Abstract
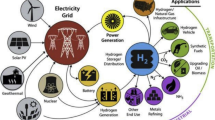
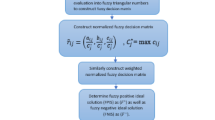
Due to its various advantages in different industrial fields, hydrogen can provide energy based on sustainability goals and recreates a critical function in the economy of countries. In this regard, evaluating hydrogen production technologies on an industrial scale is necessary for industrial development and economic growth. Therefore, this study proposes a comprehensive, integrated framework of hybrid fuzzy decision-making for assessing hydrogen production technologies in Iran. In addition to considering sustainability factors, political, technical, and reliability indicators are also assessed in this research to make a comprehensive assessment. The Fuzzy Step-wise Weight Assessment Ratio Analysis (F-SWARA) technique determines the importance of indicators, and the Fuzzy Weighted Aggregates Sum-Product Assessment (F-WASPAS) approach ranks technologies. The weighing findings indicated that the sub-indices of investment cost, technical infrastructure development, and implementation costs were introduced as the most significant sub-indices with weights of 0.226, 0.151, and 0.126, respectively. The evaluation findings with the F-WASPAS method and comparative analysis with various decision-making methods revealed that electrolysis based on solar energy and electrolysis based on wind energy technologies had the highest preference. In this regard, the infrastructure and costs of hydrogen production can be improved by presenting various incentives, such as improving financial conditions while attracting investment and increasing cooperation with top companies. So, sustainable development, economic growth, and industrial development are provided.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- F-ARAS:
-
Fuzzy Additive Ratio Assessment
- F-CoCoSo:
-
Fuzzy Combined Compromise Solution
- F-SWARA:
-
Fuzzy Step-wise Weight Assessment Ratio Analysis
- F-TOPSIS:
-
Fuzzy Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution
- F-WASPAS:
-
Fuzzy Weighted Aggregates Sum-Product Assessment
- MCDM:
-
Multi-criteria decision-making
- \({P}_{i}\) :
-
The crisp relative importance of option i based on the WPM model
- \({\widetilde{P}}_{i}\) :
-
The fuzzy relative importance of option i based on the WPM model
- \({Q}_{i}\) :
-
The crisp relative importance of option i based on the WSM model
- \({\widetilde{Q}}_{i}\) :
-
The fuzzy relative importance of option i based on the WSM model
- \(\widetilde{{q}_{j}}\) :
-
The fuzzy value of the initial significance of the factor j
- \({\tilde{w}}_{j}\) :
-
The fuzzy value of the final significances of the factor j
- \({WPS}_{i}\) :
-
The crisp score of option i
- \({\widetilde{x}}_{ij}\) :
-
The fuzzy value for alternative i in factor j
- \({\widetilde{\overline{x}} }_{ij}\) :
-
The normalized fuzzy value for alternative i in factor j
- \({\widetilde{\widehat{X}}}_{q}\) :
-
The matrix of the WSM model
- \({\widetilde{\widehat{X}}}_{p}\) :
-
The matrix of the WPM model
- \(\theta\) :
-
Interactive variable for exchange between WSM and WPM models
References
Abdel-Basset M, Gamal A, Chakrabortty RK, Ryan MJ (2021) Evaluation of sustainable hydrogen production options using an advanced hybrid MCDM approach: a case study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:4567–4591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.232
Acar C, Beskese A, Temur GT (2018) Sustainability analysis of different hydrogen production options using hesitant fuzzy AHP. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:18059–18076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.08.024
Alamri FS, Saeed MH, Saeed M (2024) A hybrid entropy-based economic evaluation of hydrogen generation techniques using multi-criteria decision making. Int J Hydrogen Energy 49:711–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.10.324
Almutairi K, Hosseini Dehshiri SS, Hosseini Dehshiri SJ et al (2022) An economic investigation of the wind-hydrogen projects: a case study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:25880–25898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.070
Arsad SR, Ker PJ, Hannan MA et al (2024) Patent landscape review of hydrogen production methods: assessing technological updates and innovations. Int J Hydrogen Energy 50:447–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.09.085
Aziz G, Sarwar S, Khan MS, Waheed R (2024) The prospect of green hydrogen in Saudi Arabia: an overview of theoretical and empirical approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 31:6597–6609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31301-1
Chang PL, Hsu CW, Chang PC (2011) Fuzzy Delphi method for evaluating hydrogen production technologies. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:14172–14179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.05.045
d’Amore-Domenech R, Santiago Ó, Leo TJ (2020) Multicriteria analysis of seawater electrolysis technologies for green hydrogen production at sea. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 133:110166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110166
Dehshiri SJ, Amiri M, Mostafaeipour A, Le T (2024) Evaluation of renewable energy projects based on sustainability goals using a hybrid pythagorean fuzzy-based decision approach. Energy 297:131272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2024.131272
Dhumras H, Bajaj RK (2024) On potential strategic framework for green supply chain management in the energy sector using q-rung picture fuzzy AHP & WASPAS decision-making model. Expert Syst Appl 237:121550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121550
Dumrul C, Bilgili F, Zarali F et al (2024) The evaluation of renewable energy alternatives in Turkey using intuitionistic-fuzzy EDAS methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31:15503–15524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31816-7
Fetanat A, Tayebi M (2024) Sustainability and reliability-based hydrogen technologies prioritization for decarbonization in the oil refining industry: a decision support system under single-valued neutrosophic set. Int J Hydrogen Energy 52:765–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.08.229
Gorji AA, Martek I (2023) Renewable energy policy and deployment of renewable energy technologies: the role of resource curse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:91377–91395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28851-9
Heidary Dahooie J, Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Banaitis A, Binkytė-Vėlienė A (2020) Identifying and prioritizing cost reduction solutions in the supply chain by integrating value engineering and gray multi-criteria decision-making. Technol Econ Dev Econ 26:1311–1338. https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2020.13534
Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Amiri M (2023a) An integrated multi-criteria decision-making framework under uncertainty for evaluating sustainable hydrogen production strategies based on renewable energies in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:46058–46073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25489-5
Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Amiri M (2023b) Evaluating the risks of the internet of things in renewable energy systems using a hybrid fuzzy decision approach. Energy 285:129493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.129493
Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Amiri M (2024) Evaluation of blockchain implementation solutions in the sustainable supply chain: a novel hybrid decision approach based on Z-numbers. Expert Syst Appl 235:121123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121123
Hosseini Dehshiri SS, Hosseini Dehshiri SJ (2022) Locating wind farm for power and hydrogen production based on Geographic information system and multi-criteria decision making method: an application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:24569–24583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.03.083
Hosseini Dehshiri SS, Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Firoozabadi B (2023) Evaluation of using solar energy in Iran’s textile industry towards cleaner production: sustainable planning and feasibility analysis. J Clean Prod 421:138447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138447
Hosseini Dehshiri SJ, Amiri M, Hosseini Bamakan SM (2024) Evaluating the blockchain technology strategies for reducing renewable energy development risks using a novel integrated decision framework. Energy 289:129987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.129987
Kakavand A, Sayadi S, Tsatsaronis G, Behbahaninia A (2023) Techno-economic assessment of green hydrogen and ammonia production from wind and solar energy in Iran. Int J Hydrogen Energy 48:14170–14191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.285
Keršulienė V, Zavadskas EK, Turskis Z (2010) Selection of rational dispute resolution method by applying new step-wise weight assessment ratio analysis (Swara). J Bus Econ Manag 11:243–258. https://doi.org/10.3846/jbem.2010.12
Li W, Ren X, Ding S, Dong L (2020) A multi-criterion decision making for sustainability assessment of hydrogen production technologies based on objective grey relational analysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:34385–34395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.11.039
Luis F, Moncayo G (2021) Nature-inspired computing paradigms in systems: reliability, availability, maintainability, safety and cost (RAMS+C) and prognostics and health management (PHM). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2020-0-00587-6
Mostafaeipour A, Zarezade M, Khalifeh Soltani SR et al (2022) A conceptual new model for use of solar water heaters in hot and dry regions. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 49:101710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101710
Mostafaeipour A, Le T (2024) Evaluating strategies for developing renewable energies considering economic, social, and environmental aspects: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32612-7
Nasrabadi AM, Korpeh M (2023) Techno-economic analysis and optimization of a proposed solar-wind-driven multigeneration system; case study of Iran. Int J Hydrogen Energy 48:13343–13361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.283
Olabi AG, Abdelkareem MA, Mahmoud M et al (2024) Multiple-criteria decision-making for hydrogen production approaches based on economic, social, and environmental impacts. Int J Hydrogen Energy 52:854–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.10.293
Ourya I, Abderafi S (2023) Clean technology selection of hydrogen production on an industrial scale in Morocco. Results Eng 17:100815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100815
Pilavachi PA, Chatzipanagi AI, Spyropoulou AI (2009) Evaluation of hydrogen production methods using the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:5294–5303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.04.026
Ren J, Fedele A, Mason M et al (2013) Fuzzy multi-actor multi-criteria decision making for sustainability assessment of biomass-based technologies for hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:9111–9120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.05.074
Ren J, Gao S, Tan S et al (2015) Role prioritization of hydrogen production technologies for promoting hydrogen economy in the current state of China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:1217–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.028
Seker S, Aydin N (2022) Assessment of hydrogen production methods via integrated MCDM approach under uncertainty. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:3171–3184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.07.232
Singh T (2024) Entropy weighted WASPAS and MACBETH approaches for optimizing the performance of solar water heating system. Case Stud Therm Eng 53:103922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.103922
Statista Research Department (2023) Forecast market size of clean hydrogen worldwide from 2030 to 2050. In: Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1402050/global-market-size-of-clean-hydrogen/. Accessed 25 Aug 2023
Turskis Z, Zavadskas EK, Antucheviciene J, Kosareva N (2015) A hybrid model based on fuzzy AHP and fuzzy WASPAS for construction site selection. Int J Comput Commun Control 10:873–888. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2015.6.2078
Ulutaş A, Karakuş CB, Topal A (2020) Location selection for logistics center with fuzzy SWARA and CoCoSo methods. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 38:4693–4709. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-191400
Xu D, Li W, Ren X et al (2020) Technology selection for sustainable hydrogen production: a multi-criteria assessment framework under uncertainties based on the combined weights and interval best-worst projection method. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:34396–34411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.030
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8:338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X
Zavadskas EK, Turskis Z, Antucheviciene J, Zakarevicius A (2012) Optimization of weighted aggregated sum product assessment. Elektron Ir Elektrotechnika 122:3–6. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.eee.122.6.1810
Zhao H, Guo S (2014) Selecting green supplier of thermal power equipment by using a hybrid MCDM method for sustainability. Sustain 6:217–235. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6010217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, supervision, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, and writing—the original draft was done by Seyyed Jalaladdin Hosseini Dehshiri. Supervision, software, and resources were done by Ali Mostafaeipour. Validation and writing—review and editing were performed by Ttu Le and Ali Rezaeian Sabagh. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Seyyed Jalaladdin Hosseini Dehshiri and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini Dehshiri, S.J., Mostafaeipour, A., Le, T. et al. Evaluation of sustainable hydrogen production technologies on an industrial scale using comparative analysis of decision-making methods. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33535-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33535-z