Abstract
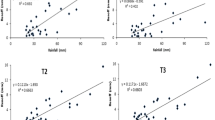
Eutrophication is recognized as one of the major environmental problems in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Contour hedgerows have been used as a major soil and water conservation measure in this area. Accordingly, a two-year study was conducted to investigate the effects of contour hedgerow intercropping on nutrient loss from sloping farmland in this area. Four treatments were applied: (1) Maize + Soybean, (2) Maize, (3) Maize + Alfalfa, and (4) Maize + Hemerocallis citrina Baroni. Results indicated that nutrient loss in the control treatment (Maize) was serious, especially the average loss flux of total nitrogen (2245.8 mg) and total phosphate (2434.2 mg) in a typical rainfall event. However, the nutrient losses by runoff in the other three treatments with contour hedgerow intercropping showed significant reduction. Compared with the control treatment, the total nitrogen loss in the Alfalfa and Hemerocallis citrina Baroni decreased by 80.9% and 85.0%, respectively, and the total phosphorus loss in the two treatments decreased by 91.2% and 92.5%, respectively. Therefore, it is concluded that nutrient losses could be reduced by using contour hedgerows in the Three Gorges Region. Reducing runoff volume and sediment loss was the main mechanisms of contour hedgerow intercropping to reduce nutrient loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Angima, S.D., Stott, D.E., ONeill, M.K. Ong C.K. Weesies GA, Usda ARS, Usda NRCS (2002) Use of calliandra-Napier grass contour hedges to control erosion in central Kenya. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment 91: 15–23.
Bu CF, Cai QG, Yuan ZJ (2006) Erosion and nutrient cycling in the Vetiveria zizanioides hedgerow intercropping system with fertilization or mulching measures in humid slopeland. Transactions of the CSAE 22(5):55–60. (In Chinese)
Bu CF, Cai QG, Ng SL, Chau KC, Ding SW (2008) Effects of hedgerows on sediment erosion in Three Gorges Dam Area, China. International Journal of Sediment Research 23(2): 119–129.
Cai QG, Bu CF (2004) Benefit of hedgerow agroforestry technical measure. Resources Science 26(Suppl.):7–12. (In Chinese)
Du RH, Shi DM, Yuan J (1994) The impact of soil and water losses upon ecosystem and environment in the Three Gorges Area of the Changjiang River. Since Press, Beijing, China. (In Chinese)
Gomez JA, Sobrinho TA, Giraldez JV, Fereres E (2009) Soil management effects on runoff, erosion and soil properties in an olive grove of Southern Spain. Soil & Tillage Research 102(1): 5–13.
Guo ZL, Zhong C, Cai CF, Ding SW, Wang ZM (2008) Nitrogen competition in contour hedgerow systems in subtropical China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 81: 71–83.
He YH, Tang Y, Sun H, Chen KM (2001) Effects of contour hedgerow on surface flow and soil erosion control in Arid valley of Jinsha river. Paper presented at the International Symposium on Mountain Agriculture in the Hindu Kush Himalayan Region. Organized by International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD). Katmandu, Nepal. Pp 21–24.
Knapen A, Poesen J, Govers G, DE Baets S (2008) The effect of conservation tillage on runoff erosivity and soil erodibility during concentrated flow.Hydrological Processes 22(10): 1497–1508.
Li Wenhua (1999) Flood of Yangtze river and ecological restoration. Journal of Natural Resources 14: 1–8. (In Chinese)
Li XP, Wang ZQ, Chen X, Fang ZG (2002) Research on soil and water conservation effect and mechanism of hedgerows under rainfall simulation in red soil slope field. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 16(2): 36–40. (in Chinese)
Li XB (1995) Living terrace edge: an effective way for slopeland utilization in east China. Asia-Pac Uplands 9:1–8
Li XB, Peng YX, Jiang C, Li XC (1998) The contour hedgerow technology in enhancing sustainable productivity of slopelands — a case study of the Three Gorges Area. Geographical Research 17:309–315. (In Chinese)
Maurizio B, Mattro P, Mara T, Tempesta T (2010) Multiple functions of buffer strips in farming areas. European Journal of Agronomy 32: 103–111.
Ng SL, Cai QG, Ding SW, Chau KC, Qin J (2008) Effects of contour hedgerows on water and soil conservation, crop productivity and nutrient budget for slope farmland in the Three Gorges Region (TGR) of China. Agroforestry Systems 74: 279–291.
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page, A L et al. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, second ed. In: Agron Monoger, ASA and SSSA, Madison WI, 9,pp 403–429.
Owino JO, Owido SFO, Chemelil MC (2006) Nutrients in runoff from a clay loam soil protected by narrow grass strips. Soil Tillage Research 88: 116–122.
Pansak W, Dercon G, Hilger T, Kongkaew T, Cadisch G (2007) C-13 isotopic discrimination: a starting point for new insights in competition for nitrogen and water under contour hedgerow systems in tropical mountainous regions. Plant and Soil 298(1–2): 175–189.
Pansak W, Hilger T, Lusiana B, Kongkaew T, Marohn C, Cadisch G (2010) Assessing soil conservation strategies for upland cropping in Northeast Thailand with the WaNuLCAS model. Agroforestry Systems 79: 123–144.
Pellek R (1992) Contour Hedgerows and Other Soil Conservation Interventions for Hilly Terrain. Agroforestry Systems 17: 135–152.
Phien T (1998) Leucaena and other shrubby green manure cover crops in contour hedgerow farming systems on sloping lands in Vietnam. Leucaena — Adaptation, Quality and Farming Systems 358: 344–349.
Shen YC (1998) Study on soil and water conservation benefit to agricultural technology of hedgerow in the Three Gorges Area. J Soil Water Conserv 4(2):61–66. (In Chinese)
Shen Zhenyao, Gong Yongwei, Li Yanhong, Liu Ruimin (2010) Analysis and modeling of soil conservation measures in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in China. Catena 81:104–112
Subhrendu P, Evan MD (1998) Valuing soil conservation benefits of agroforestry: contour hedgerows in the Eastern Visayas, Philippines. Agricultural Economics 18:31–46.
Sun H, Tang Y, Chen KM, Zhang YZ (2001) Effect of contour hedgerow intercropping on reducing runoff in sloping cropland. Bull Soil Water Conserv 21(2):48–51. (In Chinese)
Sun H, Tang Y, Xie JS (2008) Contour hedgerow intercropping in the mountains of China: a review. Agroforestry Systems 73:65–76.
Sundriyal RC (2003) Contour hedgerow farming in north-east India. Mountain Agriculture in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan Region. Proceedings of an International Symposium held in Kathmandu, Nepal, 2001, 85–90.
Wang L, Tang LL, Wang XA, et al. (2010) Effects of alley crop planting on soil and nutrient losses in the citrus orchards of the Three Gorges Region. Soil & Tillage Research 110:243–250.
Xia LZ, Yang LZ, Li YD (2007) Perennial alfalfa and contour hedgerow on reducing soil, nitrogen and phosphorus losses from uplands of purple soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 21(2): 28–31. (In Chinese)
Xu F, Cai QG, Wu SA, Zhang GY, Ding SW, Cai CF (2000) A study on soil nutrient loss by slope eco-engineering in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region Taking the contour hedgerows as an example. Geographical Research 19:303–310. (In Chinese)
Yin DX, Tang HB, Zhu Q, Li YR, Li DM, Liang DC (2001) Research on alley cropping technology integrated terracing slopeland. Journal of Soil Water Conservation 15:84–87. (In Chinese)
Zhao AJ, Xu KC, Peng YX (2004) Preliminary report on soil and water loss prevention tests by planting living hedges on purple soil slope lands. Soil Water Conservation of China 11:23–25. (In Chinese)
Zhou WC (2001) Impact of land slope and sea level elevation on the economic development in the Three Gorges Area. Resources and Environment In Yangtze Basin 10:15–21. (In Chinese)
Zobisch MA, Richter C, Heiligtag B, Schlott R (1995) Nutrient losses from cropland in central highlands of Kenya due to surface runoff and soil erosion. Soil Tillage Research 33:109–116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhu, B. & Xia, L. Effects of contour hedgerow intercropping on nutrient losses from the sloping farmland in the Three Gorges Area, China. J. Mt. Sci. 9, 105–114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2197-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2197-9