Abstract
Purpose
Sulfonamides with high mobility in the soil pose a significant threat to environmental ecology and human health. Organic matter is known to affect the sorption and transport of these antibiotics in soil, although the mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the effects of humic acid (HA) on the transport of sulfadiazine (SDZ) in soil were investigated to advance the understanding on the fate of SDZ in soil.
Materials and methods
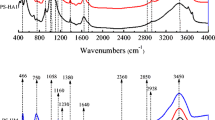
Column experiments were conducted in combination with batch sorption experiments. The sorption and transport of SDZ in soil were simulated by the convection–dispersion model coupled with a linear sorption isotherm and kinetic adsorption processes. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to evaluate the molecular interactions and mechanisms of sorption.
Results and discussion
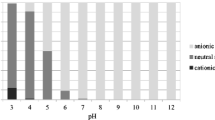
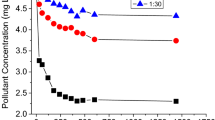
The sorption isotherms conformed to a linear model with low distribution coefficients (Kd = 9.84 L/kg). Increasing the HA content led to increased sorption and inhibited transport of SDZ in soil. The sorption of SDZ on HA decreased with increasing pH and decreasing ionic strength. The mechanisms mainly comprised hydrophobic partition, hydrogen bonding, complexation, and π-π interactions. Mineral clays also played an important role in the sorption of SDZ on soil. The sorption and transport of SDZ were adequately described by the model, which demonstrated that as the HA content of the soil increased, the sorption capacity for SDZ and proportion of the time-dependent kinetic adsorption process both increased. Retained SDZ could also release slowly into the surrounding medium posing a longer-term risk to the environment.
Conclusions
Humic acid increases the retention of SDZ in soil due to its high sorption capacity for SDZ. The sorption of SDZ on HA is dependent on solution chemistry such as pH and ionic strength. However, the retained SDZ would release slowly into the soil solution later. Thus, time-dependent sorption should be prioritized over sorption capacity in studies assessing the environmental fate and eco-toxicity of SDZ.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Ahmed AA, Thiele-Bruhn S, Leinweber P, Kuehn O (2016) Towards a molecular level understanding of the sulfanilamide-soil organic matter-interaction. Sci Total Environ 559:347–355
Bialk H, Pedersen JA (2008) NMR investigation of enzymatic coupling of sulfonamide antimicrobials with humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 42:106–112
Braschi I, Martucci A, Blasioli S, Mzini LL, Ciavatta C, Cossi M (2016) Effect of humic monomers on the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole sulfonamide antibiotic into a high silica zeolite Y: an interdisciplinary study. Chemosphere 155:444–452
Chen C, Li J, Chen P, Ding R, Zhang P, Li X (2014) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistances in soils from wastewater irrigation areas in Beijing and Tianjin, China. Environ Pollut 193:94–101
Chen K, Liu L, Chen W (2017) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils. Environ Pollut 231:1163–1171
Dong S, Gao B, Sun Y, Shi X, Xu H, Wu J, Wu J (2016) Transport of sulfacetamide and levofloxacin in granular porous media under various conditions: experimental observations and model simulations. Sci Total Environ 573:1630–1637
Doretto KM, Rath S (2013) Sorption of sulfadiazine on Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 90:2027–2034
Du L, Liu W (2012) Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A Review Agron Sustain Dev 32:309–327
Fan Z, Casey FXM, Hakk H, Larsen GL, Khan E (2011) Sorption, fate, and mobility of sulfonamides in soils. Water Air Soil Poll 218:49–61
Gao J, Pedersen JA (2005) Adsorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to clay minerals. Environ Sci Technol 39:9509–9516
Gao J, Pedersen JA (2010) Sorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to humic acid-clay complexes. J Environ Qual 39:228–235
Goyne KW, Chorover J, Kubicki JD, Zimmerman AR, Brantley SL (2005) Sorption of the antibiotic ofloxacin to mesoporous and nonporous alumina and silica. J Colloid Interf Sci 283:160–170
Guo X, Tu B, Ge J, Yang C, Song X, Dang Z (2016) Sorption of tylosin and sulfamethazine on solid humic acid. J Environ Sci 43:208–215
Hu S, Zhang Y, Shen G, Zhang H, Yuan Z, Zhang W (2019) Adsorption/desorption behavior and mechanisms of sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole in agricultural soil systems. Soil till Res 186:233–241
Junge T, Meyer KC, Ciecielski K, Adams A, Schaffer A, Schmidt B (2011) Characterization of non-extractable 14C- and 13C-sulfadiazine residues in soil including simultaneous amendment of pig manure. J Environ Sci Heal B 46:137–149
Lehmann J, Kleber M (2015) The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 528:60–68
Leng Y, Xiao H, Li Z, Liu Y, Wan J (2020) Transformation of sulfadiazine in humic acid and polystyrene microplastics solution by horseradish peroxidase coupled with 1-hydroxybenzotriazole. Chemosphere 269:128705
Limousin G, Gaudet JP, Charlet L, Szenknect S, Barthes V, Krimissa M (2007) Sorption isotherms: a review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl Geochem 22:247–275
Lin Q, Xu SH (2012) Parameter uncertainty analysis of solute transport in saturated porous media based on GLUE method. J Hydraul Eng 43:1017–1024 (in Chinese)
Liu ZF, Han YT, Jing M, Chen JW (2015) Sorption and transport of sulfonamides in soils amended with wheat straw-derived biochar: effects of water pH, coexistence copper ion, and dissolved organic matter. J Soils and Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1319-8
Mikutta R, Kleber M, Kaiser K, Jahn R (2005) Review: organic matter removal from soils using hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, and disodium peroxodisulfate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:120–135
Pan M, Chu LM (2017) Transfer of antibiotics from wastewater or animal manure to soil and edible crops. Environ Pollut 231:829–836
Park JY, Huwe B (2016) Effect of pH and soil structure on transport of sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soils. Environ Pollut 213:561–570
Qin X, Liu F, Zhao L, Hou H, Wang G, Li F, Weng L (2016) Adsorption of levofloxacin to goethite: batch and column studies. Environ Eng Sci 33:235–241
Shen G, Zhang Y, Hu S, Zhang H, Yuan Z, Zhang W (2017) Adsorption and degradation of sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole in an agricultural soil system under an anaerobic condition: kinetics and environmental risks. Chemosphere 194:266–274
Šimůnek J, Šejna M, Saito H, Sakai M, van Genuchten MT (2009) The Hydrus-1d Software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside, Riverside, California version 4.08, HYDRUS software series 3
Song X, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wang M, Wang S, Guo G (2015) Impact of organic matter removal on phosphate-induced Pb stabilization in soil. J Agro Environ Sci 34:1522–1527 (in Chinese)
Srinivasan P, Sarmah AK, Manley-Harris M (2013) Co-contaminants and factors affecting the sorption behaviour of two sulfonamides in pasture soils. Environ Pollut 180:165–172
Sukul P, Lamshoeft M, Zuehlke S, Spiteller M (2008) Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 73:1344–1350
Tasho RP, Cho JY (2016) Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: a review. Sci Total Environ 563–564:366–376
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten HR, Leinweber P (2004) Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. J Environ Qual 33:1331–1342
Tiedje JM, Wang F, Manaia CM, Virta M, Sheng H, Ma LP, Zhang T, Topp E (2019) Antibiotic resistance genes in the human-impacted environment: a one health perspective. Pedosphere 29:273–282
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406
Urdiales C, Gacitua M, Villacura L, Pizarro C, Escudey M, Canales C, Antilén M (2020) Variable surface charge of humic acid-ferrihydrite composite: influence of electrolytes on ciprofloxacin adsorption. J Hazard Mater 385:121520
Wang S, Wang H (2015) Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: a critical review. Front Env Sci Eng 9:565–574
Wehrhan A, Kasteel R, Simunek J, Groeneweg J, Vereecken H (2007) Transport of sulfadiazine in soil columns — experiments and modelling approaches. J Contam Hydrol 89:107–135
Xu Y, Yu X, Xu B, Peng D, Guo X (2021) Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on soil and soil components: influencing factors and mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 753:141891
Zhang H, Xu S H, Lin Q (2021) Influence of metal cation and surface iron oxide on the transport of sulfadiazine in saturated porous media. Sci Total Environ 758:143621
Zhang L, Dong D, Hua X, Guo Z (2019) Sorption of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ofloxacin by aquatic sediments: influence of biofilm development at the sediment-water interface. J Soils and Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02356-w
Zhao H, Liu X, Cao Z, Zhan Y, Shi X, Yan Y, Zhou J, Xu J (2016) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of chloramphenicols, sulfonamides, and non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 310:235–245
Zhi D, Yang D, Zheng Y, Yang Y, He Y, Luo L, Zhou Y (2019) Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil. J Environ Manage 251:109598
Zuo X, Qian C, Ma S, Xiong J (2020) Sulfonamide antibiotics sorption by high silica ZSM-5: effect of pH and humic monomers (vanillin and caffeic acid). Chemosphere 248:126061
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807010) and National Key R & D Program of China under Grant No. 2016YFC0402807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL designed the study and wrote the manuscript; BLL conducted the data analysis of sorption and transport experiments; XWL conducted the data analysis of FTIR; BDZ conducted sorption and transport experiments; and SHX provided advice on the design of the research and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yanzheng Gao
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Q., Li, B., Liu, X. et al. Insights into sorption and leaching behavior of sulfadiazine in soil as affected by humic acid. J Soils Sediments 22, 809–817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03110-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03110-x