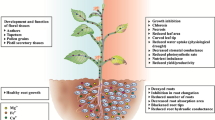
Abstract
Purpose
Glufosinate-ammonium (GLA) is commonly used in tropical agriculture. The frequency and dosage of GLA applications far exceeded the recommended amounts, causing a substantial portion to leach into the soil, becoming a pseudo-persistent pollutant. The earthworm (Eisenia fetida) is a critical bio-indicator of soil health. The effects of pesticides on earthworms are significant to analyzing pesticides’ harm to the soil. Therefore, it is urgent to study the toxicity of GLA to earthworms.
Materials and methods
The artificial soil method was adopted to test the toxicity of GLA on earthworms from the aspects of acute toxicity, growth, reproductive toxicity, the activity of antioxidant and detoxification enzymes, and DNA damage.
Results
GLA exhibited low toxicity (LC50 > 2000 mg/kg) to earthworms in 7-day and 14-day soil tests. But at the individual level, exposure to GLA could decrease the earthworms’ weight, cocoons, and larvae, even under low-concentration stress. The effect of GLA on the individual level of earthworm may be due to the impact on the microscopic level, so the enzyme activity and DNA damage were determined. At the protein level, exposure to GLA could change the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione s-transferase (GST), guaiacol peroxidase (POD), and acetylcholine esterase (AChE) of earthworms. Furthermore, at the molecular level, the comet assay suggests that the olive tail moment (OTM) increased dramatically under the GLA treatments.
Conclusions
The results will be helpful for further understanding the negative influence of GLA on the earthworm and provide a foundation for the rational use of GLA and eco-environmental risks of soil pesticide contamination.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves PRL, Niemeyer JC, Cardoso EJBN (2017) Ecotoxicology and genotoxicology: non-traditional terrestrial models. In: Larramendy ML (ed) Section I: terrestrial invertebrates as experimental models chapter 1. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge. The use of nonstandardized invertebrates in soil ecotoxicology pp 1–30
Bamidele JA, Idowu AB, Ademolu KO, Akinloye OA, Bamgbola AA (2015) Heavy metal accumulation and biochemical evaluation of earthworms from sawmills in Abeokuta. South-Western Nigeria Rev Biol Trop 63:1213–1221
Bandeira FO, Alves P, Hennig TB, Schiehl A, Cardoso E, Baretta D (2019) Toxicity of imidacloprid to the earthworm Eisenia andrei and collembolan Folsomia candida in three contrasting tropical soils. J Soils Sediments 20:1997–2007
Banerjee BD, Seth V, Ahmed RS (2001) Pesticide-induced oxidative stress: perspectives and trends. Rev Environ Health 16:1–40
Calas A, Richard O, Même S, Beloeil JC, Doan BT, Gefflaut T, Même W, Crusio WE, Pichon J, Montécot C (2008) Chronic exposure to glufosinate-ammonium induces spatial memory impairments, hippocampal MRI modifications and glutamine synthetase activation in mice. Neurotoxicology 29:740-747
Carpenter D, Boutin C (2010) Sublethal effects of the herbicide glufosinate ammonium on crops and wild plants: short-term effects compared to vegetative recovery and plant reproduction. Ecotoxicology 19:1322–1336
Cha YS, Kim H, Lee Y, Choi EH, Kim HI, Kim OH, Cha KC, Lee KH, Hwang SO (2017) The relationship between serum ammonia level and neurologic complications in patients with acute glufosinate ammonium poisoning: a prospective observational study. Hum Exp Toxicol 37:571-579
Chen X, Wang X, Gu X, Jiang Y, Ji R (2017) Oxidative stress responses and insights into the sensitivity of the earthworms Metaphire guillelmi and Eisenia fetida to soil cadmium. Sci Total Environ 574:300–306
Cheng C, Huang L, Ma R, Zhou Z, Diao J (2015) Enantioselective toxicity of lactofen and its metabolites in Scenedesmus obliquus. Algal Res 10:72–79
Dhawan A, Bajpayee M, Parmar D (2009) Chapter 7: detection of DNA damage in Drosophila and Mouse. Issue Toxicol 5:157–170
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25:61–67
Ferramosca A, Lorenzetti S, Giacomo MD, Murrieri F, Coppola L, Zara V (2020) Herbicides glyphosate and glufosinate ammonium negatively affect human sperm mitochondria respiration efficiency. Reprod Toxicol 99:48–55
Jiang L, Lin JL, Jia LX, Liu Y, Pan B, Yang Y, Lin Y (2016) Effects of two different organic amendments addition to soil on sorption-desorption, leaching, bioavailability of penconazole and the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Environ Manage 167:130–138
Jiang L, Pan B, Liang J, Wang B, Yang Y, Lin Y (2021) Earthworm casts restrained the accumulation and phytotoxicity of soil glyphosate to cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) plants. Chemosphere 279:130571
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 534:15–20
Lacourse EJ, Hernandez-Viadel M, Jefferies JR, Svendsen C, Spurgeon DJ, Barrett J, Morgan AJ, Kille P, Brophy PM (2009) Glutathione transferase (GST) as a candidate molecular-based biomarker for soil toxin exposure in the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Environ Pollut 157:2459–2469
Lajmanovich RC, Attademo AM, Lener G, Cuzziol Boccioni AP, Peltzer PM, Martinuzzi CS, Demonte LD, Repetti MR (2021) Glyphosate and glufosinate ammonium, herbicides commonly used on genetically modified crops, and their interaction with microplastics: ecotoxicity in anuran tadpoles. Sci Total Environ 804:150177
Li L, Yang D, Song Y, Shi Y, Huang B, Yan J, Dong XJ (2017) Effects of bifenthrin exposure in soil on whole-organism endpoints and biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 168:41–48
Liu J, Xiong K, Ye X, Zhang J, Yang Y, Ji L (2015) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of bromadiolone to earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 135:250-256
Ma D, Yang S, Jiang J, Zhu J, Li B, Mu W, Dou D, Liu, F (2021) Toxicity, residue and risk assessment of tetraniliprole in soil-earthworm microcosms. Ecotoxic Environ Safety 213:112061
Masiol M, Giannì B, Prete M (2018) Herbicides in river water across the northeastern Italy: occurrence and spatial patterns of glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium. Environ Pollut Res 25:1–11
Ning YC, Zhou HR, Wang SB, Li X, Liu D, Xu WY, Zhou DX (2020) Temporal dynamics of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) microbial communities after cadmium stress based on a compound mathematical model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:16326–16338
OECD (1984) Test No. 207: earthworm acute toxicity tests. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris
OECD (2004) Test No. 222: earthworm reproduction tests (Eisenia foetida/Eisenia andrei). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris
Perally SR, Lacourse EJ, Campbell AM, Brophy PM (2008) Heme transport and detoxification in nematodes: subproteomics evidence of differential role of glutathione transferases. J Proteome Res 7:4557–4565
Sauer H, Wartenberg M, Hescheler J (2001) Reactive oxygen species as intracellular messengers during cell growth and differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem 11:173–186
Shao YT, Wang J, Du ZK, Li B, Zhu LS, Wang JH, Zhang SM (2018) Toxiceffect of [Omim]BF4 and [Omim]Br on antioxidant stress and oxidative damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 60:37–44
Shi Z, Tang Z, Wang C (2017) A brief review and evaluation of earthworm biomarkers in soil pollution assessment. Environ Pollut Res 24:13284-13294
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1998) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Tang Z, Zhang J, Yu J, Wang C, Zhang D (2017) Allelopathic effects of volatile organic compounds from Eucalyptus grandis rhizosphere soil on Eisenia fetida assessed using avoidance bioassays, enzyme activity, and comet assays. Chemosphere 173:307–317
Wang Y, Wu S, Chen L, Wu C, Yu R, Wang Q, Zhao X (2012) Toxicity assessment of 45 pesticides to the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 88:484–491
Xu XB, Shi YJ, Lu YL, Zheng XQ, Ritchie RJ (2015) Growth inhibition and altered gene transcript levels in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:1–7
Yang Y, Xiao Y, Chang Y, Cui Y, Klobučar GIV, Li M (2018) Intestinal damage, neurotoxicity and biochemical responses caused by tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate and tricresyl phosphate on earthworm. Ecotox Environ Safe 158:78-86
Zhang L, Diao J, Chen L, Wang Z, Zhang W, Li Y, Tian Z, Zhou Z (2019) Hepatotoxicity and reproductive disruption in male lizards (Eremias argus) exposed to glufosinate-ammonium contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 246:190–197
Zhou H, Zhang T, Zhuang J, Xu M, Liu X, Shi Q, Zhou D (2020) Study on the regulation of earthworm physiological function under cadmium stress based on a compound mathematical model. Environ Toxic Pharmac 80:103499
Zhu Y, Zhang J, Liu Y, Su G, Zhu L, Lin D (2019) Environmentally relevant concentrations of the flame retardant tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate inhibit the growth and reproduction of earthworms in soil. Environ Sci Technol Lett 6:277–282
Funding
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (No. 320QN308) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (No. 1630042017018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Meththika Vithanage
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Jiang, L., Pan, B. et al. Toxicity of glufosinate-ammonium in soil to earthworm (Eisenia fetida). J Soils Sediments 22, 1469–1478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03146-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03146-7