Abstract
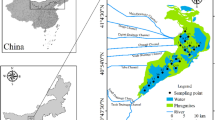
Forms of phosphorus in sediments from 25 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River were analyzed by the sequential extraction procedure. Contents and spatial distrubution of algal available phosphorus (AAP) in sediments of Lake Taihu, the third largest freshwater lake of China, were also studied. Relationships between phosphorus forms in sediment and macrophytes coverage in sample sites, as well as phosphorus forms in sediments and chlorophyal contents in lake water were discussed. Exchangeable form of phosphorus (Ex-P) in surface sediments was significantly positive correlative to total phosphorus (TP), dissolved total phosphorus (DTP) and soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) contents in the lake water. Bioavailable phosphorus (Bio-P) contents in sediments from macrophytes dominant sites were significantly lower than that in no macrophyte sites. In Lake Taihu, Ex-P content in top 3 cm sediment was highest. However, content of ferric fraction phosphorus (Fe-P) was highest in 4–10 cm. Bioavalilble phosphorus (Bio-P) contents in surface sediments positively correlated to Chlorophyll a contents in water of Lake Taihu with significant difference. Therefore, contents of Bio-P and AAP could be acted as the indicators of risks of internal release of phosphorus in the shallow lakes. It was estimated that there were 268.6 ton AAP in top 1 cm sediments in Lake Taihu. Sediment suspension caused by strong wind-induced wave disturbance could carry plenty of AAP into water in large shallow lakes like Lake Taihu.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, S. M., Dou, H. S., Chinese Lakes (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1998.
Qin, B. Q., Approaches to mechanisms and control of eutrophication of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2002, 14(3): 193–202.
Qin, B. Q., Hu, W. P., Gao, G. et al., Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(1): 54–64.
Havensa, K. E., Jamesa, R. T., Easta, T. L. et al., N:P ratios, light limitation, and cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution, Environmental Pollution, 2003, 122: 379–390.
Havens, K. E., Fukushima, T., Xie, P. et al., Nutrient dynamics and the eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA), Environmental Pollution, 2001, 111: 263–272.
Zhu, G. W., Qin, B. Q., Gao, G., Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind wave disturbance, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(6): 577–582.
Huang, Q. H., Wang, Z. J., Wang, D. H. et al., Origins and Mobility of Phosphorus forms in the Sediments of Lakes Taihu and Chaohu, China, Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2005, 40(1): 91–102.
Huang, Q. H., Wang, D. H., Wang, C. X. et al., Relation between phosphorus forms in the sediments and lake eutrophication, China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 2003, 23(6): 583–586.
Huang, Q. H., Wang, D. H., Wang, C. X. et al., Vertical variation of the phosphorus form in the sediments of Meiliang Bay and Wuli Lake of Taihu Lake, China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 2004, 24(4): 147–150.
Huang, Q. H., Wang, Z. J., Wang, D. H. et al., Phosphorus sorption capacity of the surface sediment in the Lake Taihu and risk assessment of phosphorus release, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2004, 16(2): 97–104.
Zhang, L., Fan, C. X., Chi, Q. Q. et al., Phosphorus forms distribution of sediments in Lake Taihu and its main inflow rivers, Geochimica (in Chinese), 2004, 33(4): 423–432.
Zhang, L., Fan, C. X., Wang, J. J. et al., Comparison of physicochemical characters of pore water in grass/algae type zone in Lake Taihu, China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 2004, 24(5): 556–560.
Zhu, G. W., Qin, B. Q., Gao, G., Fractionation of phosphorus in sediments and its relation with soluble phosphorus contents in shallow lakes located in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, China, Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (in Chinese), 2004, 24(3): 381–388.
Ruttenberg, K. C., Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments, Limnology & Oceanography, 1992, 37(7): 1460–1482.
Zhou, Q. X., Gibson, C. E., Zhu, Y. M., Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK, Chemosphere, 2001, 42: 221–225.
Wetzel, R. G., Likens, G. E., Limnological Analyses, Second Edition, New York: Academic Press, 1990.
Xia, W. L., Xue, B., Determination of sedimentation rate by 210Pb and 137Cs dating methods in Xiaolongwan Lake, Jilin Province, China, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 2004, 24(1): 124–125.
Eggleton, J., Thomas, K. V., A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events, Environmental International, 2004, 30: 973–980
Liu, S. M., Zhang, J., Chemical extraction of phosphorus in sediments, Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 2001, 25(1): 22–25.
Aminot, A., Andrieux, F., Concept and determination of exchangeable phosphate in aquatic sediments, Water Research, 1996, 30(11): 2805–2811.
Saavedra, C., Delgado, A., Iron-related phosphorus in eroded sediments from agricultural soils of Mediterranean areas, Geoderma, 2005, 125: 1–9.
Hyacinthe, C., Van Cappellen, P., An authigenic iron phosphate phase in estuarine sediments: composition, formation and chemical reactivity, Marine Chemistry, 2004, 91: 227–251.
Horppila, J., Nurminen, L., Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in Lake Hiidenvesi (southern Finland), Water Research, 2003, 37: 4468–4474.
Liu, En F., Shen, J., Zhu, Y. X., Source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2004, 16(2): 113–119.
Lu, M., Zhang, W. G., Shi, Y. X. et al., Vertical variations of metals and nutrients in sediments from northern Taihu Lake and the influencing factors, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2003, 15(3): 213–220.
Rose, N. L., Boyle, J. F., Du, Y. et al., Sedimentary evidence for changes in the pollution status of Taihu in the Jiangsu region of eastern China, Journal of Paleolimnology, 2004, 32: 41–51.
Hu, W. P., Qin, B. Q., Pu, P. M., Three-dimensional numerical experiments on hydrodynamics in Lake Taihu-3. Influence of the reclamation in Mashan district on wind-driven current, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 12(4): 335–342.
Zhang, Y. L., Qin, B. Q., Study prospect and evolution of eutrophication in Lake Taihu, Shanghai Environmental Sciences (in Chinese), 2001, 20(6): 263–265.
Luo, L. C, Qin, B. Q, Zhu, G. W., Sediment distribution pattern mapped from the combination of objective analysis and geostatistics in the large shallow Taihu Lake, China, Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 16(6): 908–911.
Qin, B. Q., Hu, W. P., Chen, W. M., Processes and Mechanisms of Water Environmental Evolution in Lake Taihu (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 2004, 166–170.
Novics, V., Osztoics, A., Honti, M., Dynamics and ecological significance of daily internal load of phosphorus in shallow Lake Balaton, Freshwater Biology, 2004, 49: 232–252.
Zhu, G. W., Qin, B. Q., Gao, G., Vertical distribution of the concentrations of phosphorus and suspended solid in Taihu Lake affected by wind-induced wave, Advances in Water Research (in Chinese), 2004, 15(6): 775–780.
Qin, B. Q., Hu, W. P., Chen, W. M. et al., Studies on the hydrodynamic processes and related factors in Meiliang Bay, Northern Taihu Lake, China, Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 12(4): 327–334.
Robarts, D. R, Waiser, M. J, Hadas, O. et al. Relaxation of phosphorus limitation due to typhoon-induced mixing in two morphologically distinct basins of Lake Biwa, Japan, Limnology and Oceanography, 1998, 43(6): 1023–1036.
Luo, L. C., Qin, B. Q., Zhu, G. W., Calculation of total and resuspendable sediment volume in Lake Taihu, Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 2004, 35(6): 491–496.
Fan, C. X., Zhang, L., Qin, B. Q. et al., Estimation on dynamic release of phosphorus from wind-induced suspended particulate matter in Lake Taihu, Science in China, Ser. D, 2004, 47(8): 710–719.
Gao, G., Zhu, G. W., Qin, B. Q. et al., Alkaline phosphatase activity and the phosphorus mineralization rate in Lake Taihu, Science in China, Ser. D, 2006, 49(Suppl. I): 176–185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Qin, B. & Zhang, L. Phosphorus forms and bioavailability of lake sediments in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. SCI CHINA SER D 49 (Suppl 1), 28–37 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-006-8103-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-006-8103-y