Abstract
Purpose
The dynamics of phosphorus in lake sediment have received much attention due to their potential to trigger eutrophication. This study was aimed to reveal the distribution pattern of phosphorus forms, total nitrogen (TN), and total organic carbon (TOC), estimate the contributions of different phosphorus forms to total phosphorus, and evaluate the ecological risks of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in the sediments from Daye Lake, Central China.
Method
Thirty-nine surface sediment samples were collected in the dry season. TOC and TN were analyzed by an elemental analyzer. Phosphorus forms were determined based on the European standard SMT (Standard Measurements and Testing) method. The integrated pollution index method was used to assess the TN and TP pollution levels of sediment. The relationships between different phosphorus forms and TOC and TN in sediments were also discussed.
Result and discussion
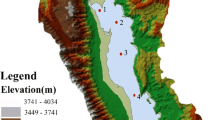
TOC, TN, and TP contents in the sediments of Daye Lake were 0.96–6.15%, 859.8–5562.533 mg kg−1, and 973.06–7982.86 mg kg−1, respectively. The average contents of phosphorus in various forms were IP (1605.24 mg kg−1) > Ca-P (1093.39 mg kg−1) > OP (897.49 mg kg−1) > Fe/Al-P (523.79 mg kg−1). The contents of different phosphorus forms showed certain spatial differences due to the impact of human activities, agricultural, and industrial production. IP was the most important form of phosphorus in sediments, accounting for 49 ~ 63% of TP. TOC/TN ratio in the sediments ranged from 7.23 to 11.35, indicating that endogenous pollution was the main source. The results of TN and TP pollution in the surface sediments of Daye Lake evaluated by single pollution standard index method showed that the standard index of the TN (STN) ranged from 0.86 to 5.56 and the standard index of the TP (STP) ranged from 1.62 to 13.30. It indicated that N and P in sediments of Daye Lake were seriously polluted, and there was a potential risk of endogenous pollutant release which may further aggravate the eutrophication of water body.
Conclusion
The distribution of TN, TP, and TOC in the sediments showed a gradual decreasing trend from the downstream to the upstream in Daye Lake. TP in the sediments mainly existed in the form of IP. IP content was mainly influenced by Fe/Al-P and Ca-P. The ecological risk of nitrogen and phosphorous in the sediments was serious, and the water body was threatened by eutrophication.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data analyzed/generated are included and available in the manuscript.
References
Amini S, Masic A, Bertinetti L, Teguh JS, Herrin JS, Zhu X, Su H, Miserez A (2014) Textured fluorapatite bonded to calcium sulphate strengthen stomatopod raptorial appendages. Nat Commun 5:3187. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4187
Barik SK, Bramha S, Bastia TK, Behera D, Mohanty PK, Rath P (2019) Distribution of geochemical fractions of phosphorus and its ecological risk in sediment cores of a largest brackish water lake, South Asia. Int J Sediment Res 34:251–261
Beutler SJ, Pereira MG, Loss A, Perin A, Anjos L (2015) Humic substances and phosphorus fractions in areas with crop-livestock integration, pasture and natural cerrado vegetation in Goiás, Brazil. Trop Subtrop Agroecosys 18:11–25
Bhutto SUA, Xing X, Shi M, Mao Y, Hu T, Tian Q, Cheng C, Liu W, Chen Z, Qi SH (2021) Occurrence and distribution of OCPs and PAHs in water, soil and sediment of Daye lake. J Geochem Explor 226:106769
Chen C, Deng W, Xu X, He J, Wang S, Jiao L, Zhang Y (2015) Phosphorus adsorption and release characteristics of surface sediments in Dianchi Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 74:3689–3700
Deng J, Lu X, Hu W, Xu Z (2022) Nutrients and organic matter in the surface sediment of a submerged macrophyte zone in a eutrophic lake: implications for lake management. Int J Sediment Res 37:307–316
Fang JQ, Chuang QI, Zhang XH, Han RM, Huang HX, Wang ZS, Wang GX (2019) Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in sediments of Zhushan Bay at Taihu Lake Environ Sci 40:5367–5374 (in Chinese)
Feng YZ, Zhang HC, Chang FQ, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Tian YY, He LQ, Liu BY (2020) Spatial distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus and pollution assessment in Lake Jianhu, Yunnan Province. Quaternary Sci 40:1251–1263 (in Chinese)
Gao W, Cheng GW, Yan CA, Chen Y (2021) Identifying spatiotemporal alteration of nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of Lake Dianchi and its driving forces during 1988–2018. J Lake Sci 33:64–73 (in Chinese)
Gonsiorczyk T, Casper P, Koschel R (1998) Phosphorus-binding forms in the sediment of an oligotrophic and an eutrophic hardwater lake of the Baltic Lake District (Germany). Water Sci Technol 37:51–58
Gunnars A, Blomqvist S (1997) Phosphate exchange across the sediment-water interface when shifting from anoxic to oxic conditions an experimental comparison of freshwater and brackish-marine systems. Biogeochemistry 37:203–226
Han CN (2018) Characteristics of phosphorus transport and transformation and its influence mechanism in the Three Gorges Reserveoir. Ph.D. thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Hantke B, Fleischer P, Domany I, Koch M, Pleß P, Wiendl M, Melzer A (1996) P-release from DOP by phosphatase activity in comparison to P excretion by zooplankton. Studies in hardwater lakes of different trophic level. Hydrobiologia 317:151–162
He Y, Gu XY, Cao JX, Pei GF (2014) Variation of phosphorus content and composition of benthic algae mat in the mesocosms experiment. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 20:523–528 (in Chinese)
Huang TL, Liu F, Shi JC (2016) Distribution characteristics and pollution status evaluation of sediments nutrients in a drinking water reservoir. Environ Sci 37:166–172 (in Chinese)
Jiang X, Jin X, Yao Y, Li L, Wu F (2008) Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 42:2251–2259
Jiang Y, Wu ZS, Zhao ZH, Wang XL, Liu X, Li QY, Cai YJ (2016) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Yangcheng, Jiangsu Province. China Res Environ Sci 29:1590–1599 (in Chinese)
Jin X, Wang S, Pang Y, Wu F (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 139:288–295
Li B, Wang ZQ (2012) Estimation of nitrogen and phosphorus release rates at sediment-water interface of Nansi Lake, China. Adv Mater Res 573–574:573–577
Li ZQ, Fang P, Huang B, Lu SY, Wan Q, Xiong J, Zhang GG (2020) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals in surface sediments of typical internal lakes in Dongting Lake area. Res Environ Sci 33:1409–1420 (in Chinese)
Liu H, Li W (2011) Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River region, China. Environ Earth Sci 62:1503–1511
Liu J, Luo X, Zhang N, Wu Y (2016) Phosphorus released from sediment of Dianchi Lake and its effect on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16321–16328
Lv S, Li X, Wang R, Wang Y, Dong Z, Zhou T, Liu Y, Lin K, Liu L (2022) Autochthonous sources and drought conditions drive anomalous oxygen-consuming pollution increase in a sluice-controlled reservoir in eastern China. Sci Total Environ 841:156739
Mayers PA, Ishiwatari R (1993) Lacustrine organic geochemistry-anoverview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis inlake sediments. Org Geochem 20:867–900
Murphy J, Riley J (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Mudroch A, Azcue JM (1995) Manual of aquatic sediment sampling. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida
Norberg J (1998) Effects of temperature and light on the composition of brackish-water rock pool ecosystems. Aquat Ecol 32:323–334
Pan X, Gu WJ, Li H, Hu Y, Zhang W, Lin L (2021) Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in sediments of Honghu Lake: spatial distribution and pollution evaluation. J Yangtze River Sci Res Institute 38:41–46 (in Chinese)
Pan X, Lin L, Huang Z, Liu M, Dong L, Chen J, Crittenden J (2019) Distribution characteristics and pollution risk evaluation of the nitrogen and phosphorus species in the sediments of Lake Erhai, Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22295–22304
Paytan A, Mclaughlin K (2007) The oceanic phosphorus cycle. Chem Rev 2007(107):563–576
Persaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Ontario Ministry of the Environment and Energy, Ottawa, p 3
Pu J, Ni Z, Wang S (2020) Characteristics of bioavailable phosphorus in sediment and potential environmental risks in Poyang Lake: the largest freshwater lake in China. Ecol Indic 115:106409
Ramm K, Scheps V (1997) Phosphorus balance of a polytrophic shallow lake with the consideration of phosphorus release. In: Kufel L, Prejs A, Rybak JI (eds) Shallow Lakes ’95: Trophic Cascades in Shallow Freshwater and Brackish Lakes. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 43–53
Robertson GP, Bruulsema TW, Gehl RJ, Kanter D, Mauzerall DL, Rotz CA, Williams CO (2013) Nitrogen–climate interactions in US agriculture. Biogeochemistry 114:41–70
Ruban V, López-Sánchez JF, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (2001) Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments – a synthesis of recent works. Fresen J Anal Chem 370:224–228
SanClements MD, Fernandez IJ, Norton SA (2009) Soil and sediment phosphorus fractions in a forested watershed at Acadia National Park, ME, USA. Forest Ecol Manag 258:2318–2325
Stutter M, Richards S, Ibiyemi A, Watson H (2021) Spatial representation of in-stream sediment phosphorus release combining channel network approaches and in-situ experiments. Sci Total Environ 795:148790
Wang L, Liang T (2016) Distribution patterns and dynamics of phosphorus forms in the overlying water and sediment of Dongting Lake. J Great Lakes Res 42:565–570
Wang S, Jin X, Bu Q, Jiao L, Wu F (2008) Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloid Surface A 316:245–252
Wang SJ, Liu YG, Zhang C, Hou L, Wang Y (2017) Distribution and pollution risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in inlet rivers of Erhai Basin. J Lake Sci 29:69–77 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Huang Y, Tian J, Li C, Yu K, Zhang M, Lang X, Sun T (2021) A sediment record of terrestrial organic matter inputs to Dongting Lake and its environmental significance from 1855 to 2019. Ecol Indic 130:108090
Wang YP, Xu WW, Han C, Hu WP (2020) Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Chaohu sediments and pollution evaluation. Environ Sci 42:699–711 (in Chinese)
Xiang SL, Zhou WB (2011) Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China. Int J Sediment Res 26:230–238
Xiang S, Nie F, Wu D, Liu X (2015) Nitrogen distribution and diffusive fluxes in sediment interstitial water of Poyang Lake. Environ Earth Sci 74:2609–2615
Xing X, Chen M, Wu Y, Tang Y, Li C (2021) The decomposition of macrozoobenthos induces large releases of phosphorus from sediments. Environ Pollut 283:117104
Xu D, Yan P, Liu Z, Zhang M, Yan W, Liu Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y (2021) Spatial distribution of phosphorus forms and the release risk of sediments phosphorus in West Lake, Hangzhou. China Ecol Eng 173:106421
Yu ZT, Wang XJ, Zhang EL, Zhao CY, Liu XQ (2015) Spatial distribution and sources of organic carbon in the surface sediment of Bosten Lake, China. Biogeosciences 12:6605–6615
Yuan H, Wang H, Zhou Y, Jia B, Yu J, Cai Y, Yang Z, Liu E, Li Q, Yin H (2021) Water-level fluctuations regulate the availability and diffusion kinetics process of phosphorus at lake water–sediment interface. Water Res 200:117258
Yuan HZ, Shen J, Liu EF, Wang JJ, Meng XH (2010) Space distribution characteristics and diversity analysis of phosphorus from overlying water and surface sediments in Taihu Lake. Environ Sci 31:954–960 (in Chinese)
Zeng H, Wu J (2013) Heavy metal pollution of lakes along the mid-lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China: intensity, sources and spatial patterns. Int J Environ Res Pub He 10:793–807
Zhang J, Li ZH, Chen J, Wang M, Tao R, Liu D (2014) Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environ Earth Sci 72:1279–1288
Zhang JQ, Tian Q, Xu DM, Zhan CL, Liu T, Yao RZ, Liu XL, Xiao WS (2017a) Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment from Daye Lake. Environ Sci 38:2355–2363 (in Chinese)
Zhang JQ, Hu TP, Xing XL, Zheng H, Zhang L, Zhan CL, Liu HX, Xiao WS, Qi SH (2017b) Distribution, sources and risk assessment of the pahs in the surface sediments and water from the Daye Lake. Environ Sci 38:170–179 (in Chinese)
Zhang Z, Lv Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Sun C, Marhaba T (2015) Phosphorus, organic matter and nitrogen distribution characteristics of the surface sediments in Nansi Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 73:5669–5675
Zhou Q, Gibson CE, Zhu Y (2001) Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere 42:221–225
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Zhang L (2006) Phosphorus forms and bioavailability of lake sediments in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Sci China: Ser D Earth Sci 49:28–37
Zhu G, Yang Y (2018) Variation laws and release characteristics of phosphorus on surface sediment of Dongting Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:12342–12351
Zhu M, Zhu G, Li W, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Gu Z (2013) Estimation of the algal-available phosphorus pool in sediments of a large, shallow eutrophic lake (Taihu, China) using profiled SMT fractional analysis. Environ Pollut 173:216–223
Zhu Y, Jin X, Tang W, Meng X, Shan B (2019) Comprehensive analysis of nitrogen distributions and ammonia nitrogen release fluxes in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J Environ Sci 76:319–328
Funding
This work was supported by the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students (202110920004), the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology (No. SKLLQG1935), the Key Project of Hubei Polytechnic University (No. 19XJK01Z), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41603117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zijian Qiu: investigation; software; writing, original draft. Qian Liu: investigation; data curation. Ruiqi Zhang: investigation; software. Changlin Zhan: conceptualization; writing, review and editing; funding acquisition. Shan Liu: investigation; review and editing; supervision. Jiaquan Zhang: investigation; validation. Hongxia Liu: investigation, review and editing. Wensheng Xiao: review and editing; supervision. Xianli Liu: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Shiming Ding
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Z., Liu, Q., Zhang, R. et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of phosphorus forms, TOC, and TN in the sediments of Daye Lake, Central China. J Soils Sediments 23, 1023–1036 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03398-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03398-3