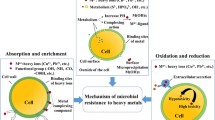
Abstract
Rhizosphere soil ecological functioning behavior is of critical importance for regulating phytoremediation efficiency during microbial-assisted phytoremediation for multi-heavy metal–polluted soils. In this study, Trifolium repens L. and its endophyte Pseudomonas putida were used to investigate the ecological responses of the microbe-plant-soil system in Cd, Cr, and Pb co-contaminated soil. The results showed that endophyte Pseudomonas putida significantly increased plant biomass by 22.26–22.78% and phytoremediation efficiency by 29.73–64.01%. The increased phytoremediation efficiency may be related to the improvement of photosynthetic pigment content and antioxidant enzyme activities in leaves and the enhancement of rhizosphere soil ecological functioning. With endophyte application, soil nutrient content was significantly increased and heavy metal bioavailability was enhanced that residual fraction was reduced by 3.79–12.87%. Besides, the relative abundance of ecologically beneficial rhizobacteria such as Bacteriovorax and Arthrobacter was increased by 3.04–8.53% and 0.80–1.64%, respectively. Endophyte inoculation also significantly increased all the functional genes involved in cellular processes, genetic information processing, environmental information processing, and metabolism. This study indicated that the application of endophytes has a positive effect on the biochemical responses of Trifolium repens L. and could significantly improve rhizosphere ecological functioning in multi-heavy metal contamination, which provided clear strategies for regulating phytoremediation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
AlAli HA, Khalifa A, Almalki M (2021) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from Ocimum basilicum improve growth of Phaseolus vulgaris and Abelmoschus esculentus. S Afr J Bot 139:200–209
Ali S, Charles TC, Glick BR (2014) Amelioration of high salinity stress damage by plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes that contain ACC deaminase. Plant Physiol Bioch 80:160–167
Amirikhah R, Etemadi N, Sabzalian MR, Nikbakht A, Eskandari A (2021) Gamma radiation negatively impacted seed germination, seedling growth and antioxidant enzymes activities in tall fescue infected with Epichloë endophyte. Ecotox Environ Safe 216:112169
Bafana A, Krishnamurthi K, Patil M, Chakrabarti T (2010) Heavy metal resistance in Arthrobacter ramosus strain G2 isolated from mercuric salt-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 177:481–486
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils – to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166
Chen B, Tan S, Zeng Q, Wang A, Zheng H (2019) Soil nutrient heterogeneity affects the accumulation and transfer of cadmium in Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) pers.). Chemosphere 221:342–348
Chen Y, Wang Y, Wu W, Lin Q, Xue S (2006) Impacts of chelate-assisted phytoremediation on microbial community composition in the rhizosphere of a copper accumulator and non-accumulator. Sci Total Environ 356:247–255
Dey S, Paul AK (2018) Influence of metal ions on biofilm formation by Arthrobacter sp. SUK 1205 and evaluation of their Cr(VI) removal efficacy. Int Biodeter Biodegr 132:122–131
Du E, Dong D, Zeng X, Sun Z, Jiang X, de Vries W (2017) Direct effect of acid rain on leaf chlorophyll content of terrestrial plants in China. Sci Total Environ 605–606:764–769
Fang X, Peng B, Wang X, Song Z, Zhou D, Wang Q, Qin Z, Tan C (2019) Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan province, China. Sci Total Environ 689:557–570
Fässler E, Evangelou MW, Robinson BH, Schulin R (2010) Effects of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) on sunflower growth and heavy metal uptake in combination with ethylene diamine disuccinic acid (EDDS). Chemosphere 80:901–907
Frankenberg C, Fisher JB, Worden J, Badgley G, Saatchi SS, Lee J, Toon GC, Butz A, Jung M, Kuze A, Yokota T (2011) New global observations of the terrestrial carbon cycle from GOSAT: Patterns of plant fluorescence with gross primary productivity. Geophys Res Lett 38(17). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL048738
Gao D, Bai E, Yang Y, Zong S, Hagedorn F (2021) A global meta-analysis on freeze-thaw effects on soil carbon and phosphorus cycling. Soil Biol Biochem 159:108283
Guo J, Qin S, Rengel Z, Gao W, Nie Z, Liu H, Li C, Zhao P (2019) Cadmium stress increases antioxidant enzyme activities and decreases endogenous hormone concentrations more in Cd-tolerant than Cd-sensitive wheat varieties. Ecotox Environ Safe 172:380–387
He H, Li W, Yu R, Ye Z (2017) Illumina-based analysis of bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities in paddy fields under mixed heavy metal contamination. Pedosphere 27:569–578
Hernández-Soberano C, Ruíz-Herrera LF, Valencia-Cantero E (2020) Endophytic bacteria Arthrobacter agilis UMCV2 and Bacillus methylotrophicus M4–96 stimulate achene germination, in vitro growth, and greenhouse yield of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 261:109005
Hou L, Li X, He X, Zuo Y, Zhang D, Zhao L (2021) Effect of dark septate endophytes on plant performance of Artemisia ordosica and associated soil microbial functional group abundance under salt stress. Appl Soil Ecol 165:103998
Ju W, Liu L, Fang L, Cui Y, Duan C, Wu H (2019) Impact of co-inoculation with plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on the biochemical responses of alfalfa-soil system in copper contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 167:218–226
Khalid M, Ur-Rahman S, Hassani D, Hayat K, Zhou P, Hui N (2021) Advances in fungal-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. Pedosphere 31:475–495
Khalid S, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Dumat C (2017) A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J Geochem Explor 182:247–268
Kidd PS, Álvarez A, Álvarez-López V, Cerdeira-Pérez A, Rodríguez-Garrido B, Prieto-Fernández Á, Chalot M (2021) Beneficial traits of root endophytes and rhizobacteria associated with plants growing in phytomanaged soils with mixed trace metal-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination. Chemosphere 277:130272
Kumar A, Tripti, Voropaeva O, Maleva M, Panikovskaya K, Borisova G, Rajkumar M, Bruno LB (2021) Bioaugmentation with copper tolerant endophyte Pseudomonas lurida strain EOO26 for improved plant growth and copper phytoremediation by Helianthus annuus. Chemosphere 266:128983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128983
Lin H, Jiang X, Li B, Dong Y, Qian L (2021a) Soilless revegetation: an efficient means of improving physicochemical properties and reshaping microbial communities of high-salty gold mine tailings. Ecotox Environ Safe 207:111246
Lin H, Liu C, Li B, Dong Y (2021b) Trifolium repens L. regulated phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by promoting soil enzyme activities and beneficial rhizosphere associated microorganisms. J Hazard Mater 402:123829
Liu C, Li B, Dong Y, Lin H (2022) Endophyte colonization enhanced cadmium phytoremediation by improving endosphere and rhizosphere microecology characteristics. J Hazard Mater 434:128829
Liu C, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, Liu Y (2018) Investigation on microbial community in remediation of lead-contaminated soil by Trifolium repensL. Ecotox Environ Safe 165:52–60
Liu C, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, Wang L (2019) Identification and characterization of plant growth–promoting endophyte RE02 from Trifolium repens L. in mining smelter. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:17236–17247
Liu C, Lin H, Li B, Dong Y, GueretYadiberetMenzembere ER (2021a) Endophyte Pseudomonas putida enhanced Trifolium repens L growth and heavy metal uptake: a promising in-situ non-soil cover phytoremediation method of nonferrous metallic tailing. Chemosphere 272:129816
Liu S, Wei J, Lin K, Chen Z, Lin X, Yan D (2021) Characteristics of pigments and main biochemical component contents and their relationships in young shoot of chlorophyll-deficient tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica 41:808–816
Ma Y, Oliveira RS, Nai F, Rajkumar M, Luo Y, Rocha I, Freitas H (2015) The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 156:62–69
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Zhang C, Freitas H (2016) Beneficial role of bacterial endophytes in heavy metal phytoremediation. J Environ Manage 174:14–25
Manoj SR, Karthik C, Kadirvelu K, Arulselvi PI, Shanmugasundaram T, Bruno B, Rajkumar M (2020) Understanding the molecular mechanisms for the enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals through plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: a review. J Environ Manage 254:109779
Mao C, Song Y, Chen L, Ji J, Li J, Yuan X, Yang Z, Ayoko GA, Frost RL, Theiss F (2019) Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. CATENA 175:339–348
Mo T, Jiang D, Shi D, Xu S, Huang X, Huang Z (2022) Remediation mechanism of “double-resistant” bacteria—Sedum alfredii Hance on Pb- and Cd-contaminated soil. Ecol Process 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00347-9
Oleńska E, Małek W, Wójcik M, Swiecicka I, Thijs S, Vangronsveld J (2020) Beneficial features of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving plant growth and health in challenging conditions: a methodical review. Sci Total Environ 743:140682
Pan F, Luo S, Shen J, Wang Q, Ye J, Meng Q, Wu Y, Chen B, Cao X, Yang X, Feng Y (2017) The effects of endophytic bacterium SaMR12 on Sedum alfredii Hance metal ion uptake and the expression of three transporter family genes after cadmium exposure. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:9350–9360
Rafique R, Zahra Z, Virk N, Shahid M, Pinelli E, Park TJ, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2018) Dose-dependent physiological responses of Triticum aestivum L. to soil applied TiO2 nanoparticles: alterations in chlorophyll content, H2O2 production, and genotoxicity. Agr Ecosyst Environ 255:95–101
Rani R, Kumar V, Gupta P, Chandra A (2021) Potential use of Solanum lycopersicum and plant growth promoting rhizobacterial (PGPR) strains for the phytoremediation of endosulfan stressed soil. Chemosphere 279:130589
Rasool A, Imran Mir M, Zulfajri M, Hanafiah MM, AzeemUnnisa S, Mahboob M (2021) Plant growth promoting and antifungal asset of indigenous rhizobacteria secluded from saffron (Crocus sativus L.) rhizosphere. Microb Pathogenesis 150:104734
Roberts R, Jackson RW, Mauchline TH, Hirsch PR, Shaw LJ, Döring TF, Jones HE (2017) Is there sufficient Ensifer and Rhizobium species diversity in UK farmland soils to support red clover (Trifolium pratense), white clover (T. repens), lucerne (Medicago sativa) and black medic (M. lupulina)? Appl Soil Ecol 120:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.06.030
Rojjanateeranaj P, Sangthong C, Prapagdee B (2017) Enhanced cadmium phytoremediation of Glycine max L. through bioaugmentation of cadmium-resistant bacteria assisted by biostimulation. Chemosphere 185:764–771
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721
Shi L, Deng X, Yang Y, Jia Q, Wang C, Shen Z, Chen Y (2019) A Cr(VI)-tolerant strain, Pisolithus sp1, with a high accumulation capacity of Cr in mycelium and highly efficient assisting Pinus thunbergii for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 224:862–872
Wang L, Lin H, Dong Y, He Y, Liu C (2018) Isolation of vanadium-resistance endophytic bacterium PRE01 from Pteris vittata in stone coal smelting district and characterization for potential use in phytoremediation. J Hazard Mater 341:1–9
Wang L, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, He Y (2020a) Effects of endophytes inoculation on rhizosphere and endosphere microecology of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) grown in vanadium- contaminated soil and its enhancement on phytoremediation. Chemosphere 240:124891
Wang L, Wang N, Guo D, Shang Z, Zhang Y, Liu S, Wang Y (2023) Rhizobacteria helps to explain the enhanced efficiency of phytoextraction strengthened by Streptomyces pactum. J Environ Sci-China 125:73–81
Wang L, Zhan H, Wang Q, Wu G, Cui D (2019) Enhanced aerobic granulation by inoculating dewatered activated sludge under short settling time in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresource Technol 286:121386
Wang X, Cui Y, Zhang X, Ju W, Duan C, Wang Y, Fang L (2020b) A novel extracellular enzyme stoichiometry method to evaluate soil heavy metal contamination: evidence derived from microbial metabolic limitation. Sci Total Environ 738:139709
Wen C, Xue M, Liang H, Zhou S (2014) Evaluating the potential of marine Bacteriovorax sp. DA5 as a biocontrol agent against vibriosis in Litopenaeus vannamei larvae. Vet Microbiol 173:84–91
Xu Z, Wang D, Tang W, Wang L, Li Q, Lu Z, Liu H, Zhong Y, He T, Guo S (2020) Phytoremediation of cadmium-polluted soil assisted by D-gluconate-enhanced Enterobacter cloacae colonization in the Solanum nigrum L. rhizosphere. Sci Total Environ 732:139265
Yang J, Huang Y, Zhao G, Li B, Qin X, Xu J, Li X (2022) Phytoremediation potential evaluation of three rhubarb species and comparative analysis of their rhizosphere characteristics in a Cd- and Pb-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 296:134045
Yin T, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, He Y, Liu C, Chen X (2021) A novel constructed carbonate-mineralized functional bacterial consortium for high-efficiency cadmium biomineralization. J Hazard Mater 401:123269
You Y, Wang Z, Xu W, Wang C, Zhao X, Su Y (2019) Phthalic acid esters disturbed the genetic information processing and improved the carbon metabolism in black soils. Sci Total Environ 653:212–222
Yu L, Luo S, Gou Y, Xu X, Wang J (2021) Structure of rhizospheric microbial community and N cycling functional gene shifts with reduced N input in sugarcane-soybean intercropping in South China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 314:107413
Zhang Y, Liu G (2018) Effects of cesium accumulation on chlorophyll content and fluorescence of Brassica juncea L. J Environ Radioactiv 195:26–32
Zhou J, Li P, Meng D, Gu Y, Zheng Z, Yin H, Zhou Q, Li J (2020) Isolation, characterization and inoculation of Cd tolerant rice endophytes and their impacts on rice under Cd contaminated environment. Environ Pollut 260:113990
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51874018), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1805002), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-MP-20–35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chenjing Liu: conceptualization, writing—original draft, investigation, formal analysis, data curation.
Hai Lin: conceptualization, supervision, validation, resources, writing—review & editing, funding acquisition, project administration.
Yingbo Dong: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review & editing.
Qian Song: investigation, formal analysis.
Linhuazhi Ao: investigation, formal analysis.
Nan Zhang: investigation, formal analysis.
Haowen An: investigation, formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Song, Q., Ao, L. et al. Highly promoted phytoremediation with endophyte inoculation in multi-contaminated soil: plant biochemical and rhizosphere soil ecological functioning behavior. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 89063–89080 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21689-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21689-7