Abstract
Purpose
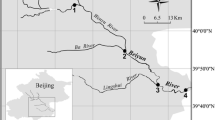
Though the process and players of nitrification are important in the ecology and biogeochemistry of Arctic fjords; there are very limited studies available on the ecology of ammonia oxidizers. Hence, we studied the abundance, diversity, and niche separation of ammonia oxidizers in the surface sediment of two high Arctic fjords (Kongsfjorden and Krossfjorden) to explore their ecology in the Arctic system.
Materials and methods
Surface sediment samples were collected from eight stations (four stations from each fjord). The diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and archaea (AOA) were analyzed using ammonia monooxygenase A (amoA) gene from the sediment metagenome. Environmental variables including bottom temperature and salinity, and sediment characteristics such as total carbon (TC), total nitrogen (TN), total sulfur (TS), and total organic carbon (TOC), were measured.
Results and discussion
AOA were more abundant than AOB in most of the samples and AOA/AOB ratios ranged from 0.63 to 17.11. AOA were dominated by Nitrosopumilus lineage (67.5%), followed by Nitrososphaera lineage (32.2%). Most of the AOB were affiliated with Nitrosospira lineage (82.2%), and comparatively lesser contribution (18.2%) was observed for Nitrosomonas. We could not observe comammox bacteria in our samples. The distribution of ammonia oxidizers had a significant influence with the total nitrogen and total organic carbon content.
Conclusions
Both AOA and AOB showed spatial variations in community composition within the fjords and between the fjords with a domination of freshwater/soil communities in the inner fjord stations. Freshwater and soil influx from glacial melt had a significant influence in controlling the environmental variables in the fjords which in turn regulated the distribution and niche selection of ammonia oxidizers.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Arrigo KR, van Dijken G, Pabi S (2008) Impact of a shrinking Arctic ice cover on marine primary production. Geophys Res Lett 35:1–6
Beman JM, Bertics VJ, Braunschweiler T, Wilson J (2012) Quantification of ammonia oxidation rates and the distribution of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in marine sediment depth profiles from Catalina Island, California. Front Microbio 3:263–272
Bernhard AE, Donn T, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2005) Loss of diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria correlates with increasing salinity in an estuary system. Environ. Microbiol 7:1289–1297
Bernhard AE, Landry ZC, Blevins A, José R, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2010) Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient in relation to potential nitrification rates. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1285–1289
Bourgeois S, Kerhervé P, Calleja ML, Many G, Morata N (2016) Glacier inputs influence organic matter composition and prokaryotic distribution in a high Arctic fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). J Mar Syst 164:112–127
Bouskill NJ, Eveillard D, Chien D, Jayakumar A, Ward BB (2012) Environmental factors determining ammonia-oxidizing organism distribution and diversity in marine environments. Environ Microbiol 14:714–729
Brochier-Armanet C, Boussau B, Gribaldo S, Forterre P (2008) Mesophilic Crenarchaeota: proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:245–252
Calleja ML, Kerhervé P, Bourgeois S, Kędra M, Leynaert A, Devred E, Babin M, Morata N (2017) Effects of increase glacier discharge on phytoplankton bloom dynamics and pelagic geochemistry in a high Arctic fjord. Prog Oceanogr 159:195–210
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu J-D (2011a) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in sediments from the coastal Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100:545–551
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu J-D (2011b) Phylogenetic diversity and ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the surface sediments of the Western Pacific. Microb Ecol 62:813–826
Christman GD, Cottrell MT, Popp BN, Gier E, Kirchman DL (2011) Abundance, diversity, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in the coastal Arctic Ocean in summer and winter. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2026–2034
Clarke KR, Gorley R, Somerfield PJ, Warwick R (2014) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Primer-E Ltd,
Cottier F, Tverberg V, Inall M, Svendsen H, Nilsen F, Griffiths C (2005) Water mass modification in an Arctic fjord through cross-shelf exchange: the seasonal hydrography of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. J Geophys Res: Oceans 110:1–18
Dai L, Liu C, Yu L, Song C, Peng L, Li X, Tao L, Li G (2018) Organic matter regulates ammonia-oxidizing bacterial and archaeal communities in the surface sediments of Ctenopharyngodon idellus aquaculture ponds. Front Microbio 9:2290–2305
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P, Han P, Herbold C, Albertsen M, Jehmlich N, Palatinszky M, Vierheilig J, Bulaev A (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528:504–509
Dang H, Li J, Chen R, Wang L, Guo L, Zhang Z, Klotz MG (2010a) Diversity, abundance, and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing Betaproteobacteria in response to environmental gradients and coastal eutrophication in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4691–4702
Dang H, Luan X-W, Chen R, Zhang X, Guo L, Klotz MG (2010b) Diversity, abundance and distribution of amoA-encoding archaea in deep-sea methane seep sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:370–385
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:855–869
Forwick M, Vorren TO, Hald M, Korsun S, Roh Y, Vogt C, Yoo K-C (2010) Spatial and temporal influence of glaciers and rivers on the sedimentary environment in Sassenfjorden and Tempelfjorden, Spitsbergen. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 344:163–193
Francis CA, O'Mullan GD, Ward BB (2003) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase (amoA) genes across environmental gradients in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Geobiology 1:129–140
Gubry-Rangin C, Hai B, Quince C, Engel M, Thomson BC, James P, Schloter M, Griffiths RI, Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2011) Niche specialization of terrestrial archaeal ammonia oxidizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:21206–21211
Hagen JO, Kohler J, Melvold K, Winther JG (2003) Glaciers in Svalbard: mass balance, runoff and freshwater flux. Polar Res 22:145–159
Hammer Ø, Harper DA, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia electronica 4:9
Hatzenpichler R (2012) Diversity, physiology, and niche differentiation of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7501–7510
He H, Zhen Y, Mi T, Lu X, Yu Z (2015) Seasonal and spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing microorganism communities in surface sediments from the East China Sea. Acta Oceanol Sin 34:83–92
Hop H, Falk-Petersen S, Svendsen H, Kwasniewski S, Pavlov V, Pavlova O, Søreide JE (2006) Physical and biological characteristics of the pelagic system across Fram Strait to Kongsfjorden. Prog Oceanogr 71:182–231
Hop H, Pearson T, Hegseth EN, Kovacs KM, Wiencke C, Kwasniewski S, Eiane K, Mehlum F, Gulliksen B, Wlodarska-Kowalczuk M, Lydersen C (2002) The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Res 21:167–208
Kalanetra KM, Bano N, Hollibaugh JT (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in the Arctic Ocean and Antarctic coastal waters. Environ. Microbiol 11:2434–2445
Kolde R (2015) Pheatmap: pretty heatmaps. R package version 1.0. 8. 2015 differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets Molecular biology and evolution. 33:1870-1874
Lagostina L, Goldhammer T, Røy H, Evans TW, Lever MA, Jørgensen BB, Petersen DG, Schramm A, Schreiber L (2015) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the Nitrosospira cluster 1 dominate over ammonia-oxidizing archaea in oligotrophic surface sediments near the South Atlantic Gyre. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:404–413
Li M, Wei G, Shi W, Sun Z, Li H, Wang X, Gao Z (2018) Distinct distribution patterns of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in sediment and water column of the Yellow River estuary. Sci Rep 8:1–10
Lipsewers YA, Bale NJ, Hopmans EC, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Villanueva L (2014) Seasonality and depth distribution of the abundance and activity of ammonia oxidizing microorganisms in marine coastal sediments (North Sea). Front Microbio 5:472
Liu S, Shen L, Lou L, Tian G, Zheng P, Hu B (2013) Spatial distribution and factors shaping the niche segregation of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in the Qiantang River, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4065–4071
Liu Y, Liu J, Yao P, Ge T, Qiao Y, Zhao M, Zhang X-H (2018) Distribution patterns of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in sediments of the eastern China marginal seas. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:658–668
Luo Z-H, Xu W, Li M, Gu J-D, Zhong T-H (2015) Spatial distribution and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in deep-sea sediments of the Pacific Ocean. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:329–342
Magalhães CM, Machado A, Bordalo AA (2009) Temporal variability in the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria vs. archaea in sandy sediments of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Aquat Microb Ecol 56:13–23
Martens-Habbena W, Berube PM, Urakawa H, José R, Stahl DA (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature 461:976–979
Molina V, Belmar L, Ulloa O (2010) High diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in permanent and seasonal oxygen-deficient waters of the eastern South Pacific. Environ Microbiol 12:2450–2465
Mortimer RJ, Harris SJ, Krom MD, Freitag TE, Prosser JI, Barnes J, Anschutz P, Hayes PJ, Davies IM (2004) Anoxic nitrification in marine sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 276:37–52
Nunoura T, Nishizawa M, Kikuchi T, Tsubouchi T, Hirai M, Koide O, Miyazaki J, Hirayama H, Koba K, Takai K (2013) Molecular biological and isotopic biogeochemical prognoses of the nitrification-driven dynamic microbial nitrogen cycle in hadopelagic sediments. Environ Microbiol 15:3087–3107
O'Mullan G, Ward B (2005) Relationship of temporal and spatial variabilities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria to nitrification rates in Monterey Bay, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:697–705
Park H-D, Wells GF, Bae H, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5643–5647
Park S-J, Park B-J, Rhee S-K (2008) Comparative analysis of archaeal 16S rRNA and amoA genes to estimate the abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in marine sediments. Extremophiles 12:605–616
Park S-J, Rhee S-K (2014) Diversity Analysis for Archaeal amoA Gene in Marine Sediment of Svalbard. Arctic Circle. Korean J. Microbiol 50:164–168
Pester M, Rattei T, Flechl S, Gröngröft A, Richter A, Overmann J, Reinhold-Hurek B, Loy A, Wagner M (2012) amoA-based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ Microbiol 14:525–539
Petrenko D, Pozdnyakov D, Johannessen J, Counillon F, Sychov V (2013) Satellite-derived multi-year trend in primary production in the Arctic Ocean. Int. J Remote Sens 34:3903–3937
Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2012) Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: the quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends Microbiol 20:523–531
Qin W, Amin SA, Martens-Habbena W, Walker CB, Urakawa H, Devol AH, Ingalls AE, Moffett JW, Armbrust EV, Stahl DA (2014) Marine ammonia-oxidizing archaeal isolates display obligate mixotrophy and wide ecotypic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:12504–12509
Rotthauwe J-H, Witzel K-P, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Sahan E, Muyzer G (2008) Diversity and spatio-temporal distribution of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in sediments of the Westerschelde estuary. FEMS Microbiol Rev 64:175–186
Sakami T, Kakehi S (2019) Distribution and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in coastal sediments in response to sediment material gradients at Sendai Bay, Japan. Marine Metagenomics. Springer, In, pp 161–181
Santoro AE, Casciotti KL, Francis CA (2010) Activity, abundance and diversity of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the central California Current. Environ Microbiol 12:1989–2006
Serreze MC, Francis JA (2006) The Arctic amplification debate. Climatic Change 76:241–264
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S, McIntosh S, Miles RJ, Mueller R, Reed R, Hu Z (2012) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46:4121–4129
Smith JM, Mosier AC, Francis CA (2015) Spatiotemporal relationships between the abundance, distribution, and potential activities of ammonia-oxidizing and denitrifying microorganisms in intertidal sediments. Microb Ecol 69:13–24
Spang A, Hatzenpichler R, Brochier-Armanet C, Rattei T, Tischler P, Spieck E, Streit W, Stahl DA, Wagner M, Schleper C (2010) Distinct gene set in two different lineages of ammonia-oxidizing archaea supports the phylum Thaumarchaeota. Trends microbiol 18:331–340
Stehr G, Böttcher B, Dittberner P, Rath G, Koops H-P (1995) The ammonia-oxidizing nitrifying population of the River Elbe estuary. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17:177–186
Stein LY, Arp DJ, Berube PM, Chain PS, Hauser L, Jetten MS, Klotz MG, Larimer FW, Norton JM, Op den Camp HJ, Shin M (2007) Whole-genome analysis of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, Nitrosomonas eutropha C91: implications for niche adaptation. Environ Microbiol 9:2993–3007
Tait K, Kitidis V, Ward B, Cummings D, Jones M, Somerfield P, Widdicombe S (2014) Spatio-temporal variability in ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidising bacteria and archaea in coastal sediments of the western English Channel. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 511:41–58
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7:1985–1995
Urakawa H, Martens-Habbena W, Huguet C, de la Torre JR, Ingalls AE, Devol AH, Stahl DA (2014) Ammonia availability shapes the seasonal distribution and activity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers in the Puget Sound Estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 59:1321–1335
Van Hoek A, van Alen TA, Sprakel V, Hackstein J, Vogels GD (1998) Evolution of anaerobic ciliates from the gastrointestinal tract: phylogenetic analysis of the ribosomal repeat from Nyctotherus ovalis and its relatives. Mol Biol Evol 15:1195–1206
Venter JC, Remington K, Heidelberg JF, Halpern AL, Rusch D, Eisen JA, Wu D, Paulsen I, Nelson KE, Nelson W, Fouts DE (2004) Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304:66–74
Vipindas PV, Jabir T, Jasmin C, Balu T, Rehitha TV, Adarsh BM, Nair S, Abdulla MH, Abdulaziz A (2018) Diversity and seasonal distribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the water column of a tropical estuary along the southeast Arabian Sea. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:188–192
Walczowski W, Piechura J, Goszczko I, Wieczorek P (2012) Changes in Atlantic water properties: an important factor in the European Arctic marine climate. ICES J Mar Sci 69:864–869
Walker CB, De La Torre JR, Klotz MG, Urakawa H, Pinel N, Arp DJ, Brochier-Armanet C, Chain PS, Chan PP, Gollabgir A, Hemp J (2010) Nitrosopumilus maritimus genome reveals unique mechanisms for nitrification and autotrophy in globally distributed marine crenarchaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8818–8823
Wang J, Kan J, Zhang X, Xia Z, Zhang X, Qian G, Miao Y, Leng X, Sun J (2017) Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in deep-sea sediments of the Eastern Indian Ocean—from the equator to the Bay of Bengal. Front Microbio:415
Webster G, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of β-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30
Wiencke C, Hop H (2016) Ecosystem Kongsfjorden: new views after more than a decade of research. Springer
Winkelmann D, Knies J (2005) Recent distribution and accumulation of organic carbon on the continental margin west off Spitsbergen. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 6:1–22
Wright ES, Yilmaz LS, Noguera DR (2012) DECIPHER, a search-based approach to chimera identification for 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:717–725
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJ, Herfort L, van Bleijswijk J, Timmers P, Strous M, Teira E, Herndl GJ, Middelburg JJ, Schouten S (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12317–12322
Xu W, Li M, Ding J-F, Gu J-D, Luo Z-H (2014) Bacteria dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in a hydrothermal vent site at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge of the South Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 98:7993–8004
Yu S, Yao P, Liu J, Zhao B, Zhang G, Zhao M, Yu Z, Zhang X-H (2016) Diversity, abundance, and niche differentiation of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in mud deposits of the eastern China marginal seas. Front Microbiol 7:137–148
Zhang Y, Chen L, Sun R, Dai T, Tian J, Zheng W, Wen D (2016) Population and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in a pollutants’ receiving area in Hangzhou Bay. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 100:6035–6045
Zheng Y, Hou L, Newell S, Liu M, Zhou J, Zhao H, You L, Cheng X (2014) Community dynamics and activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:408–419
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Director, NCPOR, Ministry of Earth Sciences, for support and encouragement. This work was carried out as a part of Indian scientific expedition to the Arctic-2017. We are grateful to Dr. C T Achuthankutty, Chief Scientist (Retd.), and Dr. Shanta Nair Chief Scientist (Retd.), CSIR-National Institute of Oceanography, for critically reviewing the manuscript for content and language. NCPOR contribution number: xxxx.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. PVV, TVR, and TJ conducted the laboratory experiments. PVV and TJ contributed in bioinformatics analysis. PVV and TVR analyzed the data. PVV wrote the manuscript under the supervision of KPK. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 461 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vipindas, P.V., Jabir, T., Rehitha, T.V. et al. Distinct community composition and abundance of ammonia oxidizers in the high Arctic fjord sediments of Svalbard. J Soils Sediments 21, 1890–1904 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02905-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02905-2