Abstract
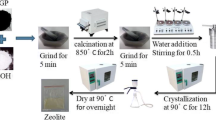
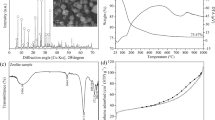
In this study, Tunisian raw clay (RC) was utilized as a cheap source of silicium and aluminum for the preparation of faujasite zeolite (FAUsyn) using the alkaline fusion technique. The zeolite’s structural analysis was carried out using the XRD, nitrogen adsorption–desorption, and SEM–EDX techniques. The data collected demonstrate that the produced zeolite only included one homogeneous faujasite phase. Textural analysis shows that the FAUsyn prepared from RC has a hierarchical porosity (micro-, meso-, and macropores). The total porosity was found to be 0.33 cm3/g as well as the BET area was equal to 360 m2/g. Adsorption experiments for propene capture were performed using the FAUsyn as adsorbent material. The performance of the column was examined in relation to various parameter impacts, including flow rate (50, 100, and 150 mL/min), input concentration (4, 8, and 12 mg/L), and bed depth (10, 14, and 18 cm). Finally, experimental and theoretical studies were investigated to predict adsorption capacities and kinetics parameters. To clarify and estimate column inputs, a model that incorporates axial dispersion, Langmuir equation, and migration within the adsorbent’s pore was improved. COMSOL Multiphysics software was used to execute the model and resolve it computationally. The results of the experiments and the expected breakthrough curves were very well agreed. Modeling obtained results can be extrapolated to industrial level.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are not available for public readers.
References
Aguilera PG, Gutiérrez Ortiz FJ (2016) Prediction of fixed-bed breakthrough curves for H2S adsorption from biogas: Importance of axial dispersion for design. Chem Eng J 289:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.075
Albright LF (2009) Albright’s chemical engineering handbook. CRC press, Boca Raton (Fla.)
Bayat M, Javanbakht V, Esmaili J (2018) Synthesis of zeolite/nickel ferrite/sodium alginate bionanocomposite via a co-precipitation technique for efficient removal of water-soluble methylene blue dye. Int J Biol Macromol 116:607–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.012
Buzanowski MA, Yang RT (1989) Extended linear driving-force approximation for intraparticle diffusion rate including short times. Chem Eng Sci 44:2683–2689. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(89)85211-X
Chahbani MH, Tondeur D (2010) Predicting the final pressure in the equalization step of PSA cycles. Sep Purif Technol 71:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.11.027
Chahbani MH (1996) Séparation de gaz par adsorption modulée en pression : modélisation des écoulements et de la cinétique de transfert de matière (phdthesis). Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine. https://hal.univ-lorraine.fr/tel-01751418
D’Alessandro DM, Smit B, Long JR (2010) Carbon dioxide capture: prospects for new materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6058–6082. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000431
Danckwerts PV (1953) Continuous flow systems. Chem Eng Sci 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(53)80001-1
Danish M, Ansari KB, Aftab RA, Danish M, Zaidi S, Trinh QT (2021) gPROMS-driven modeling and simulation of fixed bed adsorption of heavy metals on a biosorbent: benchmarking and case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13207-y
Das D, Gaur V, Verma N (2004) Removal of volatile organic compound by activated carbon fiber. Carbon 42:2949–2962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2004.07.008
Del Bubba M, Arias CA, Brix H (2003) Phosphorus adsorption maximum of sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds as measured by the Langmuir isotherm. Water Res 37:3390–3400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00231-8
Divekar S, Nanoti A, Dasgupta S, Aarti, Chauhan R, Gupta P, Garg MO, Singh SP, Mishra IM (2016) Adsorption equilibria of propylene and propane on zeolites and prediction of their binary adsorption with the ideal adsorbed solution theory. J Chem Eng Data 61:2629–2637. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.6b00294
Fakhfakh N, Dammak N, Benzina M (2018) Breakthrough modeling and experimental design for o-xylene dynamic adsorption onto clay material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:18263–18277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9386-6
Faraj SS, Alkizwini RS, Al Juboury MF (2020) Simulate permeable reactive barrier by using a COMSOL model and comparison with the Thomas, Yoon-Nelson and Clark models for CR dye remediation by composite adsorbent (sewage and waterworks sludge). Water Sci Technol 82:2902–2919. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.500
Farooq S, Qinglin H, Karimi IA (2002) Identification of transport mechanism in adsorbent micropores from column dynamics. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0104621
Feng M, Kou Z, Tang C, Shi Z, Tong Y, Zhang K (2023) Recent progress in synthesis of zeolite from natural clay. Appl Clay Sci 243:107087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2023.107087
Ferreira AFP, Santos JC, Plaza MG, Lamia N, Loureiro JM, Rodrigues AE (2011) Suitability of Cu-BTC extrudates for propane–propylene separation by adsorption processes. Chem Eng J 167:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.07.041
Finsy V, Ma L, Alaerts L, De Vos DE, Baron GV, Denayer JFM (2009) Separation of CO2/CH4 mixtures with the MIL-53(Al) metal–organic framework. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 120:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.11.007
Glueckauf E (1955) Theory of chromatography. Part 10.—Formulæ for diffusion into spheres and their application to chromatography. Trans Faraday Soc 51:1540–1551. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9555101540
Glueckauf E, Coates JI (1947) 241. Theory of chromatography. Part IV. The influence of incomplete equilibrium on the front boundary of chromatograms and on the effectiveness of separation. J Chem Soc Resumed 1315. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9470001315
Guillemot M, Mijoin J, Mignard S, Magnoux P (2007) Adsorption of tetrachloroethylene on cationic X and Y zeolites: influence of cation nature and of water vapor. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:4614–4620. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0616390
Hines AL, Maddox RN (1985) Mass transfer: fundamentals and applications, Prentice-Hall international series in the physical and chemical engineering sciences. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Ho CK, Webb SW (2006) Gas transport in porous media. The Netherlands Springer, Dordrecht
Hu Q, Li JJ, Hao ZP, Li LD, Qiao SZ (2009) Dynamic adsorption of volatile organic compounds on organofunctionalized SBA-15 materials. Chem Eng J 149:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.11.003
Huang Z-H, Kang F, Liang K-M, Hao J (2003) Breakthrough of methyethylketone and benzene vapors in activated carbon fiber beds. J Hazard Mater 98:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00284-4
Huang Y, Wang K, Dong D, Li D, Hill MR, Hill AJ, Wang H (2010) Synthesis of hierarchical porous zeolite NaY particles with controllable particle sizes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 127:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.07.026
Hwang KS, Jun JH, Lee WK (1995) Fixed-bed adsorption for bulk component system. Non-equilibrium, non-isothermal and non-adiabatic model. Chem Eng Sci 50:813–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(94)00433-R
Jin X, Malek A, Farooq S (2006) Production of argon from an oxygen−argon mixture by pressure swing adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:5775–5787. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060113c
Kargol M, Zajac J, Jones DJ, Rozière J (2005) Selectivity of gas phase adsorption of propene and propane onto mesoporous silica materials derivatised with Ag(I) and Cu(II) at low surface coverages: comparison between equilibrium adsorption and flow microcalorimetry studies. Thermochim Acta 434:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2005.01.003
Kim DJ, Wang J, Crocker M (2014) Adsorption and desorption of propene on a commercial Cu-SSZ-13 SCR catalyst. Catal Today 231:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2013.10.061
Krishna R, Wesselingh JA (1997) The Maxwell-Stefan approach to mass transfer. Chem Eng Sci 52:861–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(96)00458-7
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Leyva-Ramos R, Diaz-Flores PE, Leyva-Ramos J, Femat-Flores RA (2007) Kinetic modeling of pentachlorophenol adsorption from aqueous solution on activated carbon fibers. Carbon 45:2280–2289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.06.010
Ltaief OO, Siffert S, Fourmentin S, Benzina M (2015a) Synthesis of Faujasite type zeolite from low grade Tunisian clay for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous waste by batch process: Kinetic and equilibrium study. Comptes Rendus Chim 18:1123–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2015.03.013
Ltaief OO, Siffert S, Poupin C, Fourmentin S, Benzina M (2015b) Optimal synthesis of Faujasite-type zeolites with a hierarchical porosity from natural clay. Eur J Inorg Chem 2015:4658–4665. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201500537
Lua AC, Jia Q (2009) Adsorption of phenol by oil–palm-shell activated carbons in a fixed bed. Chem Eng J 150:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.034
Mastropietro TF, Brunetti A, Zito PF, Poerio T, Richter H, Weyd M, Wöhner S, Drioli E, Barbieri G (2015) Study of the separation properties of FAU membranes constituted by hierarchically assembled nanozeolites. Sep Purif Technol 156:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.10.018
Moate JR, LeVan MD (2010) Temperature swing adsorption compression: effects of nonuniform heating on bed efficiency. Appl Therm Eng 30:658–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2009.11.013
Moreno-Villoslada I (2003) Retention of metal ions in ultrafiltration of mixtures of divalent metal ions and water-soluble polymers at constant ionic strength based on Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. J Membr Sci 215:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(02)00613-0
Motazedi K, Mahinpey N, Karami D (2016) Preparation and application of Faujasite-type Y zeolite-based catalysts for coal pyrolysis using sodium silicate solution and colloidal silica as silicon source. Chem Eng Commun 203:300–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2014.996636
Mulgundmath VP, Tezel FH, Saatcioglu T, Golden TC (2012) Adsorption and separation of CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 by 13X zeolite. Can J Chem Eng 90:730–738. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20592
Novembre D, Di Sabatino B, Gimeno D, Garcia-Vallès M, Martínez-Manent S (2004) Synthesis of Na–X zeolites from tripolaceous deposits (Crotone, Italy) and volcanic zeolitised rocks (Vico volcano, Italy). Microporous Mesoporous Mater 75:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2004.06.022
Ottiger S, Pini R, Storti G, Mazzotti M (2008) Competitive adsorption equilibria of CO2 and CH4 on a dry coal. Adsorption 14:539–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9114-0
OuledLtaief O, Dammak N, Benzina M (2018) Fixed bed adsorption dynamics experimental study and modeling of C3H6 capture into Faujasite type zeolite. In: Kallel A, Ksibi M, Ben Dhia H, Khélifi N (eds) Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 183–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70548-4_60
Perry RH, Green DW (1998) Perry’s chemical engineers’ handbook. Choice Rev Online 35:35-3079–35-3079. https://doi.org/10.5860/CHOICE.35-3079
Peter SA, Baron GV, Gascon J, Kapteijn F, Denayer JFM (2013) Dynamic desorption of CO2 and CH4 from amino-MIL-53(Al) adsorbent. Adsorption 19:1235–1244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9564-x
Ray MS (2008) Diffusion in zeolites and other microporous solids, by J. Karger and D. M. Ruthven, John Wiley, New York, USA (1992). 605 pages. ISBN 0–47 1–50907–8. Dev Chem Eng Miner Process 4:254–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.5500040311
Reid RC, Prausnitz JM, Poling BE (1987) The properties of gases and liquids. McGraw-Hill, United States
Rutherford SW, Do DD (2000) Adsorption dynamics measured by permeation and batch adsorption methods. Chem Eng J 76:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(99)00111-4
Ruthven DM (1984) Principles of adsorption and adsorption processes, A Wiley-Interscience publication. Wiley, New York
Sausen MG, Scheufele FB, Alves HJ, Vieira MGA, Da Silva MGC, Borba FH, Borba CE (2018) Efficiency maximization of fixed-bed adsorption by applying hybrid statistical-phenomenological modeling. Sep Purif Technol 207:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.002
Serra-Crespo P, Berger R, Yang W, Gascon J, Kapteijn F (2015) Separation of CO 2 /CH 4 mixtures over NH 2 -MIL-53—an experimental and modelling study. Chem Eng Sci 124:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2014.10.028
Shafeeyan MS, Daud WMAW, Shamiri A, Aghamohammadi N (2015) Modeling of carbon dioxide adsorption onto ammonia-modified activated carbon: kinetic analysis and breakthrough behavior. Energy Fuels 29:6565–6577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00653
Skaf M, Aouad S, Hany S, Cousin R, Abi-Aad E, Aboukaïs A (2014) Physicochemical characterization and catalytic performance of 10% Ag/CeO 2 catalysts prepared by impregnation and deposition–precipitation. J Catal 320:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2014.10.006
Sulaymon AH, Yousif SA, Al-Faize MM (2014) Competitive biosorption of lead mercury chromium and arsenic ions onto activated sludge in fixed bed adsorber. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:325–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.06.034
Vermeiren W, Gilson J-P (2009) Impact of zeolites on the petroleum and petrochemical industry. Top Catal 52:1131–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9271-8
Wang Y, Jia X, Li L, Yang J, Li J (2022) Selective adsorption of propene over propane on Li-decorated poly (triazine imide). Green Energy Environ 7:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2020.10.001
Wehner JF, Wilhelm RH (1956) Boundary conditions of flow reactor. Chem Eng Sci 6:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(56)80014-6
Yaneva Z, Marinkovski M, Markovska L, Meshko V, Koumanova B (2008) Dynamic studies of nitrophenols sorption on perfil in a fixed-bed column. Maced. J Chem Chem Eng 27:123. https://doi.org/10.20450/mjcce.2008.232
Yang RT, Doong SJ (1985) Gas separation by pressure swing adsorption: a pore-diffusion model for bulk separation. AIChE J 31:1829–1842. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690311109
Ye P, Fang Z, Su B, Xing H, Yang Y, Su Y, Ren Q (2010) Adsorption of propylene and ethylene on 15 activated carbons. J Chem Eng Data 55:5669–5672. https://doi.org/10.1021/je100601n
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Nadim Fakhfakh, Olfa Ouled Ltaief, Nesrine Dammak, Stéphane Siffert, and Mourad Benzina. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Nadim Fakhfakh and Olfa Ouled Ltaief and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All authors assure that this material is their own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper properly credits the meaningful contributions of co-authors. Finally, all authors assume their whole ethical responsibilities in publishing this paper.
Consent to participate
All authors confirm their participation to the present work.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish the present paper in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Zeolite synthesized from raw Tunisian clay is an effective adsorbent for the treatment of C3H6 emissions.
• The results of structural characterization show that prepared zeolite presented only one phase of a pure faujasite type with a hierarchical porosity (trimodal macro-meso-microporous structure).
• Experimental breakthrough curves at different bed heights, flow rate and inlet C3H6concentrations were studied.
• A suitable adsorption model has been developed to simulate the measured data, based on the nature of the various equilibrium relationships solid-gas and diverse descriptions of the mass transfer processes within of the adsorbent particle.
• The experiments can be always reproduced by simulation with high correlation coefficients.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fakhfakh, N., Ltaief, O.O., Dammak, N. et al. New zeolite made from Tunisian raw clay: study and modeling for C3H6 breakthrough dynamic adsorption onto zeolite material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 29357–29373 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32970-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32970-2