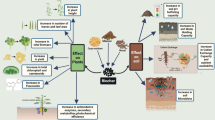
Abstract
Purpose
Poor structure, nutrient deficiency, and acidification are core factors restricting the reclamation of rare earth mining wasteland soil (REMWS). Sewage sludge, bagasse, and molybdenum tailings, all of which need proper disposal, have great potentials in REMWS reclamation. The goal of this study was to explore the remediation effect on rare earth mining wasteland soil with the combined application of sewage sludge compost (SSC), bagasse, and modified molybdenum tailings (MMT).
Materials and methods
SSC (T1), SSC + bagasse (T2), and SSC + bagasse + MMT (T3) were applied in REMWS as amendments in a 4-month pot experiment, and their effects on REMWS properties and heavy metals (HMs) toxicity were tested with Eucalyptus urophylla, which grows fast, resists environment stress, and is a promising plant in REMWS reclamation.
Results
The application of SSC (T1) improved REMWS fertility, but increased Cu, Zn, Cd, and Ni contents in soil and E. urophylla seedlings, and inhibited E. urophylla growth. Bagasse application (T2) alleviated growth inhibition and further addition of bagasse + MMT (T3) significantly improved E. urophylla growth. Moreover, T3 improved soil physical properties, organic carbon content, pH, and reduced soil HMs bioavailability and plant HMs content as compared to T1 and T2. Structural equation modeling results revealed that plant nutrient accumulation increased plant HMs accumulation, the latter inhibited plant nutrient accumulation in turn, and soil pH played a key role in retarding HMs uptake and improving E. urophylla growth and nutrients uptake.
Conclusion
These results suggested that the combined application of SSC, bagasse, and MMT is an effective approach for REMWS amelioration and land disposal of solid waste resources.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is not available at this time as the data forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Abd El-Halim AA, Kumlung A (2015) Modification of sandy soil hydrophysical environment through bagasse additive under laboratory experiment. Int Agrophys 29:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1515/intag-2015-0008
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad M (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 119:186–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.011
Aggangan NS, Aggangan BJS (2012) Selection of ectomycorrhizal fungi and tree species for rehabilitation of Cu mine tailings in the Philippines. J Environ Sci Manag 15(1):59–71
Ai Y, Li F, Gu H, Chi X, Yuan X, Han D (2020) Combined effects of green manure returning and addition of sewage sludge compost on plant growth and microorganism communities in gold tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(25):31686–31698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09118-z
Alaboudi KA, Ahmed B, Brodie G (2018) Phytoremediation of Pb and Cd contaminated soils by using sunflower (Helianthus annuus) plant. Ann Agr Sci 63(1):123–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2018.05.007
Alokika A, Kumar A, Kumar V, Singh B (2021) Cellulosic and hemicellulosic fractions of sugarcane bagasse: potential, challenges and future perspective. Int J Biol Macromol 169:564–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.175
Alvarenga P, Mourinha C, Farto M, Santos T, Palma P, Sengo J, Morais M, Cunha-Queda C (2015) Sewage sludge, compost and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manage 40:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.027
Bai Y, Zang C, Gu M, Gu C, Shao H, Guan Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Feng K (2017) Sewage sludge as an initial fertility driver for rapid improvement of mudflat salt-soils. Sci Total Environ 578:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.083
Bao S (ed) (2000) Soil and agro-chemistry analysis, 3rd edn. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Curtin D (2003) Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metals transformation and bioavailability. Adv in Agron 78:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(02)78006-1
Chao Y, Liu W, Chen Y, Chen W, Zhao L, Ding Q, Tang Z, Zhang T, Qiu R (2016) Structure, variation, and co-occurrence of soil microbial communities in abandoned sites of a rare earth elements mine. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11481–11490. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02284
Chen D, Meng Z, Chen Y (2019) Toxicity assessment of molybdenum slag as a mineral fertilizer: a case study with pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Chemosphere 217:816–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.216
Chen G, Shi L (2016) A multi-element mineral conditioner: a supplement of essential cations for red soil and crops growth. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 44(12):1690–1699. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500684
Chu S, Jacobs DF, Liao D, Liang LL, Wu D, Chen P, Lai C, Zhong F, Zeng S (2018) Effects of landscape plant species and concentration of sewage sludge compost on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and heavy metal removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:35184–35199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3416-x
Chu S, Wu D, Liang LL, Zhong F, Hu Y, Hu X, Lai C, Zeng S (2017) Municipal sewage sludge compost promotes Mangifera persiciforma tree growth with no risk of heavy metal contamination of soil. Sci Rep 7:13408. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13895-y
Długosz J, Piotrowska-Długosz A, Kotwica K, Przybyszewska E (2020) Application of multi-component conditioner with clinoptilolite and Ascophyllum nodosum extract for improving soil properties and Zea mays L. growth and yield. Agron 10:2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10122005
Elmi A, AlOlayan M (2020) Sewage sludge land application: balancing act between agronomic benefits and environmental concerns. J Clean Prod 250:119512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119512
Fang W, Wei Y, Liu J (2016) Comparative characterization of sewage sludge compost and soil: heavy metal leaching characteristics. J Hazard Mater 310:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.025
Fang Y, Singh BP, Collins D, Armstrong R, Van Zwieten L, Tavakkoli E (2020) Nutrient stoichiometry and labile carbon content of organic amendments control microbial biomass and carbon-use efficiency in a poorly structured sodic-subsoil. Biol Fertil Soils 56:219–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01413-3
Gao S, Cui X, Kang S, Ding Y (2020) Sustainable applications for utilizing molybdenum tailings in concrete. J Clean Prod 266:122020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122020
Gibson MJ, Farmer JG (1986) Multi-step sequential chemical extraction of heavy metals from urban soils. Environ Pollut 11(2):117–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-148x(86)90039-x
Goncalves AR, Benar P, Costa SM, Ruzene DS, Moriya RY, Luz SM, Ferretti LP (2005) Integrated processes for use of pulps and lignins obtained from sugarcane bagasse and straw. Appl Biochem Biotech 123:821–826. https://doi.org/10.1385/abab:123:1-3:0821
Gower JC (1971) A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 27:857–871. https://doi.org/10.2307/2528823
Henckens MLCM, Driessen PPJ, Worrell E (2018) Molybdenum resources: their depletion and safeguarding for future generations. Resour Conserv Recy 134:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.03.002
Hoa HT, Wang C, Wang C (2015) The effects of different substrates on the growth, yield, and nutritional composition of two oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus cystidiosus). Mycobiology 43(4):423–434. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2015.43.4.423
International Molybdenum Association (IMOA) (2020) Global production & use. https://www.imoa.info/molybdenum/molybdenum-global-production-use.php. Accessed 25 June 2022
Kamari A, Putra WP, Yusoff SNM, Ishak CF, Hashim N, Mohamed A, Isa IM, Bakar SA (2015) Immobilisation of Cu, Pb and Zn in scrap metal yard soil using selected waste materials. B Environ Contam Tox 95(6):790–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1650-1
Kaur R, Bhatti SS, Singh S, Singh J, Singh S (2018) Phytoremediation of heavy metals using cotton plant: a field analysis. B Environ Contam Tox 101(5):637–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2472-8
Khoo RZ, Chow WS, Ismail H (2018) Sugarcane bagasse fiber and its cellulose nanocrystals for polymer reinforcement and heavy metal adsorbent: a review. Cellulose 25:4303–4330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1879-z
Li H, Feng X, Qin L (2020) Remote sensing monitoring of land damage and restoration in rare earth mining areas in 6 counties in southern Jiangxi based on multisource sequential images. J Environ Manage 267:110653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110653
Li L, Zhu C, Liu X, Li F, Li H, Ye J (2018) Biochar amendment immobilizes arsenic in farmland and reduces its bioavailability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 348:34091–34102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3021-z
Liang B, Ma C, Fan L, Wang Y, Yuan Y (2018) Soil amendment alters soil physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure of a replanted apple orchard. Microbiol Res 216:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.07.010
Liu C, Yang Z, Hu Y (2015) Drought resistance of wheat alien chromosome addition lines evaluated by membership function value based on multiple traits and drought resistance index of grain yield. Field Crop Res 179:103–112
Liu S, Qi X, Han C, Liu J, Sheng X, Li H, Luo A, Li J (2017) Novel nano-submicron mineral-based soil conditioner for sustainable agricultural development. J Clean Prod 149:896–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.04.016
Mao LC, Ye H (2018) Influence of redox potential on heavy metal behavior in soils: a review. Res Environ Sci 31:1669–1676. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.07.19
McBride MB, Li X (2022) Toxic metal persistence and bioavailability in agricultural soil 40 years after sewage sludge incorporation. J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03314-9
Melo RF, Dias LE, Assis IRD (2016) Behavior of Eucalyptus urophylla and Eucalyptus citriodora seedlings grown in soil contaminated by arsenate. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 40:e0150310. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20150310
Mohamed B, Olivier G, François G, Laurence A, Bourgeade P, Badr A, Lotfi A (2018) Sewage sludge as a soil amendment in a Larix decidua plantation: effects on tree growth and floristic diversity. Sci Total Environ 621:291–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.283
Moubarik A, Grimi N (2015) Valorization of olive stone and sugar cane bagasse by-products as biosorbents for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution. Food Res Int 73:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.07.050
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Hashimoto Y, Hou D, Bolan NS, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2020) Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Int 134:105046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105046
Pandey A, Socool CA, Nigam P, Socool VT (2000) Biotechnological potential of agro-industrial residues. I: Sugarcane bagasse. Bioresource Technol 74:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00142-x
Peccia J, Westerhoff P (2015) We should expect more out of our sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 49:8271–8276. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01931
Peña A, Mingorance MD, Rossini-Oliva S (2015) Soil quality improvement by the establishment of a vegetative cover in a mine soil added with composted municipal sewage sludge. J Geochem Explor 157:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.06.014
Pérez-Gimeno A, Navarro-Pedreño J, Almendro-Candel MB, Gómez I, Zorpas AA (2019) The use of wastes (organic and inorganic) in land restoration in relation to their characteristics and cost. Waste Manag Res 37(5):502–507. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X19828171
Qi G, Jia Y, Liu W, Wei Y, Du B, Fang W, Guo Y, Guo F, Wu Y, Zou Q, Liu J (2020) Leaching behavior and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in Southwestern China soils applied with sewage sludge compost under acid precipitation based on lysimeter trials. Chemosphere 249:126212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126212
Rodríguez-Berbel N, Soria R, Ortega R, Lucas-Borja ME, Miralles I (2022) Benefits of applying organic amendments from recycled wastes for fungal community growth in restored soils of a limestone quarry in a semiarid environment. Sci Total Environ 806:151226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151226
Sarker TC, Azam SMGG, El-Gawad AMA, Gaglione SA, Bonanomi G (2017) Sugarcane bagasse: a potential low-cost biosorbent for the removal of hazardous materials. Clean Technol Envir 19:2343–2362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1429-7
Seth CS (2012) A review on mechanisms of plant tolerance and role of transgenic plants in environmental clean-up. Bot Rev 78:32–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-011-9092-x
Singh P, Singh P, Singh J (2021) Sugarcane bagasse: a potential and economical source for raising sugarcane nursery in sub-tropical India. Sugar Tech 23(6):1211–1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-021-01028-9
Song U, Lee E (2010) Environmental and economical assessment of sewage sludge compost application on soil and plants in a landfill. Resour Conserv Recy 54:1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.03.005
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a017
Thijs S, Sillen W, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J (2016) Phytoremediation: state-of-the-art and a key role for the plant microbiome in future trends and research prospects. Int J Phytoremediat 19(1):23–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1216076
Wang A, Liu H, Hao X, Wang Y, Liu X, Li Z (2019) Geopolymer synthesis using garnet tailings from molybdenum mines minerals. Minerals 9(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9010048
Wang H, Xie M, Li H, Feng Q, Zhang C, Bai Z (2021) Monitoring ecosystem restoration of multiple surface coal mine sites in China via LANDSAT images using the Google Earth Engine. Land Degrad Dev 32(10):2936–2950. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3914
Wang L, Ji B, Hu Y, Liu R, Sun W (2017) A review on in situ phytoremediation of mine tailings. Chemosphere 184:594–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.025
Wei Z, Hao Z, Li X, Guan Z, Cai Y, Liao X (2019) The effects of phytoremediation on soil bacterial communities in an abandoned mine site of rare earth elements. Sci Total Environ 670:950–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.118
Wu D, Feng J, Chu S, Jacobs DF, Tong X, Zhao Q, Chen X, Zeng S (2019) Integrated application of sewage sludge, earthworms and Jatropha curcas on abandoned rare-earth mine land soil. Chemosphere 214:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.087
Wu Z, Li H, Wang Y (2021) Mapping annual land disturbance and reclamation in rare-earth mining disturbance region using temporal trajectory segmentation. Environ Sci Pollut R 28:69112–69128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15480-3
Xu N, Bhadha JH, Rabbany A, Swanson S, McCray JM, Li YC, Strauss SL, Mylavarapu R (2021a) Crop nutrition and yield response of bagasse application on sugarcane grown on a mineral soil. Agron 11(8):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081526
Xu Y, Feng J, Li H (2021b) Water management increased rhizosphere redox potential and decreased Cd uptake in a low-Cd rice cultivar but decreased redox potential and increased Cd uptake in a high-Cd rice cultivar under intercropping. Sci Total Environ 751:141701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141701
Xu Y, Feng J, Li H (2021c) How intercropping and mixed systems reduce cadmium concentration in rice grains and improve grain yields. J Hazard Mater 402:123762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123762
Yan X, Shi L, Gong L (2018) Mechanism analysis of soil amelioration and phosphorus recovery by using a mineral soil conditioner in southern China. J Soils Sediments 18:1884–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1923-5
Yang G, Zhang G, Wang H (2015) Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Res 78:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.002
Yang XJ, Lin A, Li X, Wu Y, Zhou W, Chen Z (2013) China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ Dev 8:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2013.03.006
Yao S, Nie S, Yuan Y, Wang S, Qin C (2015) Efficient extraction of bagasse hemicelluloses and characterization of solid remainder. Bioresource Technol 185:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.052
Zeeshan M, Ahmad W, Hussain F, Ahamd W, Numan M, Shah M, Ahmad I (2020) Phytostabalization of the heavy metals in the soil with biochar applications, the impact on chlorophyll, carotene, soil fertility and tomato crop yield. J Clean Prod 255:120318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120318
Zhang J, Mu G, Zhang Z, Huang X, Fang H (2021a) Speciation variation and bio-activation of soil heavy metals (Cd and Cr) in rice-rape rotation lands in Karst regions. Int J Env Re Pub He 18(3):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031364
Zhang R, Hussain S, Wang Y, Liu Y, Li Q, Chen Y, Wei H, Gao P, Dai Q (2021a) Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm at the germination stage. Agron 11(8):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081569
Zhao C, Guo E, Shao Y, Zhang W, Zhang C, Liu Y, Li Y, Zou X, Fu S (2021) Impacts of litter addition and root presence on soil nematode community structure in a young Eucalyptus plantation in southern China. Forest Ecol Manag 479:11863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118633
Zhao C, Shi X, Xie S, Liu W, He E, Tang Y, Qiu R (2019) Ecological risk assessment of neodymium and yttrium on rare earth element mine sites in Ganzhou, China. B Environ Contam Tox 103:565–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02690-2
Zhou L, Li Z, Liu W, Liu S, Zhang L, Zhong L, Luo X, Liang H (2015) Restoration of rare earth mine areas: organic amendments and phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:17151–17160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4875-y
Zhu L, Wu L (2019) Effects of the successive planting of Eucalyptus urophylla on the soil bacterial and fungal community structure, diversity, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity. Land Degrad Dev 30(6):636–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3249
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31971629, 42177011, 41807112) and the Forestry Science and Technology Innovation Project of Guangdong Province (2022KJCX015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiayi Feng: methodology, data curation, writing—original draft. Yuantong Yang: methodology, data curation. Kejin Ruan: investigation. Daoming Wu: investigation. Yanggui Xu: investigation. Douglass F. Jacobs: writing—review and editing. Shucai Zeng: Supervision, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jianming Xue.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Yang, Y., Ruan, K. et al. Combined application of sewage sludge, bagasse, and molybdenum tailings ameliorates rare earth mining wasteland soil. J Soils Sediments 23, 1775–1788 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03437-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03437-7