Abstract
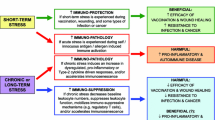
Psychological stress has extreme adverse consequences on health. However, the molecular mechanisms that mediate and accelerate the process of aging due to stress hormone are not well defined. This review has focused on diverse molecular paths that come out in response to chronic psychological stress via releasing of excessive glucocorticoids (GCs), involved in the aging process. GCs suppress transcription of nuclear cell adhesion molecules which impair synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and cognitive ability. Again, GCs promote muscle atrophy by means of motivating ubiquitin proteasome system and can repress muscle protein synthesis by inhibition of PI3-kinase/Akt pathway. GCs also inhibit interleukin-2 synthesis through suppressing T cell receptor signal that leads to loss of T cell activation, proliferation, and B-cell activation. Moreover, GCs increase the expression of collagenase-3, RANK ligand, and colony stimulating factor-1 that induce bone resorption. In general, stress-induced GCs can play causal role for aging and age-related disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ager JW, Balooch G, Ritchie RO (2006) Fracture, aging, and disease in bone. J Mater Res 21:1878–1892
Anderson DM et al (1997) A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic cell function. Nature 390:175–179
Anthony TG, Anthony JC, Yoshizawa F, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS (2001) Oral administration of leucine stimulates ribosomal protein mRNA translation but not global rates of protein synthesis in the liver of rats. J Nutr 133:1171–6
Artyomov MN, Lis M, Devadas S, Davis MM, Chakraborty AK (2010) CD4 and CD8 binding to MHC molecules primarily acts to enhance Lck delivery. PNAS 107(39):16917
Aubert G, Lansdorp PM (2008) Telomeres and aging. Physiol Rev 88:557–579
Barnes PJ (1998) Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: molecular mechanisms. Clin Sci 94:557–572
Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G (1995) Cell 83:851–857
Bhattacharyya S, Zhao Y, Kay YWH, Muglia LJ (2011) Glucocorticoids target suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and type 1 interferons to regulate Toll-like receptor-induced STAT1 activation. PNAS 108(23):9554–9559
Bijlmakers MJ, Marsh M (2000) Hsp90 is essential for the synthesis and subsequent membrane association, but not the maintenance, of the Src-kinase p56 (Lck). Mol Biol Cell 11:1585–1595
Bodine SC et al (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294:1704–1708
Borish L et al (1992) Detection of alveolar macrophage-derived IL-1 beta in asthma. Inhibition with corticosteroids. J Immunol 149:3078–3082
Bosscher KD et al (1997) Glucocorticoid-mediated repression of nuclear factor-κB dependent transcription involves direct interference with transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13504–13509
Boylan JM, Anand P, Gruppuso PA (2001) Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation and function during late gestation liver development in the rat. J Biol Chem 276:44457–44463
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423:337–342
Bross R, Storer T, Bhasin S (1999) Aging and muscle loss. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10(5):194–198
Buckingham JC (2006) Glucocorticoids: exemplars of multi-tasking. Br J Pharmacol 147:S258–S268
Buckingham JC, Loxly HD, Christian HC, Philip JG (1996) Activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis by immuno insults: the role and interactions of cytokines, eicosanoids and glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:285–298
Cai D, Lee KKH, Li M, Tang MK, Chan KM (2004) Ubiquitin expression is up-regulated in human and rat skeletal muscles during aging. Arch Biochem Biophys 425:42–50
Canalis E, Delany AM (2002) Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action in bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci 966:73–81
Castle SC (2000) Clinical relevance of age-related immune dysfunction. Clin Infect Dis 31:578–585
Cesari M et al (2004) Inflammatory markers and physical performance in older persons: the in Chianti study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 59:242–248
Cohan VL et al (1989) Dexamethasone does not inhibit the release of mediators from human mast cells residing in airway, intestine, or skin. Am Rev Respir Dis 140:951–954
Colwell G, Lj B, Forrest D, Brackenbur R (1992) Conserved regulatory elements in the promoter region of the N-CAM gene. Genomics 14:875–882
Combaret L et al (2005) USP19 is a ubiquitin-specific protease regulated in rat skeletal muscle during catabolic states. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E693–E700
Csermely P, Sőti C (2006) Cellular networks and the aging process. Arch Physiol Biochem 112:60–64
Datson NA, Perk JVD, Kloet ERD, Vreugdenhil E (2001) Identification of corticosteroid-responsive genes in rat hippocampus using serial analysis of gene expression. Eur J Neurosci 14:675–689
Datta HK, Ng WF, Walker JA, Tuck SP, Varanasi SS (2008) The cell biology of bone metabolism. J Clin Pathol 61:577–587
Doga M, Bonadonna S, Giustina A (2004) Glucocorticoids and bone: cellular, metabolic and endocrine effects. Hormones 3:184–190
Engelmann M, Landgraf R, Wotjak CT (2004) The hypothalamic neurohypophysial system regulates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis under stress: an old concept revisited. Front Neuroendocrinol 25(3–4):132–149
Evans PM, O’Connor BJ, Fuller RW, Barnes PJ, Chung KF (1993) Effect of inhaled corticosteroids on peripheral blood eosinophil counts and density profiles in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 91:643–650
Goll DE, Dayton WR, Singh I, Robson RM (1991) Studies of the alpha-actinin/actin interaction in the Z-Disk by using calpain. J Biol Chem 266:8501–8510
Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J (2003) The calpain system. Physiol Rev 83:731–801
Goll DE, Neti G, Mares SW, Thompson VF (2008) Myofibrillar protein turnover: the proteasome and the calpains. J Anim Sci 86:E19–E35
Gomez CR, Boehmer ED, Kovacs EJ (2005) The aging innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 17:457–462
Graham JE, Christian LM, Kiecolt-Glaser JK (2006) Stress, age, and immune function: toward a lifespan approach. J Behavior Med 29:389–400
Aubrey DN, de Grey J (1999) Molecular biology intelligence unit 9 the mitochondrial free radical theory of aging. RG Landes, Austin, TX, USA
Hamilton JA (2008) Colony-stimulating factors in inflammation and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 8:533–544. doi:10.1038/nri2356
Hasselgren PO, Wray C, Mammen J (2002) Molecular regulation of muscle cachexia: it may be more than the proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:1–10
Ho RC, Neo LF, Chua AN, Cheak AA, Mak A (2010) Research on psychoneuroimmunology: does stress influence immunity and cause coronary artery disease? Ann Acad Med 39:191–196
Hof PR, Morrison JH (2004) The aging brain: morphomolecular senescence of cortical circuits. TRENDS Neurosci 27:607–613
Hofbauer LC et al (1999) Stimulation of osteoprotegerin ligand and inhibition of osteoprotegerin production by glucocorticoids in human osteoblastic lineage cells: potential paracrine mechanism of glucocorticoids-induced osteoporosis. Endocrinology 140:4382–4389
Hu Z, Wang H, Lee IH, Du J, Mitch WE (2009) Endogenous glucocorticoids and impaired insulin signaling are both required to stimulate muscle wasting under pathophysiological conditions in mice. J Clin Investig 119:3059–3069
Huchison KA et al (1993) Biochem 32:3953–3957
John M et al (1998) Inhaled corticosteroids increase interleukin-10 but reduce macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interferon-gamma release from alveolar macrophages in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:256–262
Karin M, Chang L (2001) AP-1–glucocorticoid receptor crosstalk taken to a higher level. J Endocrinol 169:447–451
Kashiwakura J, Kawakami Y, Yuki K, Zajonc DM, Hasegawa S, Tomimori Y, Caplan B, Saito H, Furue M, Oettgen HC, Okayama Y, Kawakami T (2009) Polyclonal IgE induces mast cell survival and cytokine production. Allergol Int 58:411–419
Kayali AG, Young VR, Goodman MN (1987) Sensitivity of myofibrillar proteins to glucocorticoid-induced muscle proteolysis. Am J Physiol 252:E621–E626
Khosla S (2001) The OPG/RANKL/RANK system. Endocrinology 142:5050–5055
Kiss JZ, Troncoso E, Djebbara Z, Vutskits L, Muller D (2001) The role of neural cell adhesion molecules in plasticity and repair. Brain Res Rev 36:175–184
Kitajima T, Ariizumi K, Bergstresser PR, Takashima A (1996) A novel mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced immune suppression: the inhibition of T cell-mediated terminal maturation of a murine dendritic cell line. J Clin Invest 98:142–147
Koivisto K, Reinikainen KJ, Hamrinen T, Vanhanen M, HeIkaIa EL, Mykkarren L, Laakso M, Pyorala K, Riekkinen PJS (1995) Prevalence of age-associated memory impairment in a randomly selected population from eastern Finland. Neurology 45:741–747
Lacey DL et al (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176
Lau WM, Qiu G, Helmeste DM, Lee TMC, Tang SW, So KF, Tange SW (2007) Corticosteroid decreases subventricular zone cell proliferation, which could be reversed by paroxetine. Restor Neurol Neurosci 25:17–23
Lecker SH, Solomon V, Mitch WE, Goldberg AL (1999) Muscle protein breakdown and the critical role of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in normal and disease states. J Nutr 129:227S–237S
Lovatt M, Filby A, Parravicini V, Werlen G, Palmer E, Zamoyska R (2006) Lck regulates the threshold of activation in primary t cells, while both lck and fyn contribute to the magnitude of the extracellular signal-related kinase response. Mol Cell Biol 26(22):8655–8665
Löwenberg M et al (2005) Rapid immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids mediated through Lck and Fyn. Blood 106:1703–1710
Löwenberg M et al. (2006) Glucocorticoids cause rapid dissociation of a T-cell receptor-associated protein complex containing LCK and FYN. EMBO reports 7
Lian JB, Stein GS (2001) Osteoblast biology. In: Marcus R, Feldman D, Kelsey J (eds) Osteoporosis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 21–71
Matsuo H et al (1997) Structure of translation factor eIF4E bound to m7GDP and interaction with 4E-binding protein. Nat Struct Biol 4:717–724
McGrath JA, Goldspink DF (1982) Glucocorticoid action on protein synthesis and protein breakdown in isolated skeletal muscles. Biochem J 206:641–645
McLay RN, Freeman SM, Harlin RE, Ide CF, Kastin AJ, Jadina JE (1997) Aging in the hippocampus: interrelated actions of neurotrophins and glucocorticoids. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:615–629
Mora A, Sakamoto K, McManus EJ, Alessi DR (2005) Role of the PDK1-PKB-GSK3 pathway in regulating glycogen synthase and glucose uptake in the heart. FEBS Lett 579:3632–3638
Murachia T (1983) Calpain and calpastatin. Trends Biochem Sci 8:167–169
Murase S, Schuman EM (1999) The role of cell adhesion molecules in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:549–553
Murasko DM, Weiner P, Kaye D (1987) Decline in mitogen induced proliferation of lymphocytes with increasing age. Clin Exp Immunol 70:440–448
Nalla RK, Kruzic JJ, Kinney JH, Ritchie RO (2004) Effect of aging on the toughness of human cortical bone: evaluation by R-curves. Bone 35:1240–1246
Nika K, Soldani C, Salek M, Paster W, Gray A, Etzensperger R, Fugger L, Polzella P, Cerundolo V, Dushek O, Höfer T, Viola A, Acuto O (2010) Constitutively active Lck kinase in T cells drives antigen receptor signal transduction. Immunity 32(6):766–777. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.011
Noorlander CW, De Graan PNE, Middeldorp J, Van Beers JJBC, Visser GHA (2006) Ontogeny of hippocampal corticosteroid receprors: effects of antenatal glucocorticoids in human and mouse. J Comp Neurol 499:924–934
Orlowski M, Wilk S (2003) Ubiquitin-independent proteolytic functions of the proteasome. Arch Biochem Biophys 415:1–5
Owen WFJ et al (1987) Regulation of human eosinophil viability, density, and function by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the presence of 3T3 fibroblasts. J Exp Med 166:129–141
Palacios EH, Weiss A (2004) Function of the Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and activation. Oncogene 23:7990–8000
Papadimitriou A, Priftis KN (2009) Regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Neuroimmunomodulation 16(5):265–271
Plas DR, Thompson CB (2005) Akt-dependent transformation: there is more to growth than just surviving. Oncogene 24:7435–7442
Porter NM, Landfield PW (1998) Stress hormones and brain aging: adding injury to insult? Nat Neurosci 1:3–4
Purves D et al (2004) Neuroscience, 3rd edn. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA, pp 575–582
Ravid T, Hochstrasser M (2008) Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:679–689
Rentero C, Magenau A, Williamson D, Tedla N, Gaus K (2008) Membrane domains as signaling centers in macrophages and T-cells: from concepts to experiments. Immun Endoc Metab Agents Med Chem 8:336–348
Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turner CH (2006) Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:455–498
Ronn LCB, Berezin V, Bock E (2000) The neural cell adhesion molecule in synaptic plasticity and ageing. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:193–199
Rose AJ, Vegiopoulos A, Herzig S (2010) Role of glucocorticoids and the glucocorticoid receptor in metabolism: insights from genetic manipulations. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 122(1–3):10–20
Rubin J et al (1998) Dexamethasone promotes expression of membrane-bound macrophage colony-stimulating factor in murine osteoblast-like cells. Endocrinology 139:1006–1012
Saad MJ, Folli F, Kahn JA, Kahn CR (1993) Modulation of insulin receptor, insulin receptor substrate-1, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in liver and muscle of dexamethasone-treated rats. J Clin Invest 92:2065–2072
Salmond RJ, Filby A, Qureshi I, Caserta S, Zamoyska R (2009) T-cell receptor proximal signaling via the Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, influences T-cell activation, differentiation, and tolerance. Immunol Rev 228(1):9–22
Samson WK, Taylor MM, Follwell M, Ferguson AV (2002) Orexin actions in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: physiological consequences and cellular correlates. Regulatory Peptides 104(1–3):97–103
Sandi C (2004) Stress, cognitive impairment and cell adhesion molecules. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:917–930
Sato K, Minegishi S, Takano J, Plattner F, Saito T, Asada A, Kawahara H, Iwata N, Saido TC, Hisanaga S (2011) Calpastatin, an endogenous calpain-inhibitor protein, regulates the cleavage of the Cdk5 activator p35 to p25. J Neurochem 117(3):504–515. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07222.x
Schakman O, Gilson H, Thissen JP (2008) Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. J Endocrinol 197:1–10
Schakman O, Gilson H, Kalista S, Thissen JP (2009) Mechanisms of muscle atrophy induced by glucocorticoids. Horm Res 72(Suppl 1):36–41
Scheid MP, Woodgett JR (2001) PKB/AKT: functional insights from genetic models. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:760–768
Senthil D, Choudhury GG, Abboud HE, Sonenberg N, Kasinath BS (2002) Regulation of protein synthesis by IGF-I in proximal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F1226–F1236
Simpson CS, Morris BJ (2000) Regulation of neuronal cell adhesion molecule expression by NF-κB. J Biol Chem 275:16879–16884
Slominski AA (2007) Nervous breakdown in the skin: stress and the epidermal barrier. J Clin Invest 117:3166–3169
Sobhani ME, Molla MAW, Rahman MS (2010) A review on biomolecular basis of the role of psychological stress in the development and progression of cancer. Mag Euro Med Oncol 3:136–141. doi:10.1007/s12254-010-0217-4
Stahna C, Löwenberg M, Hommesc DW, Buttgereita F (2007) Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists. Mol Cell Endocrinol 275(1–2):71–78
Stolzing A, Jones E, McGonagle D, Scutt A (2008) Age-related changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: consequences for cell therapies. Mech Ageing Dev 129:163–173
Ströhle A, Holsboer F (2003) Stress responsive neurohormones in depression and anxiety. Pharmacopsychiatry 36:207–214
Takeuchi Y, Fukunaga K (2004) Different activation of NF-κB by stimulation of dopamine D2L and D2S receptors through calcineurin activation. J Neurochem 90:155–163
Tamuraa Y, Okinagab H, Takamic H (2004) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother 58:500–504
Tan FC, Goll DE, Otsuka Y (1988) Some properties of the millimolar Ca2+-dependent proteinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 20:983–997
Timiras PS (2007) Physiological basis of aging and geriatrics, 4th edn. Informa Healthcare, New York, pp 40–64
Tisdale MJ (2005) The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway as a therapeutic target for muscle wasting. J Support Oncol 3:209–217
Tseng YH, Ueki K, Kriauciunas KM, Kahn CR (2002) Differential roles of insulin receptor substrates in the anti-apoptotic function of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin. J Biol Chem 277:31601–31611
Volonte D, Galbiati F (2009) Caveolin-1, cellular senescence and pulmonary emphysema. Aging 01:831–835
Vreugdenhil E, Kloet ERD, Schaaf M, Datson NA (2001) Genetic dissection of corticosterone recepto rfunction in the rat hippocampus. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:423–430
Weinert BT, Timiras PS (2003) Physiology of aging invited review: theories of aging. J Appl Physiol 95:1706–1716
Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Parfitt AM, Manolagas SC (1998) Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids. Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J Clin Invest 102:274–282
Welle S, Bhatt K, Thornton C (1996) Polyadenylated RNA, Actin mRNA, and myosin heavy chain mRNA in young and old human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 270:E224–E229
Wempe JB et al (1992) Blood eosinophil numbers and activity during 24 hours: effects of treatment with budesonide and bambuterol. J Allergy Clin Immunol 90:757–765
Woodruff-Pak DS (1988) Psychology and aging. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Yeh JY, Ou BR, Forsberg NE (1994) Effects of dexamethasone on muscle protein homeostasis and on calpain and calpastatin activities and gene expression in rabbits. J Endocrinol 141:209–217
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. M. P. Mattson, National Institute of Ageing, Baltimore, MD, USA and Dr. Karl Riabowol, Dept. of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and Oncology, Calgary University, Canada for critical reading and comments. The authors also like to acknowledge those of KUBIOTECH/MagBiotech group who supplied us hundreds of article on aging, GCs and psychological stress.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, K.M.M., Rahman, M.S., Arif, K.M.T. et al. Psychological stress and aging: role of glucocorticoids (GCs). AGE 34, 1421–1433 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-011-9319-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-011-9319-0