Abstract
Purpose
Phosphorus (P) plays an important role in enhancing plant yield. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) could enhance soil P availability. This study aimed to determine the effects of PSB inoculation on soil P fractions and bacterial community and reveal the comprehensive linkages among soil bacteria, P fractions, and nutrient contents.
Materials and methods
In this study, PSB, Klebsiella ZP-2, was inoculated into soil with four different inoculation rates (2%, 4%, 6%, and 8%, bacterial suspension/soil weight = v:w); soil phosphatase activity, P fractions, function gene, and 16S rRNA were detected to comprehensively assess the effects of strain ZP-4 on soil properties, P fractions, and bacterial community.
Results and discussion
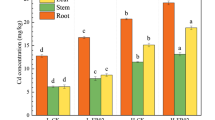
Soil available P and N were significantly higher in the treatments with 4% and 6% inoculation rates than that in the control. Compared with control, the contents of soil inorganic P extracted by sodium hydroxide (NaOH-Pi), water (H2O-Pi), and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3-Pi) were significantly increased. However, inorganic P extracted by hydrochloric acid (HCl-Pi) and residual P (residual-P) contents were significantly decreased, especially in the 4% inoculation rates. The strain ZP-2 stimulated functional genes (phoC and phoD) and soil phosphatase activity to active soil P. Meanwhile, the bacterial community structures were also significantly changed following the strain ZP-2 inoculation.
Conclusion
The strain ZP-2 inoculation improved soil available N and P contents, stimulated phosphatase activity to accelerate P cycling, and altered soil bacterial community. The ZP-2 strain has the potential to be used as a biofertilizers to improve soil fertility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai B, Yang X, Zhao Q, Liu R (2020) Inoculations with Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus cereus affect the soil enzyme activity, growth and rhizosphere microbial diversity of Taxus chinensis var. mairei. Plant Soil 455:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04660-8
Bao SD (2000) Soil agro-chemistrical analysis. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Butterfield CN, Li Z, Andeer P, Spaulding S (2016) Proteogenomic analyses indicate bacterial methylotrophy and archaeal heterotrophy are prevalent below the grass root zone. PeerJ 4:e2687. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2687
Chen L, Zhang C, Duan W (2016) Temporal variations in phosphorus fractions and phosphatase activities in rhizosphere and bulk soil during the development of Larix olgensis plantations. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 179:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201500060Fig
Chen X, Jiang N, Condron LM, Dunfield KE, Chen Z, Wang J (2019) Impact of long-term phosphorus fertilizer inputs on bacterial phoD gene community in a maize field, Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 669:1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.172
Chen Z, Ma S, Liu L (2008) Studies on phosphorus solubilizing activity of a strain of phosphobacteria isolated from chestnut type soil in China. Bioresour Technol 99:6702–6707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.03.064
Cong W, Suriyagoda L, Lambers H (2020) Tightening the phosphorus cycle through phosphorus-efficient crop genotypes. Trends Plant Sci 25:967–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.04.013
Cordell D, White S (2014) Life’s bottleneck: sustaining the world’s phosphorus for a food secure future. Annu Rev Environ Resour 39:161–188. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-010213-113300
Cross AF, Schlesinger WH (1995) A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma 64:197–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7061(94)00023-4
Cui H, Zhou Y, Gu Z, Zhu H, Fu S (2015) The combined effects of cover crops and symbiotic microbes on phosphatase gene and organic phosphorus hydrolysis in subtropical orchard soils. Soil Biol Biochem 82:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.01.003
Fraser TD, Lynch DH, Gaiero J, Khosla K (2017) Quantification of bacterial non-specific acid (phoC) and alkaline (phoD) phosphatase genes in bulk and rhizosphere soil from organically managed soybean fields. Appl Soil Ecol 111:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.11.013
Gahoonia T, Asmar F, Giese H (2000) Root-released organic acids and phosphorus uptake of two barley cultivars in laboratory and field experiments. Eur J Agron 12:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(00)00052-6
Guo Y, Du Q, Li G, Ni Y, Zhang Z, Ren W, Hou X (2016) Soil phosphorus fractions and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity following long-term grazing exclusion on semi-arid steppes in Inner Mongolia. Geoderma 269:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.01.039
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB, Chauhan BS (1982) Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by Laboratory Incubations1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:970–976. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600050017x
Heppell J, Payvandi S, Talboys P, Zygalakis, KC, Fliege J, Langton D, Sylvester-Bradley R (2016) Modelling the optimal phosphate fertiliser and soil management strategy for crops. Plant Soil 401:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2543-0
Hou E, Luo Y, Kuang Y, Chen C, Lu X, Jiang L, Luo X, Wen D (2020) Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat Commun 11:637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14492-w
Hu B, Yang B, Pang X, Bao W, Tian G (2016) Responses of soil phosphorus fractions to gap size in a reforested. Geoderma 279:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.05.023
Huse M, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12:1889–1898. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02193.x
Li Y, Niu S, Yu G (2016) Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 22:934–943. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13125
Liang J, Liu J, Jia P, Yang T, Zeng Q, Zhang S, Liao B, Shu W, Li J (2020) Novel phosphate-solubilizing bacteria enhance soil phosphorus cycling following ecological restoration of land degraded by mining. ISME J 14:1600–1613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0632-4
Liang X, Jin Y, He M, Liu Y, Hua G, Wang S, Tian G (2017) Composition of phosphorus species and phosphatase activities in a paddy soil treated with manure at varying rates. Agric Ecosyst Environ 237:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.12.033
Liu J, Qi W, Li Q, Wang S, Song C, Yuan X (2020) Exogenous phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria changed the rhizosphere microbial community indirectly. Biotech 10:164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2099-4
Liu S, Chen Q, Ma T, Wang M, Ni J (2018a) Genomic insights into metabolic potentials of two simultaneous aerobic denitrification and phosphorus removal bacteria, Achromobacter sp. GAD3 and Agrobacterium sp. LAD9. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94:fiy020. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy020
Liu Y, Zhu Z, He X, Yang C (2018b) Mechanisms of rice straw biochar effects on phosphorus sorption characteristics of acid upland red soils. Chemosphere 207:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.086
Liu Z, Li C, Zhang S, Fu Y, Fan X, Patel JS, Zhang M (2015) Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from calcareous soils. Appl Soil Ecol 96:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.08.003
Lupwayi NZ, Harker KN, Dosdall LM, Turkington TK (2009) Changes in functional structure of soil bacterial communities due to fungicide and insecticide applications in canola. Agric Ecosyst Environ 130:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.12.002
Maharjan M, Maranguit D, Kuzyakov Y (2018) Phosphorus fractions in subtropical soils depending on land use. Eur J Soil Biol 87:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2018.04.002
Man Y, Fang S, Jacqueline M, Xu J, Yuan Z (2020) Isolation and characterization of Burkholderia cenocepacia CR318, a phosphate solubilizing bacterium promoting corn growth. Microbiol Res 233:126395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2019.126395
Meason DF, Travis WI, Friday JB (2009) Effects of fertilisation on phosphorus pools in the volcanic soil of a managed tropical forest. For Ecol Manag 258:2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.04.001
Moulin L, Munive A, Deryfus B, Boivin-Masson C (2001) Nodulation of legumes by members of the beta-subclass of Proteobacteria. Nature 411:948. https://doi.org/10.1038/35091106
Nesme T, Metson GS, Bennett EM (2018) Global phosphorus flows through agricultural trade. Glob Environ Change 50:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.04.004
Niu Y, Zhang MY, Bai SH, Xu ZH, Liu YQ (2020) Mineral fertilization and soil depth slightly affected aggregate structures despite significantly altered microbial properties in surface forest soils. J Soils Sediments 10:3615–3636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02752-7
Panke-Buisse K, Poole AC, Goodrich JK (2014) Selection on soil microbiomes reveals reproducible impacts on plant function. ISEM J 14:1751–7362. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.196
Pennanen T (2001) Microbial communities in boreal coniferous forest humus exposed to heavy metals and changes in soil pH-a summary of the use of phospholipid fatty acids, Biologw@ and 3H-thymidine incorporation methods in field studies. Geoderma 100:91–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(00)00082-3
Perez E, Sulbaran M, Ball MM (2007) Isolation and characterization of mineral phosphate-solubilizing bacteria naturally colonizing a limonitic crust in the south-eastern Venezuelan region. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2905–2914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.06.017
Rfaki A, Zennouhi O, Aliyat FZ, Nassiri L, Ibijbijen J (2019) Isolation, selection and characterization of root-associated rock phosphate solubilizing bacteria in moroccan wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Geomicrobiol J 37:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2019.1694106
Rose TJ, Hardiputra B, Rengel Z (2010) Wheat, canola and grain legume access to soil phosphorus fractions differs in soils with contrasting phosphorus dynamics. Plant Soil 326:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9990-4
Sakurai M, Wasaki J, Tomizawa Y, Shinano T (2008) Analysis of bacterial communities on alkaline phosphatase genes in soil supplied with organic matter. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 54:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00210.x
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Singh RP, Jha N, Jha PN (2015) The plant-growth-promoting bacterium Klebsiella sp. SBP-8 confers induced systemic tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 184:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2015.07.002
Song Y, Li X, Yao S, Yang X, Jiang X (2020) Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci Total Environ 728:138439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138439
Vaccari DA (2009) Phosphorus: a looming crisis. Sci Am 300:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican0609-54
Vesssy JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026037216893
Vitousek PM, Farrington H (1996) Nutrient limitation and soil development: experimental test of a biogeochemical theory. Biogeochemistry 37:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005757218475
Wang J, Ren C, Cheng H, Zou Y (2017) Conversion of rainforest into agroforestry and monoculture plantation in China: consequences for soil phosphorus forms and microbial community. Sci Total Environ 595:769–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.012
Wei Y, Zhao Y, Wang H, Lu Q, Cao Z, Cui H (2016) An optimized regulating method for composting phosphorus fractions transformation based on biochar addition and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Bioresour Technol 221:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.038
Yan X, Wei Z, Hong Q, Lu Z, Wu J (2017) Phosphorus fractions and sorption characteristics in a subtropical paddy soil as influenced by fertilizer sources. Geoderme 295:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.012
Yang X, Chen X, Yang X (2019) Effects of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res 2019:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.11.016
Yousefi AA, Khavazi K, Moezi AA, Rejali F, Nadian HA (2011) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi impacts on inorganic phosphorus fractions and wheat growth. World Appl Sci J 15:1301–1318
Yuan Y, Li Y, Mou Z, Kuang L, Wu W, Zhang J, Wang F, Hui D, Peñuelas J, Sardans J, Lambers H (2021) Phosphorus addition decreases microbial residual contribution to soil organic carbon pool in a tropical coastal forest. Glob Chang Biol 27:454–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15407
Zhang M, Zhang J, Ye X (2021) Linking soil nutrient cycling and microbial community with vegetation cover in riparian zone. Geoderma 384:114801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114801
Zhang M, Zhang W, Bai SH, Niu Y, Hu D, Ji H, Xu Z (2019) Minor increases in Phyllostachys edulis (Moso bamboo) biomass despite evident alterations of soil bacterial community structure after phosphorus fertilization alone: based on field studies at different altitudes. For Ecol Manag 451:117561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117561
Zhang Y, Bhattacharyya R, Dalal RC, Wang P (2020) Impact of land use change and soil type on total phosphorus and its fractions in soil aggregates. Land Degrad Dev 31:828–841. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3501
Acknowledgements
We thank the funding provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31560204) and Central Financial Project (9022107941) to Wenyuan Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dulce Flores-Rentería
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Hosseini Bai, S., Wang, J. et al. Strain Klebsiella ZP-2 inoculation activating soil nutrient supply and altering soil phosphorus cycling. J Soils Sediments 22, 2146–2157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03221-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03221-z