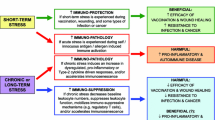
Both aging processes and psychological stress affect the immune system: Each can dysregulate immune function with a potentially substantial impact on physical health. Worse, the effects of stress and age are interactive. Psychological stress can both mimic and exacerbate the effects of aging, with older adults often showing greater immunological impairment to stress than younger adults. In addition, stressful experiences very early in life can alter the responsiveness of the nervous system and immune system. We review the unique impact of aging and stress on immune function, followed by evidence of interactions between age and stress. Further, we suggest that prenatal or early life stress may increase the likelihood of maladaptive immune responses to stress in late life. An understanding of the interactive effects of stress and age is critical to efforts to determine underlying mechanisms, clarify the directionality of effects, and develop effective interventions in early and late life.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ballou, S. P., Lozanski, F. B., Hodder, S., Rzewnicki, D. L., Mion, L. C., Sipe, J. D., Ford, A. B., and Kushner, I. (1996). Quantitative and qualitative alterations of acute-phase proteins in healthy elderly persons. Age Ageing 25: 224–230.
Ballow, M., Cates, K. L., Rowe, J. C., Goetz, C., and Desbonnet, C. (1986). Development of the immune system in very low birth weight (less than 1500g) premature infants: Concentrations of plasma immunoglobulins and patterns of infection. Pediatr. Res. 20: 899–904.
Barker, D. J. P. (1998). In utero programming of chronic disease. Clinical Science 95: 115–128.
Berczi, I. (1998). The stress concept and neuroimmunoregulation in modern biology. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 851: 3–12.
Black, P. H. (2003). The inflammatory response is an integral part of the stress response: Implications for atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome X. Brain. Behav. Immun. 17: 350–364.
Bodnar, J., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (1994). Caregiver depression after bereavement: Chronic stress isn't over when it's over. Psychol Aging 9: 372–380.
Burns, E. A., and Goodwin, J. S. (1990). Immunology and infectious disease. In Cassel, C. K., Riesenberg, D. E., and Sorensen, L. B. (Eds.), Geriatric Med., Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 312–329.
Burns, E. A., and Goodwin, J. S. (1997). Immunodeficiency of aging. Drugs Aging 11: 374–397.
Capitanio, J. P., and Lerche, N. W. (1991). Psychosocial factors and disease progression in simian AIDS: A preliminary report. AIDS 5: 1103–1106.
Carrion, V. G., Weems, C. F., Ray, R. D., Glaser, B., Hessl, D., and Reiss, A. L. (2002). Diurnal salivary cortisol in pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 51: 575–582.
Castle, S. C. (2000). Clinical relevance of age-related immune dysfunction. Clinical Infectious Diseases 31: 578–585.
Cesari, M., Penninx, B. W. J. H., Pahor, M., Lauretani, F., Corsi, A. M., Williams, G. R., Guralnik, J. M., and Ferrucci, L. (2004). Inflammatory markers and physical performance in older persons: The InCHIANTI Study. J. Gerontol. 59A: 242–248.
Coe, C. L., and Crispen, H. R. (2000). Social stress in pregnant monkeys differentially affects placental transfer of maternal antibody to male and female infants. Health Psychol. 19: 1–6.
Coe, C. L., Kramer, M. S., Kirschbaum, C., Netter, P., and Fuchs, E. (2002). Prenatal stress diminishes the cytokine response of leukocytes to endotoxin stimulation in juvenile rhesus monkeys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87: 675–681.
Coe, C. L., and Lubach, G. R. (2005). Prenatal origins of individual variation in behavior and immunity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 29: 39–49.
Coe, C. L., Lubach, G. R., Schneider, M. L., Dierschker, D. J., and Ershler, W. B. (1992). Early rearing conditions alter immune responses in the developing infant primate. Pediatrics 90: 505–509.
Cohen, S. (2005). Keynote Presentation at the Eight International Congress of Behavioral Medicine: The Pittsburgh Common Cold Studies: Psychosocial Predictors of Susceptibility to Respiratory Infectious Illness. Int. J. Behav. Med. 12: 123–131.
Cohen, S., Tyrrell, D. A., and Smith, A. P. (1991). Psychological stress and susceptibility to the common cold. N. Engl. J. Med. 325: 606–612.
Copper, R. L., Goldenberg, R. L., Elder, N., Swain, M., Norman, G., Ramsey, R., Cotroneo, P., Collins, B. A., Johnson, F., Jones, P., and Meier, A. M. (1996). The preterm prediction study: Maternal stress is associated with spontaneous preterm birth at less than thirty-five weeks’ gestation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 175: 1286–1292.
Cuschieri, R. J., Morran, C. G., Howie, J. C., and McArdle, C. S. (1985). Postoperative pain and pulmonary complications: Comparison of three analgesic regimens. Br. J. Surg. 72: 495–498.
Deinzer, R., Forster, P., Fuck, L., Herforth, A., Stiller-Winkler, R., and Idel, H. (1999). Increase of crevicular interleukin 1beta under academic stress at experimental gingivitis sites and at sites of perfect oral hygiene. J. Clin. Periodontol. 26: 1–8.
Dobbin, J. P., Harth, M., McCain, G. A., Martin, R. A., and Cousin, K. (1991). Cytokine production and lymphocyte transformation during stress. Brain. Behav. Immun. 5: 339–348.
Dole, N., Savitz, D. A., Hertz-Picciotto, I., Siega-Riz, A. M., McMahon, M. J., and Buekens, P. (2003). Maternal stress and preterm birth. Am. J. Epidemiol. 157: 14–24.
Ell, K. (1996). Social networks, social support and coping with serious illness: The family connection. Soc. Sci. Med. 42: 173–183.
Engler, H., and Stefanski, V. (2003). Social stress and T cell maturation in male rats: transient and persistent alterations in thymic function. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28: 951–969.
Epel, E. S., Blackburn, E. H., Lin, J., Dhabhar, F. S., Adler, N. E., Morrow, J. D., and Cawthon, R. M. (2004). Accelerated telomere shortening in response to life stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101: 17312–17315.
Ershler, W. B. (1993). Interleukin-6: A cytokine for gerontolgists. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 41: 176–181.
Esterling, B. A., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Bodnar, J., and Glaser, R. (1994). Chronic stress, social support, and persistent alterations in the natural killer cell response to cytokines in older adults. Health Psychol. 13: 291–299.
Esterling, B. A., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., and Glaser, R. (1996). Psychosocial modulation of cytokine-induced natural killer cell activity in older adults. Psychosom. Med. 58: 264–272.
Ferrucci, L., Corsi, A., Lauretani, F., Bandinelli, B., Taub, D. D., Guralnik, J. M., and Longo, D. L. (2005). The origins of age-related proinflammatory state. Blood 105: 2294–2299.
Ferrucci, L., Guralnik, J. M., Studenski, S., Fried, L. P., Cutler, G. B., and Walston, J. D. (2004). Designing randomized, controlled trials aimed at preventing or delaying functional decline and disability in frail, older persons: A consensus report. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 52: 625–634.
Franceschi, C., Bonafe, M., Valensin, S., Olivieri, F., De Luca, M., Ottaviani, E., and De Benedictis, G. (2000). Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 908: 244–254.
Francis, D., Diorio, J., Plotsky, P. M., and Meaney, M. J. (2002). Environmental enrichment reverses the effects of maternal separation on stress reactivity. J. Neurosci. 22: 7840–7843.
Gerra, G., Monti, D., Panerai, A. E., Sacerdote, P., Anderlini, R., Avanzini, P., Zaimovic, A., Brambilla, F., and Franceschi, C. (2003). Long-term immune-endocrine effects of bereavement: Relationships with anxiety levels and mood. Psychiatry Res. 121: 145–158.
Glaser, R., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (2005). Stress-induced immune dysfunction: Implications for health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5: 243–251.
Glaser, R., Sheridan, J. F., Malarkey, W. B., MacCallum, R. C., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (2000). Chronic stress modulates the immune response to a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. Psychosom. Med. 62: 804–807.
Gomez, C. R., Boehmer, E. D., and Kovacs, E. J. (2005). The aging innate immune system. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 17: 457–62.
Graham, J. E., Christian, L. M., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (in press-a). Close relationships and immunity. In Ader, R. (Ed.) Psychoneuroimmunology, Elsevier, Inc., Burlington, MA.
Graham, J. E., Christian, L. M., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (in press-b). Marriage, health, and immune function: A review of key findings and the role of depression. In Beach, S., and Wamboldt, M. (Eds.), Relational Processes in Mental Health, American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., Arlington, VA.
Graham, J. E., Robles, T. F., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Malarkey, W. B., Bissell, M. G., and Glaser, R. (in press-c). Hostility and pain are related to serum CRP levels in older adults. Brain. Behav. Immun.
Gunnar, M., Morison, S. J., Chisholm, K., and Schuder, M. (2001). Salivary cortisol levels in children adopted from Romanian orphanages. Dev. Psychopathol. 13: 611–628.
Hall, M., and Irwin, M. (2001). Physiological indices of functioning in bereavement. In Stroebe, M. S., Hansson, R. O., and Stroebeet, W. (Eds.), Handbook of Bereavement Research, American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp. 473–492.
Harper, S. A., Fukuda, K., Uyeki, T. M., Cox, N. J., and Bridges, C. B. (2005). Prevention and control of influenza: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). M.M.W.R. 54: 1–40.
Harris, T., Ferrucci, L., Tracy, R., Corti, M., Wacholder, S., Ettinger, W. J., Heimovitz, H., Cohen, H., and Wallace, R. (1999). Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am. J. Med. 106: 506–512.
Hawkley, L. C., and Cacioppo, J. T. (2004). Stress and the aging immune system. Brain. Behav. Immun. 18: 114–119.
Heffner, K. L., Loving, T. J., Robles, T. F., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (2003). Examining psychosocial factors related to cancer incidence and progression: In search of the silver lining. Brain. Behav. Immun. 17: S109–S111.
Heim, C., Newport, D. J., Heit, S., Graham, Y. P., Wilcox, M., Bonsall, R., Miller, A. H., and Nemeroff, C. B. (2000). Pituitary-adrenal and autonomic responses to stress in women after sexual and physical abuse. J.A.M.A. 284: 592–597.
Herbert, T. B., and Cohen, S. (1993). Depression and immunity: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 113: 472–486.
Irwin, M., Daniels, M., Smith, T. L., Bloom, E., and Weiner, H. (1987). Impaired natural killer cell activity during bereavement. Brain. Behav. Immun. 1: 98–104.
Johnston, M. (1988). Impending surgery. In Fisher, S., and Reason, J. (Eds.), Handbook of life stress, cognition and health, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 79–100.
Kang, D. H., Coe, C. L., McCarthy, D. O., and Ershler, W. B. (1997). Immune responses to final exams in healthy and asthmatic adolescents. Nurs. Res. 46: 12–19.
Kay, G., Tarcic, N., Poltyrev, T., and Weinstock, M. (1998). Prenatal stress depresses immune function in rats. Physiol. Behav. 63: 397–402.
Keller, S. E., Schleifer, S. J., Bartlett, J. A., Shiflett, S. C., and Rameshwar, P. (2000). Stress, depression, immunity, and health. In Goodkin, K., and Visser, A. P. (Eds.), Psychoneuroimmunology: Stress, mental disorders, and health, American Psychatric Press, Washington, D.C., pp. 1–25.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (1999). Norman Cousins Memorial Lecture 1998. Stress, personal relationships, and immune function: Health implications. Brain. Behav. Immun. 13: 61–72.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., and Glaser, R. (1991). Stress and immune function in humans. In Ader, R., Felten, D., and Cohen, N. (Eds.), Psychoneuroimmunology II, Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 849–867.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., and Glaser, R. (2001). Stress and immunity: Age enhances the risks. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 10: 18–21.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Glaser, R., Cacioppo, J. T., MacCallum, R. C., Snydersmith, M., Kim, C., and Malarkey, W. B. (1997). Marital conflict in older adults: Endocrinological and immunological correlates. Psychosom. Med. 59: 339–349.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Glaser, R., Gravenstein, S., Malarkey, W. B., and Sheridan, J. (1996). Chronic stress alters the immune response to influenza virus vaccine in older adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93: 3043–3047.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Loving, T. J., Stowell, J. R., Malarkey, W. B., Lemeshow, S., Dickinson, S. L., and Glaser, R. (2005). Hostile marital interactions, proinflammatory cytokine production, and wound healing. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 62: 1377–1384.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Malarkey, W. B., Chee, M., Newton, T., Cacioppo, J. T., Mao, H., and Glaser, R. (1993). Negative behavior during marital conflict is associated with immunological down-regulation. Psychosom. Med. 55: 395–409.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Marucha, P. T., Malarkey, W. B., Mercado, A. M., and Glaser, R. (1995). Slowing of wound healing by psychological stress. Lancet 346: 1194–1196.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., and Newton, T. (2001). Marriage and health: His and hers. Psychol. Bull. 127: 472–503.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Page, G. G., Marucha, P. T., MacCallum, R. C., and Glaser, R. (1998). Psychological influences on surgical recovery: Perspectives from psychoneuroimmunology. Am. Psychol. 53: 1209–1218.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Preacher, K. J., MacCallum, R. C., Atkinson, C., Malarkey, W. B., and Glaser, R. (2003). Chronic stress and age-related increases in the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100: 9090–9095.
Krabbe, K. S., Pedersen, M., and Bruunsgaard, H. (2004). Inflammatory mediators in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 39: 687–699.
Lawlor, D. A., Ronalds, G., Clark, H., Davey Smith, G., and Leon, D. A. (2005). Birth weight is inversely associated with incident coronary heart disease and stroke among individuals born in the 1950s: Findings from the Aberdeen children of the 1950s prospective cohort study. Circulation 112: 1414–1418.
Linn, B. S., and Jensen, J. (1983). Age and immune response to a surgical stress. Arch. Surg.118: 405–409.
Linn, B. S., Linn, M. W., and Klimas, N. G. (1988). Effects of psychophysical stress on surgical outcome. Psychosom. Med. 50: 230–244.
Lobel, M., DeVincent, C. J., Kaminer, A., and Meyer, B. A. (2000). The impact of prenatal maternal stress and optimistic disposition on birth outcomes in medically high-risk women. Health Psychol. 19: 544–553.
Lord, J. M., Butcher, S., Killampali, V., Lascelles, D., and Salmon, M. (2001). Neutrophil ageing and immunesenescence. Mech. Ageing Dev. 122: 1521–1535.
Lubach, G. R., Coe, C. L., and Ershler, W. B. (1995). Effects of the early rearing environment on immune responses of the infant rhesus monkey. Brain. Behav. Immun. 9: 31–46.
Lucas, A. D. (1991). Programming by early nutrition in man. In Bock, G. R., and Whelen, J. (Eds.), Environment and Adult Disease, Wiley, Chichester, pp. 38–55.
Lucas, A. D., Barker, B. A., Desal, M., and Hales, C. N. (1996). Nutrition in pregnant or lactating rats programs lipid metabolism in offspring. Br. J. Nutr.76: 605–612.
Lucas, A. D., Fewtrell, M. S., and Cole, T. J. (1999). Fetal origins of adult disease-the hypothesis revisited. Br. Med. J. 319: 245–249.
Lutgendorf, S. K., and Costanzo, E. S. (2003). Psychoneuroimmunology and health psychology: an integrative model. Brain. Behav. Immun. 17: 225–232.
Lutgendorf, S. K., Garand, L., Buckwalter, K. C., Reimer, T. T., Hong, S., and Lubaroff, D. M. (1999). Life stress, mood disturbance, and elevated interleukin-6 in healthy older women. J. Gerontol. B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 54: M434–39.
Lutgendorf, S. K., Logan, H., Costanzo, E., and Lubaroff, D. (2004). Effects of acute stress, relaxation, and a neurogenic inflammatory stimulus on interleukin-6 in humans. Brain. Behav. Immun. 18: 55–64.
Maes, M., Song, C., Lin, A., De, J. R., Van, G. A., Kenis, G., Bosmans, E., De, M. I., Benoy, I., Neels, H., Demedts, P., Janca, A., Scharpe, S., and Smith, R. (1998). The effects of psychological stress on humans: Increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a Th1-like response in stress-induced anxiety. Cytokine 10: 313–318.
Maes, M., Van Gastel, A., Delmeire, L., Kenis, G., Bosmans, E., and Song, C. (2002). Platelet alpha2-adrenoceptor density in humans: relationships to stress-induced anxiety, psychasthenic constitution, gender and stress-induced changes in the inflammatory response system. Psychol. Med. 32: 919–928.
Malarkey, W., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Pearl, D., and Glaser, R. (1994). Hostile behavior during marital conflict alters pituitary and adrenal hormones. Psychosom. Med. 56: 41–51.
Margolin, G., Burman, B., and John, R. S. (1989). Home observations of married couples reenacting naturalistic conflicts. Behav. Assess. 11: 101–118.
Marshall, G. D. J., Agarwal, S. K., Lloyd, C., Cohen, L., Henninger, E. M., and Morris, G. J. (1998). Cytokine dysregulation associated with exam stress in healthy medical students. Brain. Behav. Immun. 12: 297–307.
Marucha, P. T., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., and Favagehi, M. (1998). Mucosal wound healing is impaired by examination stress. Psychosom. Med. 60: 362–365.
Marucha, P. T., Sheridan, J. F., and Padgett, D. (2001). Stress and Wound Healing. In Ader, R., and Cohen, N. (Eds.), Psychoneuroimmunology, Academic Press, New York, pp. 613-626.
Mathews, A., and Ridgeway, V. (1981). Personality and surgical recovery: A review. Brit. J. Clin. Psychol. 20: 243–260.
Mayne, T. J., O’Leary, A., McCrady, B., Contrada, R., and Labouvie, E. (1997). The differential effects of acute marital distress on emotional, physiological and immune functions in maritally distressed men and women. Psychol. Health 12: 277–288.
McCance, R. A. (1962). Food, growth, and time. Lancet 27: 1–2.
McDade, T. W., Beck, M. A., Kuzawa, C., and Adair, L. S. (2001). Prenatal undernutrition, postnatal environments, and antibody response to vaccination in adolescence. The Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 74: 543–548.
McGuire, L., Heffner, K. L., Glaser, R., Needleman, B., Malarkey, W. B., Dickinson, S., Lemeshow, S., Cook, C., Muscarella, P., Melvin, S., Ellison, C., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (in press). Pain and wound healing in surgical patients. Ann. Behav. Med.
Miller, R. A. (1996). The aging immune system: Primer and prospectus. Science 273: 70–74.
Murasko, D. M., Weiner, P., and Kaye, D. (1987). Decline in mitogen induced proliferation of lymphocytes with increasing age. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 70: 440-448.
Nachmias, M., Gunnar, M. R., Mangelsdorf, S., Parritz, R., and Buss, K. A. (1996). Behavioral inhibition and stress reactivity: Moderating role of attachment security. Child Dev. 67: 508–522.
Nordentoft, M., Lou, H. C., Hansen, D., Nim, J., Pryds, O., Rubin, P., and Hemmingsen, R. (1996). Intrauterne growth retardation and premature delivery: the influence of maternal smoking and psychosocial factors. Am. J. Public Health 86: 347–354.
Otte, C., Neylan, T. C., Pole, N., Metzler, T., Best, S., Henn-Haase, C., Yehuda, R., and Marmar, C. R. (2005). Association between childhood trauma and catecholamine reponse to psychological stress in police academy recruits. Biol. Psychiatry 57: 27–32.
Page, G. G. (2005a). Immunologic effects of opioids in the presence or absence of pain. J. Pain Symptom Manage. 29: 25–31.
Page, G. G. (2005b). Surgery-induced immunosuppression and postopeative pain management. AACN Clin. Issues Crit. Care Nurs. 16: 302–309.
Page, G. G., Blakely, W. P., and Ben-Eliyahu, S. (2001). Evidence that postoperative pain is a mediator of the tumor-promoting effects of surgery in rats. Pain 90: 191–199.
Parham, P. (2005). The Immune System, Second Edition. Garland Science Publishing, New York.
Pasqualucci, A., Contardo, R., Da Broi, U., Colo, F., Terrosu, D. A., Sorrentino, M., Pasetto, A., and Bresadola, F. (1994). The effects of intraperitoneal local anesthetic on analgesic requirements and endocrine response after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A randomized double-blind controlled study. J. Laparoendosc. Surg. 4: 405–412.
Pearson, T. A., Mensah, G. A., Alexander, R. W., Anderson, J. L., Cannon, R. O. III, Criqui, M., Fadl, Y. Y., Fortmann, S. P., Hong, Y., Myers, G. L., Rifai, N., Smith, S. C.Jr, Taubert, K., Tracy, R. P., and Vinicor, F. (2003). Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: Application to clinical and public health practice: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation 107: 499–511.
Pezzone, M. A., Dohanics, J., and Rabin, B. S. (1994). Effects of footshock stress upon spleen and peripheral blood lymphocyte mitogenic responses in rats with lesions of the paraventricular nucleus. J. Neuroimmunol. 53: 39–46.
Pradhan, A. D., Manson, J. E., Rifai, N., Buring, J. E., and Ridker, P. M. (2001). C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. J.A.M.A. 286: 327–334.
Rabin, B. S. (1999). Stress, immune function, and health: The connection. Wiley-Liss & Sons, New York.
Repetti, R. L., Taylor, S. E., and Seeman, T. E. (2002). Risky families: family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychol. Bull. 128: 330–366.
Reyes, T. M., and Coe, C. L. (1997). Prenatal manipulations reduce the pro-inflammatory response to a cytokine challenge in juvenile monkeys. Brain Res.769: 29–35.
Rich-Edwards, J. W., Colditz, G. A., Stampfer, M. J., Willett, W. C., Gillman, M. W., Hennekens, C. H., Speizer, F. E., and Manson, J. E. (1999). Birthweight and the risk for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in adult women. Ann. Intern. Med. 130: 278–284.
Ridker, P., Rifai, N., Stampfer, M., and Hennekens, C. (2000). Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 101: 1767–1772.
Ridker, P. M. (2003). High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and cardiovascular risk: rationale for screening and primary prevention. Am. J. Cardiol. 92: 17K–22K.
Robles, T. F., Graham, J. E., Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Malarkey, W. B., Bissell, M. G., and Glaser, R. (under review). Chronic stress and elevated inflammatory markers contribute to poorer health-related quality-of-life in older adults.
Roubenoff, R., Harris, T. B., Abad, L. W., Wilson, P. W. F., Dallal, G. E., and Dinarello, C. A. (1998). Monocyte cyokine production in an elderly population: Effect of age and inflammation. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 53: M20–M26.
Sapolsky, R. M., Krey, L. C., and McEwen, B. S. (1986). The neuroendocrinology of stress and aging: The glucocorticoid cascade hypothesis. Endocr. Revs. 7: 284–301.
Schleifer, S., Keller, S., Camerino, M., Thorton, J. C., and Stein, M. (1983). Suppression of lymphocyte stimulation following bereavement. J.A.M.A. 250: 374–377.
Segerstrom, S. C., and Miller, G. E. (2004). Psychological stress and the human immune system: A meta-analytic study of 30 years of inquiry. Psychol. Bull. 130: 1–37.
Shavit, Y., Terman, G. W., Lewis, J. W., Zane, C. A., and al, e. (1986). Effects of footshock stress and morphine on natural killer lymphocytes in rats: Studies of tolerance and cross-tolerance. Brain Res. 372: 382–385.
Singer, A. J., and Clark, R. A. (1999). Cutaneous wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 341: 738–746.
Solomon, G. F., and Morley, J. E. (2001). Psychoneuroimmunology and Aging. In Ader, R., Felten, D. L., and Cohen, N. (Eds.), Psychoneuroimmunology, Third Edition, Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 701–713.
Vedhara, K., Cox, N. K. M., Wilcock, G. K., Perks, P., Hunt, M., Anderson, S., Lightman, S. L., and Shanks, N. M. (1999). Chronic stress in elderly carers of dementia patients and antibody response to influenza vaccination. Lancet 353: 627–631.
von Kanel, R., Dimsdale, J. E., Adler, K. A., Patterson, T. L., Mills, P. J., and Grant, I. (2005). Exaggerated plasma fibrin formation (D-dimer) in elderly Alzheimer caregivers as compared to noncaregiving controls. Gerontology 51: 7–13.
Wadhwa, P. D., Sandman, C. A., Porto, M., Dunkel-Schetter, C., and Garite, T. J. (1993). The association between prenatal stress and infant birth weight and gestational age at birth: a prospective study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 169: 858–865.
Watkins, L. R., and Maier, S. F. (2003). When good pain turns bad. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 12: 232–236.
Weinstock, M. (2005). The potential influence of maternal stress hormones on development and mental health of offspring. Brain. Behav. Immun. 19: 296–308.
Wust, S., Entringer, S., Federenko, I. S., Schlotz, W., and Hellhammer, D. H. (2005). Birth weight is associated with salivary cortisol responses to psychosocial stress in adult life. Psychoneuroendocrinology 30: 591–598.
Yoshikawa, T. T. (1983). Geriatric infectious diseases: An emerging problem. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 31: 34–39.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Work on this manuscript was supported by grants T32AI55411, AT002971, CA100243, AT002122, M01-RR-0034 and CA16058 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, J.E., Christian, L.M. & Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, Age, and Immune Function: Toward a Lifespan Approach. J Behav Med 29, 389–400 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-006-9057-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-006-9057-4