Abstract
Purpose
Organic matter amendment is usually used to improve soil physicochemical properties and to sequester carbon for counteracting climate change. There is no doubt that such amendment will change microbial activity and soil nitrogen transformation processes. However, the effects of straw and biochar amendment on anammox and denitrification activity and on community structure in paddy soil are unclear.
Materials and methods
We conducted a 30-day pot experiment using rice straw and rice straw biochar to deepen our understanding about the activity, microbial abundance, and community structure associated with soil nitrogen cycling during rice growth.
Results and discussion
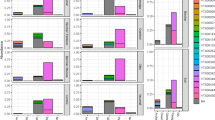
Regarding activity, anammox contributed 3.1–8.1% of N2 production and denitrification contributed 91.9–96.9% of N2 production; straw amendment resulted in the highest denitrification rate (38.9 nmol N g−1 h−1), while biochar amendment resulted in the highest anammox rate (1.60 nmol N g−1 h−1). Both straw and biochar amendments significantly increased the hzsB and nosZ gene abundance (p < 0.05). Straw amendment showed the highest nosZ gene abundance, while biochar amendment showed the highest hzsB gene abundance. Phylogenetic analysis of the anammox bacteria 16S rRNA genes indicated that Candidatus Brocadia and Kuenenia were the dominant genera detected in all treatments.
Conclusions
Straw and biochar amendments have different influences on anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification within paddy soil. Our results suggested that the changes in denitrification and anammox rates in the biochar and straw treatments were mainly linked to functional gene abundance rather than microbial community structure and that denitrification played the more major role in N2 production in paddy soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai R, Xi D, He JZ, Hu HW, Fang YT, Zhang LM (2015) Activity, abundance and community structure of anammox bacteria along depth profiles in three different paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 91:212–221
Barrow CJ (2012) Biochar: potential for countering land degradation and for improving agriculture. Appl Geogr 34:21–28
Cayuela ML, Oenema O, Kuikman PJ, Bakker RR, van Groenigen JW (2010) Bioenergy by-products as soil amendments? Implications for carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas emissions. GCB Bioenergy 2(4):201–213
Cheneby D, Bru D, Pascault N, Maron PA, Ranjard L, Philippot L (2010) Role of plant residues in determining temporal patterns of the activity, size, and structure of nitrate reducer communities in soil. Appl Environ Microb 76(21):7136–7143
Cheng Y, Cai ZC, Chang SX, Wang J, Zhang JB (2012) Wheat straw and its biochar have contrasting effects on inorganic N retention and N2O production in a cultivated black chernozem. Biol Fert Soils 48(8):941–946
Courtier-Murias D, Simpson AJ, Marzadori C, Baldoni G, Ciavatta C, Fernandez JM, Lopez-De-Sa EG, Plaza C (2013) Unraveling the long-term stabilization mechanisms of organic materials in soils by physical fractionation and NMR spectroscopy. Agric Ecosyst Environ 171:9–18
Dale OR, Tobias CR, Song B (2009) Biogeographical distribution of diverse anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in Cape Fear River estuary. Environ Microbial 11(5):1194–1207
Deenik JL, McClellan T, Uehara G, Antal MJ, Campbell S (2010) Charcoal volatile matter content influences plant growth and soil nitrogen transformations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74(4):1259–1270
Devol AH (2015) Denitrification, anammox, and N2 production in marine sediments. Annu Rev Mari Sci 7(1):403–423
Engström P, Dalsgaard T, Hulth S, Aller RC (2005) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by nitrite (anammox): implications for N2 production in coastal marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 69(8):2057–2065
Fan JL, Zhang B, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Liu FF, Guo YY, Wu HM (2013) Intermittent aeration strategy to enhance organics and nitrogen removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 141:117–122
Gori F, Tringe SG, Kartal B, Marchiori E, Jetten MS (2011) The metagenomicbasis of anammox metabolism in Candidatus “Brocadia fulgida”. Biochem Soc Trans 39:1799–1804
Graber ER, Tsechansky L, Gerstl Z, Lew B (2012) High surface area biochar negatively impacts herbicide efficacy. Plant Soil 353(1–2):95–106
Henderson SL, Dandie CE, Patten CL, Zebarth BJ, Burton DL, Trevors JT, Goyer C (2010) Changes in denitrifier abundance, denitrification gene mRNA levels, nitrous oxide emissions, and denitrification in anoxic soil microcosms amended with glucose and plant residues. Appl Environ Microb 76(7):2155–2164
Huang XC, Jiang QJ, Zhong S, Zhang YQ, Shi XJ (2015) Rice husk bio-ash impacts redox status and rice growth in a flooded soil from southwestern China. J Residuals Sci Tech 12:S75–S78
Jetten MSM, Wagner M, Fuerst J, Loosdrecht M, Kuenen G, Strous M (2001) Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘anammox’) process. Curr Opin Biotech 12(3):283–288
Jin RC, Yang GF, Yu JJ, Zheng P (2012) The inhibition of the anammox process: a review. Chem Eng J 197:67–79
Kappler A, Wuestner ML, Ruecker A, Harter J, Halama M, Behrens S (2014) Biochar as an electron shuttle between bacteria and Fe(III) minerals. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1(8):339–344
Kartal B, Kuypers MMM, Lavik G, Schalk J, Op den Camp HJM, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2007) Anammox bacteria disguised as denitrifiers: nitrate reduction to dinitrogen gas via nitrite and ammonium. Environ Microbiol 9(3):635–642
Keiluweit M, Nico PS, Johnson MG, Kleber M (2010) Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environ Sci Technol 44(4):1247–1253
Knowles OA, Robinson BH, Contangelo A, Clucas L (2011) Biochar for the mitigation of nitrate leaching from soil amended with biosolids. Sci Total Environ 409(17):3206–3210
Lattao C, Cao XY, Mao JD, Schmidt-Rohr K, Pignatello JJ (2014) Influence of molecular structure and adsorbent properties on sorption of organic compounds to a temperature series of wood chars. Environ Sci Technol 48:4790–4798
Lee CG, Fletcher TD, Sun GZ (2009) Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland systems. Eng Life Sci 9(1):11–22
Li H, Yang XR, Weng BS, Su JQ, Nie SA, Gilbert JA, Zhu YG (2016a) The phenological stage of rice growth determines anaerobic ammonium oxidation activity in rhizosphere soil. Soil Biol Biochem 100:59–65
Li SY, Gu X, Zhuang J, An TT, Pei JB, Xie HT, Li H, Fu SF, Wang JK (2016b) Distribution and storage of crop residue carbon in aggregates and its contribution to organic carbon of soil with low fertility. Soil Till Res 155:199–206
Luo J, Tillman RW, Ball PR (1999) Factors regulating denitrification in a soil under pasture. Soil Biol Biochem 31(6):913–927
Oshiki M, Shimokawa M, Fujii N, Satohl H, Okabe S (2011) Physiological characteristics of the anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacterium ‘Candidatus Brocadia sinica’. Microbiol-Sgm 157:1706–1713
Paul JW, Beauchamp EG (1989) Denitrification and fermentation in plant-residue-amended soil. Biol Fert Soils 7(4):303–309
Risgaard-Petersen N, Meyer RL, Schmid M, Jetten MSM, Enrich-Prast A, Rysgaard S, Revsbech NP (2004) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in an estuarine sediment. Aquat Microb Ecol 36(3):293–304
Schmid MC, Maas B, Dapena A, Pas-Schoonen KV, Vossenberg JV, Kartal B, Niftrik L, Schmidt I, Cirpus I, Kuenen JG, Wagner M, Damste JSS, Kuypers M, Revsbech NP, Mendez R, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2005) Biomarkers for in situ detection of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Appl Environ Microb 71(4):1677–1684
Shan J, Zhao X, Sheng R, Xia YQ, Ti CP, Quan XF, Wang SW, Wei WX, Yan XY (2016) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in typical Chinese paddy soils: rates, relative contributions, and influencing factors. Environ Sci Technol 50:9972–9980
Shu D, He YL, Yue H, Gao JL, Wang QY, Yang SC (2016) Enhanced long-term nitrogen removal by organotrophic anammox bacteria under different C/N ratio constraints: quantitative molecular mechanism and microbial community dynamics. RSC Adv 6:87593–87606
Singh BP, Hatton BJ, Singh B, Cowie AL, Kathuria A (2010) Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils. J Environ Qual 39(4):1224–1235
Steinbeiss S, Gleixner G, Antonietti M (2009) Effect of biochar amendment on soil carbon balance and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 41(6):1301–1310
Stubner S (2002) Enumeration of 16S rDNA of Desulfotomaculum lineage 1 in ricefield soil by real-time PCR with SybrGreenk detection. J Microbiol Meth 50:155–164
Thamdrup B, Dalsgaard T (2002) Production of N2 through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microb 68(3):1312–1318
Throbäck IN, Enwall K, Jarvis Å, Hallin S (2004) Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 49:401–417
Verheijen F, Jeffery S, Bastos AC, van der Velde M, Diafas I (2010) Biochar application to soils. A critical scientific review of effects on soil properties, processes and functions. European Commission Joint Research Centre. Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Luxembourg
Wang J, Gu JD (2013) Dominance of Candidatus Scalindua species in anammox community revealed in soils with different the duration of rice paddy cultivation in Northeast China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1785–1798
Wang Y, Zhu G, Harhangi HR, Zhu B, Jetten MSM, Yin C, Op den Camp HJM (2012) Co-occurrence and distribution of nitrite-dependent anaerobic ammonium and methane-oxidizing bacteria in a paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 336(2):79–88
Wu Y, Lin S, Liu T, Wan T, Hu R (2016) Effect of crop residue returns on N2O emissions from red soil in China. Soil Use Manage 32(1):80–88
Yanai Y, Toyota K, Okazaki M (2007) Effects of charcoal addition on N2O emissions from soil resulting from rewetting air-dried soil in short-term laboratory experiments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53(2):181–188
Yang XR, Li H, Nie SA, Su JQ, Weng BS, Zhu GB, Yao HY, Gilbert JA, Zhu YG (2015) Potential contribution of anammox to nitrogen loss from paddy soils in southern China. Appl Environ Microb 81(3):938–947
Zhang Y, Ji GD, Wang RJ (2016) Drivers of nitrous oxide accumulation in denitrification biofilters with low carbon:nitrogen ratios. Water Res 106:79–85
Zhao X, Xie Y, Xiong Z, Yan X, Xing G, Zhu Z (2009) Nitrogen fate and environmental consequence in paddy soil under rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu Lake region, China. Plant Soil 319:225–234
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Wang Y, Wang CX, Risgaard-Petersen N, Jetten MSM, Yin CQ (2011) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation in a fertilized paddy soil. ISME J 5(12):1905–1912
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15020301), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41471206, 41525002, 41301251), Ningbo Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (2015C1003), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences President’s International Fellowship Initiative (2013T2Z0002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Weijin Wang
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 193 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, F., Chapman, S.J., Li, Y. et al. Straw amendment to paddy soil stimulates denitrification but biochar amendment promotes anaerobic ammonia oxidation. J Soils Sediments 17, 2428–2437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1694-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1694-4