Abstract
Purpose
Agricultural nonpoint sources of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution are thought to pose great threats to the regional water quality in the Three Gorges area (TGA) of China. To explore the effects of protective methods on soil and nutrient losses from sloping arable land, rainfall runoff plot experiment was conducted from May 2010 to May 2011.
Materials and methods
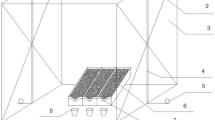
For a rotation of wheat and maize, four treatments with three replicates were set up: H1, planting Vetiveria zizanioides contour hedgerows; H2, planting alfalfa contour hedgerows; H3, wheat intercropped with horsebean and maize intercropped with soybean, reduced tillage, and ridge furrow cultivation; and H4, conventional management. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses via surface and subsurface runoff were analyzed.
Results and discussion
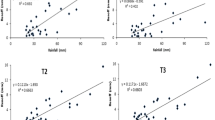
When compared with that in H4, sediment phosphorus losses from plots of H1, H2, and H3 were significantly reduced by 46.61, 30.51, and 37.29%, respectively, while surface runoff total phosphorus loss was reduced by 45.38, 28.46, and 34.62%, respectively. Sediment nitrogen and surface runoff total nitrogen losses were not reduced significantly. Sediments were highly enriched with organic matter and nutrients, and decaying organic matter from plant residuals contributed to sediment nitrogen and phosphorus losses.
Conclusions
In sandy loam sloping arable land, contour hedgerows and ridge furrow cultivation were effective in reducing phosphorus loss via surface runoff. However, subsurface runoff is the primary path for nutrient losses, especially for nitrogen loss. Accordingly, attention should be given to improve the management of fertilizer nutrients, soil water, and plant residuals in sandy loam slope land.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bu CF, Cai QG, Sai Leung NG, Cheong CK, Ding SW (2008) Effects of hedgerows on sediment erosion in Three Gorges Dam Area, China. Sediment Res 23:119–129
Cai QH, Hu ZY (2006) Studies on eutrophication problem and control strategy in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Hydrob Sinica 30:7–11
Cha SY, Li QH (1998) Soil erosion from sloping arable land in TGA and the countermeasures to deal with. Agro-Eviron Develop 15:30–33
Chaplot V, Le BY (2003) Runoff features for inter rill erosion at different rainfall intensities, slope lengths and gradients in an agricultural loessial hillslope. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:844–851
He BH, Guo T, Yao J, Huang W, Kan Y (2012) Characteristics of N and P losses in sediment of purple soil on sloping farmland with different fertilization levels. J Southwest Univ 34:1–8
He RJ, Jiang T, Mu ZJ, Ni JP, Wei SQ, Xie DT (1995) Nitrogen and phosphorus balance for the soil systems in a typical small agricultural watershed in the Three-Gorges Reservoir area. J Southwest Univ 33:95–101
Holland JM (2004) The environmental consequences of adopting conservation tillage in Europe: reviewing the evidence. Agric Ecosyst Environ 103:1–25
Hu HX, Hong TQ, Ma YH, Liu K (2007) Study on soil and sediment particle size distribution and nutrient loss. J Soil Water Conserv 21:26–29
Jia HY, Lei AL, Lei JS, Ye M, Zhao JZ (2007) Effects of hydrological processes on nitrogen loss in purple soil. Agr Water Manage 89:89–97
Jiang JD (2011) Evaluation on eco-environmental capacity for resettlement of Three Gorges region. Yangtze River 42:180–184
Kingery WL, Wood CW, Williams C (1996) Tillage and amendment effects on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization and phosphorus release. Soil Till Res 37:239–250
Li CY, Li HY, Shi LX (2011) Application of pressure membrane meter method to determination of soil moisture characteristic curve. Yellow River 33:60–61
Legout C, Leguédois S, Le BY (2004) Aggregate breakdown dynamics under rainfall compared with aggregate stability measurements. Eur J Soil Sci 56:225–238
Li FQ, Ye L, Liu RQ, Cao M, Cai QH (2008) Dynamics of main nutrient input to Xiangxi Bay of the Three-Gorges Reservoir. Acta Ecol Sin 28:2073–2079
Li YB, Shao JG, Li YC (2010) The status and prospect of land use/land cover changes in Three Gorges Reservoir area. J Chongqing Norm Univ 27:31–35
Liao XY, Chen ZJ, Liu SY, Wang HM (2005) Study on soil losses in different land use types of purple slope cropland in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. R Soil Water Conserv 12:159–161
Lin CW, Tu SH, Huang JJ, Chen YB (2007) The effects of plant hedgerows on soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farm land in the purple soil area. Acta Ecol Sin 27:2191–2198
Lin CW, Tu SH, Huang JJ, Chen YB (2009) The effect of plant hedgerows on the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farmland in the purple-soil area of China. Soil Till Res 105:307–312
Lin S, Feng ML, Hu RG, Liu RY, Wei MY, Jiang C (2010) Characteristics of nitrogen cycling in farm system in small watershed of Three Gorges Area, China. Environ Sci 31:633–638
Liu B, Wu XM, Li YE (1991) Calculate evapotranspiration through analyze the variation of soil water content. China Agri Meteor 12:26–30
Liu GD, Li QL, Huang Y (2003) Non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges area and the countermeasures to avoid water pollution. Resour Environ Yangtze River Basin 12:462–466
Lu RK (2000) Soil agrochemical analysis. China Agricultural, Soil Science Society of China, Beijing, pp 146–195
Luo ZX, Zhu B, Wang T, Tang JL, Wang D, Xin W (2008) Artificially simulated coupling characteristics of different sediment nutrient with sediment losses of slope land of purple soil, China. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 17:379–383
McDowell RW, Sharpley AN (2001) Phosphorus losses in subsurface flow before and after manure application to intensively farmed land. Sci Total Environ 278:113–125
Ning JF, Zou XZ, Yang SH, Huang Q, Wei L (2007) Progress in the research on water pollution from farmland nitrogen loss and its control. Guangzhou Environ Sci 22:5–10
Quinton JN, Catt JA, Hess TM (2001) The selective removal of phosphorus from soil: is event size important? J Environ Qual 30:538–545
Somchai D, Chaiyuth C (2012) Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the application of vetiver grass mulch in soil and water conservation. Int J Sediment Res 27:168–177
Sharpley AN, Smith SJ (1990) Phosphorus transport in agricultural runoff: the role of soil erosion. In: Boardman J, Foster IDL, Dearing JA (eds) Soil erosion on agricultural land. Wiley, Chichester, pp 351–366
Shi DM, Lu XP, Liu LZ (2005) Study on functions of soil and water conservation by mulberry hedgerow intercropping of purple soil slopping farmland in Three Gorges Reservoir region. J Soil Water Conserv 19:75–79
Tian X, Zhou YC, Liu XY, Ma LP, Cai XL (2011) Effective of hedgerow of species figuration on the interception of nutrition elements in the slope cultivated lands. Res Soil Water Conserv 18:89–93
Uri ND, Atwood JD, Sanabria J (1998) The environmental benefits and costs of conservation tillage. Sci Total Environ 216:13–32
Valentin C, Poesen J, Li Y (2005) Gully erosion: impacts, factors and control. Catena 63:132–153
Wang T, Zhu B, Xia LZ (2012) Effects of contour hedgerow intercropping on nutrient losses from the sloping farmland in the Three Gorges Area, China. J Mt Sci 9:105–114
Wei GX, Wang YB, Wang YL (2008) Using137Cs to quantify the redistribution of soil organic carbon and total N affected by intensive soil erosion in the headwaters of the Yangtze River, China. Appl Radiat Isotopes 66:2007–2012
Willis DW (2008) Hydrology field manual. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 547–597
Withers PJA, Hodgkinson RA, Bates A, Withers CL (2007) Soil cultivation effects on sediment and phosphorus mobilization in surface runoff from three contrasting soil types in England. Soil Till Res 93:438–451
Xia LZ, Yang LZ, Li YD (2007) Perennial alfalfa and contour hedgerow on reducing soil, nitrogen and phosphorus losses from uplands of purple soil. J Soil Water Conserv 21(28):31
Xia LZ, Han QZ, Xiang L (2012) Countermeasures to fertigation in citrus sloping land in the Three Gorge Area, China. Agro-environ Develop 29:12–15
Xiao B, Wang QH, Wang HF, Wu JY, Yu DF (2012) The effects of grass hedges and micro-basins on reducing soil and water loss in temperate regions: a case study of Northern China. Soil Till Res 122:22–35
Xu F, Cai QG, Wu SA, Zhang GY (1999) Effect of contour hedgerows on soil nutrient loss on slope land. J Soil Water Conserv 5:23–29
Xu KH, Milliman JD (2008) Seasonal variations of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 104:276–283
Xu Q (2007) Characteristics of the arable land resources in Three Gorges area. In: Yang LZ et al (eds) Potential productivity and eco-environmental construction in the area of the head part of the Three Gorges Reservoir area. China Water Power, Beijing, pp 14–27
Yang QG, Zhang XD, Yang XG, Liu HY (2005) Model to compute the actual evapo-transpiration in the field of rainfed wheat. Agric Res Arid Area 23(1):35–38
Zhang GF, Jiang XH, Cui YB (2005a) The research and application progress of Vetiveria zizanioioles. Pratacultural Sci 22:72–78
Zhang GH, Liu GB, Wang GL, Wang YX (2011a) Effects of vegetation cover and rainfall intensity on sediment-bound nutrient loss, size composition and volume fractal dimension of sediment particles. Pedosphere 21:676–684
Zhang HL, Gao WS, Chen F, Zhu WS (2005b) Prospects and present situation of conservation tillage. J China Agri Univ 10:16–20
Zhang L, Dong LZ, Wu BF, Zhou WC (2007) Land cover change before and after the construction of Three Gorges Reservoir. Res Environ Yangtze Basin 16:107–112
Zhang Q, Zhang ZX, Wen XM, Wang S (2011b) Comparisons of observational methods of land surface evapotranspiration and their influence factors. Adv Earth Sci 26:538–547
Zheng FL (2005) Effects of accelerated soil erosion on soil nutrient loss after deforestation on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 15:707–715
Zheng JJ, He XB, Willing D, Zhang XB, Qi YQ (2007) Assessing soil erosion rates on manually-tilled hill slopes in the Sichuan hilly basin using 137Cs and 210Pb. Pedosphere 17:273–283
Zheng SY (2008) Analysis on characteristics and stability of the Palongzangbu land slide erosion. Res Soil Water Conserv 15:46–48
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Peng Huiqin and Zhou Zongyi for their help with field experiments, and we are grateful to the anonymous referees for their excellent suggestions for revision. We are also grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30870410) and the Three Gorges Project Ecology and Environment Monitoring Network (JC-01-18-05) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Scott X. Chang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, L., Liu, G., Ma, L. et al. The effects of contour hedges and reduced tillage with ridge furrow cultivation on nitrogen and phosphorus losses from sloping arable land. J Soils Sediments 14, 462–470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0824-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0824-x