community structure in the Loess Plateau. CATENA 165:192–200
Liu WY, Wang F, Sun YM, Yang L, Wang SW (2020) Influence of dragon bamboo with different planting patterns on microbial community and physicochemical property of soil on sunny and shady slopes. J Microbiol 58(11):906–914
Liu S, Li P, Van Zwieten L, Tu J, Gan W, Lu S, Wang H, Wu L (2021) Edaphic variables influence soil bacterial structure under successive fertilization of Paulownia plantation substituting native vegetation. J Soils Sediments 21:2922–2937
Liu X, Shi Y, Kong L, Tong L, Cao H, Zhou H, Lv Y (2022) Long-term application of bio-compost increased soil microbial community diversity and altered its composition and network. Microorganisms 10(2):462
Lladó S, López-Mondéjar R, Baldrian P (2018) Drivers of microbial community structure in forest soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(10):4331–4338
Malcolm GM, Bush DS, Rice SK (2008) Soil nitrogen conditions approach preinvasion levels following restoration of nitrogen-fixing black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) stands in a pine-oak ecosystem. Restor Ecol 16(1):70–78
Nowicka B, Kruk J (2016) Powered by light: phototrophy and photosynthesis in prokaryotes and its evolution. Microbiol Res 186–187:99–118
Palaniyandi SA, Damodharan K, Yang SH, Suh JW (2014) Streptomyces sp. strain PGPA39 alleviates salt stress and promotes growth of 'Micro Tom' tomato plants. J Appl Microbiol 117(3): 766–773
Pearce DA, Newsham KK, Thorne MA, Calvo-Bado L, Krsek M, Laskaris P, Hodson A, Wellington EM (2012) Metagenomic analysis of a southern maritime antarctic soil. Front Microbiol 3:403
Pittman JJ, Zhang H, Schroder JL, Payton ME (2005) Differences of phosphorus in Mehlich 3 extracts determined by colorimetric and spectroscopic methods. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 36(11–12):1641–1659
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35(21):7188–7196
Qin SH, Yeboah S, Xu XX, Liu YH, Yu B (2017) Analysis on fungal diversity in rhizosphere soil of continuous cropping potato subjected to different furrow-ridge mulching managements. Front Microbiol 8:845
Rice SK, Westerman B, Federici R (2004) Impacts of the exotic, nitrogen-fixing black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) on nitrogen-cycling in a pine-oak ecosystem. Plant Ecol 174:97–107
Ricketts MP, Flower CE, Knight KS, Gonzalez-Meler MA (2018) Evidence of ash tree (Fraxinus spp.) specific associations with soil bacterial community structure and functional capacity. Forests 9(4):187
Romaniuk R, Giuffré L, Costantini A, Nannipieri P (2011) Assessment of soil microbial diversity measurements as indicators of soil functioning in organic and conventional horticulture systems. Ecol Indic 11(5):1345–1353
Rosado-Porto D, Ratering S, Moser G, Deppe M, Müller C, Schnell S (2022) Soil metatranscriptome demonstrates a shift in C, N, and S metabolisms of a grassland ecosystem in response to elevated atmospheric CO2. Front Microbiol 13:937021
Seipke RF, Kaltenpoth M, Hutchings MI (2012) Streptomyces as symbionts: an emerging and widespread theme? FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(4):862–876
Sethy AK, Sharma SK, Simon J (2019) Effect of flowering on physical and mechanical properties of Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. J Indian Acad Wood Sci 16:22–26
Shen H, Yan XL, Ming Z, Zheng SL, Wang XR (2002) Exudation of organic acids in common bean as related to mobilization of aluminum- and iron-bound phosphates. Environ Exp Bot 48:1–9
Shen CC, Ni YY, Liang WJ, Wang JJ, Chu HY (2015) Distinct soil bacterial communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in alpine tundra. Front Microbiol 6:582
Singh AN, Singh JS (1999) Biomass, net primary production and impact of bamboo plantation on soil redevelopment in a dry tropical region. For Ecol Manage 119:195–207
Slaughter LC, Weintraub MN, McCulley RL (2015) Seasonal effects stronger than three-year climate manipulation on grassland soil microbial community. Soil Sci Soc Am J 79:1352–1365
Song M, Peng WX, Du H, Xu QG (2019) Responses of soil and microbial C:N: P stoichiometry to vegetation succession in a Karst region of southwest China. Forests 10(9):755
Ste-Marie C, Paré D (1999) Soil, pH and N availability effects on net nitrification in the forest floors of a range of boreal forest stands. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1579–1589
Tahseen S, Chen L, Wang JY, Hui WK, Waseem H, Wei G (2022) Post-farmland conversion spatio-temporal dynamics of net soil nitrogen mineralization and availability in a chronosequence of Zanthoxylum bungeanum plantations. Land Degrad Dev 33(15):2677–2688
Venter ZS, Jacobs K, Hawkins HJ (2016) The impact of crop rotation on soil microbial diversity: a meta-analysis. Pedobiologia 59:215–223
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267
Wang YJ, Zhan H, Ding YL, Wang SG, Lin SY (2015) Variability of anatomical and chemical properties with age and height in Dendrocalamus brandisii. BioResources 11(1):1202–1213
Wang SQ, Li TX, Zheng ZC (2017) Distribution of microbial biomass and activity within soil aggregates as affected by tea plantation age. CATENA 153:1–8
Wang F, Che RX, Deng YC, Wu YB, Tang L, Xu ZH, Wang WJ, Liu HB, Cui XY (2021a) Air-drying and long time preservation of soil do not significantly impact microbial community composition and structure. Soil Biol Biochem 157:108238
Wang X, Dai WW, Filley TR, Wang C, Bai E (2021b) Aboveground litter addition for five years changes the chemical composition of soil organic matter in a temperate deciduous forest. Soil Biol Biochem 161:108381
Wu LK, Li ZF, Li J, Khan MA, Huang WM, Zhang ZY, Lin WX (2013) Assessment of shifts in microbial community structure and catabolic diversity in response to Rehmannia glutinosa monoculture. Appl Soil Ecol 67:1–9
Xu QF, Jiang PK, Xu ZH (2008) Soil microbial functional diversity under intensively managed bamboo plantations in southern China. J Soils Sediments 8:177–183
Xu YX, Du AP, Wang ZC, Zhu WK, Li C, Wu LC (2020) Effects of different rotation periods of Eucalyptus plantations on soil physiochemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure and diversity. For Ecol Manage 456:117683
Xu MP, Jian JN, Wang JY, Zhang ZJ (2021) Response of root nutrient resorption strategies to rhizosphere soil microbial nutrient utilization along Robinia pseudoacacia plantation chronosequence. For Ecol Manage 489:119053
Xu YX, Liu JJ, Liu XF, Li H, Yang Z, Wang HB, Huang XY, Lan L, An YT, Li LJ, Yao Q, Wang GH (2022) Continuous cropping of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) reduces bacterial diversity and simplifies cooccurrence networks in aeolian sandy soil. Soil Ecol Lett 4:131–143
Yang CB, Zhang XP, Ni HJ, Gai X, Huang ZC, Du XH, Zhong ZK (2021) Soil carbon and associated bacterial community shifts driven by fine root traits along a chronosequence of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) plantations in subtropical China. Sci Total Environ 752:142333
Yang Q, Lei AP, Li LN, Zan QJ, Shin PKS, Cheung SG, Tam NFY (2014) Structure and function of soil microbial community in artificially planted Sonneratia apetala and S.caseolaris forests at different stand ages in Shenzhen Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 85(2):754–763
Yu XY, Zhu YJ, Wang B, Liu D, Bai H, Jin L, Wang BT, Ruan HH, Mao LF, Jin FJ, Yang N (2021) Effects of nitrogen addition on rhizospheric soil microbial communities of poplar plantations at different ages. For Ecol Manage 494:119328
Zhang X, Hu BX, Ren H, Zhang J (2018) Composition and functional diversity of microbial community across a mangrove-inhabited mudflat as revealed by 16S rDNA gene sequences. Sci Total Environ 633:518–528
Zhang XP, Zhong ZK, Bian FY, Yang CB (2019) Effects of composted bamboo residue amendments on soil microbial communities in an intensively managed bamboo (Phyllostachys praecox) plantation. Appl Soil Ecol 136(9):178–183
Zhang XP, Gao GB, Wu ZZ, Wen X, Zhong H, Zhong ZZ, Yang CB, Bian FY, Gai X (2020) Responses of soil nutrients and microbial communities to intercropping medicinal plants in moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(2):2301–2310
Zhu LY, Wang XH, Chen FF, Li CH, Wu LC (2019) Effects of the successive planting of Eucalyptus urophylla on the soil bacterial and fungal community structure, diversity, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity. Land Degrad Dev 30(6):636–646
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the staff of Southwest Forestry University for providing the research platform and logistics services.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD2200501), Basic Research Project of Yunnan Province (202201AT070053), Agriculture Joint Special Project of Yunnan Province (202301BD070001–123), Monitoring Project of Bamboo Forest Ecosystem Positioning Observation and Research Station in Southern Yunnan Province (2022–YN–15), and China Scholarship Fund for Studying Abroad (20107855018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHZ designed and performed all experiments and wrote the manuscript draft. XTZ and WHS gave strong support in the acquisition of data. WYL, CMH, ZFZ, and RLZ gave invaluable advice in the design, experimental performance, and paper writing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jianming Xue
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Zhao, X., Hui, C. et al. Effects of different planting durations of Dendrocalamus brandisii on the soil bacterial community. J Soils Sediments 23, 3891–3902 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03556-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03556-1