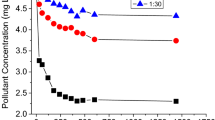
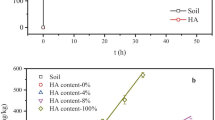
Abstract
Although sulfonamides (SAs) are among the most commonly used veterinary drugs and their presence in the environment is well documented, knowledge of their fate and behavior in the soil environment is still limited, especially for sulfisoxazole (SSX) which is characterized by the lowest (among other SAs) pK a value associated with acid-base equilibrium of sulfonamide group. Thus, this work was focused on determining the sorption potential of SSX onto natural soils differing in physicochemical properties. All the results were modeled using linear, Freundlich, Langmuir, Dubinin–Radushkevich, and Temkin sorption isotherms. The established sorption coefficients (K d ) for SSX were quite low (from 0.27 to 0.95 L kg−1), which indicated that this substance is highly mobile and has the potential to run off into surface waters and/or infiltrate ground water. The sorption data of SSX is well fitted to the Freundlich isotherm model (R 2 > 0.968). Moreover, we assessed the sorption mechanism of these compounds in the edaphic environment with respect to organic matter (OM) content, pH, and ionic strength. To clarify the current state of knowledge, these factors were examined much more thoroughly than in previous investigations concerning other SAs. The wide range of ionic strength examined showed positive correlation of this factor and sorption of SAs. The results also yielded new insight into dependency of sorption of SAs on organic matter content in soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anskjær GG, Krogh KA, Halling-Sørensen B (2014) Dialysis experiments for assessing the pH-dependent sorption of sulfonamides to soil clay fractions. Chemosphere 95:116–123
Babić S, Horvat AJM, Mutavdžić Pavlović D, Kaštelan-Macan M (2007) Determination of pKa values of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Trends Anal Chem 26:1043–1061
Baran W, Adamek E, Ziemiańska J, Sobczak A (2011) Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J Hazard Mater 196:1–15
Białk-Bielińska A, Maszkowska J, Mrozik W, Bielawska A, Kołodziejska M, Palavinskas R, Stepnowski P, Kumirska J (2012a) Sulfadimethoxine and sulfaguanidine: their sorption potential on natural soils. Chemosphere 86:1059–1065
Białk-Bielińska A, Stolte S, Matzke M, Fabiańska A, Maszkowska J, Kołodziejska M, Liberek B, Stepnowski P, Kumirska J (2012b) Hydrolysis of sulphonamides in aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 221–222:264–274
Białk-Bielińska A, Maszkowska J, Puckowski A, Stepnowski P (2014) Exposure and hazard identification of sulphonamides in the terrestrial environment. In: Soil pollution, ISBN 980-953-307-1137-6, InTech, Rijeka, Croatia. doi:10.5772/57265
Clausen L, Fabricius IL (2001) Atrazine, isoproturon, mecoprop, 2,4-D, and bentazone adsorption onto iron oxides. J Environ Qual 30:858–869
Dada AO, Olalekan AP, Olatunya AM, Dada O (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin—Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn 2+ onto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. J Appl Chem 3:38–45
De Jonge H, de Jonge LW (1999) Influence of pH and solution composition on the sorption of glyphosate and prochloraz to a sandy loam soil. Chemosphere 39:753–763
Delle-Site A (2001) Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbent/water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A review. J Phys Chem Ref Data 30:187–439
Deo RP, Halden RU (2013) Pharmaceuticals in the built and natural water environment of the United States. Water 5:1346–1365
Doretto KM, Rath S (2013) Sorption of sulfadiazine on Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 90:2027–2034
Figueroa-Diva R, Vasudevan D, MacKay AA (2010) Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere 79:786–793
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Huang H, Hu J, Shah SM, Su X (2012) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:540–546
García-Galán MJ, Silvia Díaz-Cruz M, Barceló D (2009) Combining chemical analysis and ecotoxicity to determine environmental exposure and to assess risk from sulfonamides. Trends Anal Chem 28:804–819
Gillman GP, Sumpter EA (1986) Modification to the compulsive exchange method for measuring exchange characteristics of soils. Aust J Soil Res 24:61–66
Hyland KC, Dickenson ERV, Drewes JE, Higgins CP (2012) Sorption of ionized and neutral emerging trace organic compounds onto activated sludge from different wastewater treatment configurations. Water Res 46:1958–1968
Jain M, Garg VK, Kadirvelu K (2009) Chromium (VI) removal from aqueous system using Helianthus annuus (sunflower) stem waste. J Hazard Mater 162:365–372
Johnson CA, Westall JC (1990) Effect of pH and KCI concentration on the octanol-water distribution of methylanilines. Environ Sci Technol 24:1869–1875
Kah M, Brown CD (2006) Adsorption of ionisable pesticides in soils. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 188:149–217
Kurwadkar ST, Adams CD, Meyer MT, Kolpin DW (2011) Comparative mobility of sulfonamides and bromide tracer in three soils. J Environ Manag 92:1874–1881
Leal RMP, Alleoni LRF, Tornisielo VL, Regitano JB (2013) Sorption of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in 13 Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 92:979–985
Lee L, Rao P, Nkedi-Kizza P, Delfino J (1990) Influence of solvent and sorbent characteristics on distribution of pentachlorophenol in octanol-water and soil-water systems. Environ Sci Technol 24:654–661
MacKay AA, Vasudevan D (2012) Polyfunctional ionogenic compound sorption: challenges and new approaches to advance predictive models. Environ Sci Technol 46(17):9209–9223
Maszkowska J, Kołodziesjska M, Białk-Bielińska A, Mrozik W, Kumirska J, Stepnowski P, Palavinskas P, Krüger O, Kalbe U (2013) Column and batch tests of sulfonamide leaching from different types of soil. J Hazard Mater 260:468–474
OECD (2000) Adsorption-desorption using a batch equilibrium method. OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals 106. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, pp 1–44
Regitano JB, Bischoff M, Lee LS, Reichert JM, Turco RF (1997) Retention of imazaquin in soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:397–404
Sassman SA, Lee LS (2005) Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ Sci Technol 39:7452–7459
Srinivasan P, Sarmah AK, Manley-Harris M (2013) Co-contaminants and factors affecting the sorption behaviour of two sulfonamides in pasture soils. Environ Pollut 180C:165–172
Sukul P, Spiteller M (2006) Sulfonamides in the environment as veterinary drugs. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 187:67–101
Sukul P, Lamshöft M, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2008) Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 73:1344–1350
Ter Laak TL, Gebbink WG, Tolls J (2006) The effect of pH and ionic strength on the sorption of sulfachloropyridazine, tylosin, and oxytetracycline to soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:904–911
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten H-R, Leinweber P (2004) Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. J Environ Qual 33:1331–1342
Zeng T, Ziegelgruber KL, Chin Y-P, Arnold WA (2011) Pesticide processing potential in prairie pothole porewaters. Environ Sci Technol 45:6814–6822
Zeng T, Chin Y-P, Arnold WA (2012) Potential for abiotic reduction of pesticides in prairie pothole porewaters. Environ Sci Technol 46:3177–3187
Zhang H, Weber EJ (2013) Identifying indicators of reactivity for chemical reductants in sediments. Environ Sci Technol 47:6959–6968
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the Polish National Science Centre under grant DEC-2011/03/B/NZ8/03010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Laura McConnell
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maszkowska, J., Białk-Bielińska, A., Mioduszewska, K. et al. Sorption of sulfisoxazole onto soil—an insight into different influencing factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 12182–12189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4445-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4445-3