Abstract
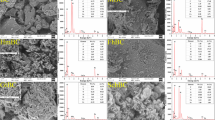
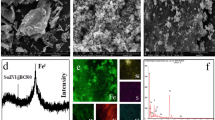
Since Cd(II) and As(III) have extremely opposite chemical characteristics, it is a huge challenging to simultaneously remove these two ions from aqueous solutions. Therefore, a novel iron sulfide-based porous biochar (FSB) was synthesized and used to evaluate its Cd(II) and As(III) removal performance and mechanisms. The characterization and batch experiments results indicated that FeS was successfully loaded on the surface of biochar and increased its adsorption sites. The iron sulfide-based porous biochar was very favorable for the removal of Cd(II) and As(III) in the weakly acidic environment. The maximum adsorption of Cd(II) and As(III) by FSB was 108.8 mg g−1 and 76.3 mg g−1, respectively, according to the Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption model, and the adsorption equilibrium time was 12 h and 4 h, respectively, according to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. In the coexisting ion system, Cd(II) adsorption was suppressed by Ca2+, Mg2+, and humic acid, but enhanced by PO43− and As(III). As(III) adsorption was inhibited by PO43− and humic acid. Precipitation and complexation are the predominant adsorption mechanisms of Cd(II) and As(III), which contribute to the formation of Cd-O, Fe-O-Cd, As-O, Fe-O-As, ternary complex Cd-Fe-As, and stable compounds FeAsO4·2H2O and CdS. Therefore, The iron sulfide-based porous biochar can be an efficient and environmentally friendly candidate for the treatment of Cd(II) and As(III) co-polluted irrigation water.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ai Y, Liu G, Wang H, Wu C, Liu W, Lin Z (2020) Role of sulfur atoms in the adsorption of antimony by greigite. Surfaces Interfaces 20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100584
Ainiwaer M, Zhang T, Zhang N, Yin X, Su S, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zeng X (2022) Synergistic removal of As(III) and Cd(II) by sepiolite-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron and a related mechanistic study. J Environ Manag 319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115658
Alchouron J, Navarathna C, Chludil HD, Dewage NB, Perez F, Hassan EB, Pittman CU Jr, Vega AS, Mlsna TE (2020) Assessing South American Guadua chacoensis bamboo biochar and Fe3O4 nanoparticle dispersed analogues for aqueous arsenic(V) remediation. Sci Total Environ 706:135943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135943
Bostick BC, Fendorf S (2003) Arsenite sorption on troilite (FeS) and pyrite (FeS2). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 67:909–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(02)01170-5
Chen YM, Dong YQ, Wu H, Chen CQ, Chi YW, Chen GN (2015) Electrochemiluminescence sensor for hexavalent chromium based on the graphene quantum dots/peroxodisulfate system. Electrochim Acta 151:552–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.068
Chen G, Wang H, Han L, Yang N, Hu B, Qiu M, Zhong X (2021) Highly efficient removal of U(VI) by a novel biochar supported with FeS nanoparticles and chitosan composites. J Mol Liquids 327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114807
Chen YJ, Lin QT, Wen XQ, He J, Luo HY, Zhong QF, Wu LB, Li JQ (2023) Simultaneous adsorption of As(III) and Pb(II) by the iron-sulfur codoped biochar composite: Competitive and synergistic effects. J Environ Sci 125:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2022.01.023
Fei YH, Hu YH (2022) Design, synthesis, and performance of adsorbents for heavy metal removal from wastewater: a review. J Mater Chem A 10:1047–1085. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta06612a
Gong Y, Tang J, Zhao D (2016) Application of iron sulfide particles for groundwater and soil remediation: A review. Water Res 89:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.063
He J, Tang J, Zhang Z, Wang L, Liu Q, Liu X (2021) Magnetic ball-milled FeS@biochar as persulfate activator for degradation of tetracycline. Chem Eng J 404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126997
Hong QF, Liu C, Wang ZB, Li RY, Liang XL, Wang YP, Zhang YT, Song ZL, Xiao ZH, Cui TY, Heng BB, Xu BB, Qi F, Ikhlaq A (2021) Electron transfer enhancing Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle by sulfur and biochar in magnetic FeS@biochar to active peroxymonosulfate for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation. Chem Eng J 417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129238
Impellitteri CA (2005) Effects of pH and phosphate on metal distribution with emphasis on As speciation and mobilization in soils from a lead smelting site. Sci Total Environ 345:175–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.10.024
Jiang W, Lv JT, Luo L, Yang K, Lin YF, Hu FB, Zhang J, Zhang SZ (2013) Arsenate and cadmium co-adsorption and co-precipitation on goethite. J Hazard Mater 262:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.030
Kavak D (2013) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by precipitation: statistical analysis and modeling. Desal Water Treat 51:1720–1726. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.714652
Kubier A, Wilkin RT, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in soils and groundwater: a review. Appl Geochem 108:104388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104388
Liu K, Li F, Cui J, Yang S, Fang L (2020) Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) by graphene-like biochar-supported zero-valent iron from irrigation waters under aerobic conditions: Synergistic effects and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122623
Liu K, Li FB, Zhao XL, Wang GY, Fang LP (2021) The overlooked role of carbonaceous supports in enhancing arsenite oxidation and removal by nZVI: Surface area versus electrochemical property. Chem Eng J 406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126851
Liu R, Zhang Y, Hu B, Wang H (2022) Improved Pb(II) removal in aqueous solution by sulfide@biochar and polysaccharose-FeS@ biochar composites: efficiencies and mechanisms. Chemosphere 287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132087
Lyu H, Tang J, Huang Y, Gai L, Zeng EY, Liber K, Gong Y (2017) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem Eng J 322:516–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.058
Lyu P, Li L, Huang X, Wang G, Zhu C (2022) Pre-magnetic bamboo biochar cross-linked CaMgAl layered double-hydroxide composite: high-efficiency removal of As(III) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions and insight into the mechanism of simultaneous purification. Sci Total Environ 823:153743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153743
Meng Q, Nan J, Wang ZB, Ji XY, Wu FM, Liu BH, Xiao QL (2019) Study on the efficiency of ultrafiltration technology in dealing with sudden cadmium pollution in surface water and ultrafiltration membrane fouling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16641–16651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04691-4
Min X, Li Y, Ke Y, Shi M, Chai L, Xue K (2017) Fe-FeS2 adsorbent prepared with iron powder and pyrite by facile ball milling and its application for arsenic removal. Water Sci Technol 76:192–200. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.204
Mladenov N, Zheng Y, Miller MP, Nemergut DR, Legg T, Simone B, Hageman C, Rahman MM, Ahmed KM, McKnight DM (2010) Dissolved organic matter sources and consequences for iron and arsenic mobilization in Bangladesh aquifers. Environ Sci Technol 44:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901472g
Navarathna CM, Karunanayake AG, Gunatilake SR, Pittman CU, Perez F, Mohan D, Mlsna T (2019) Removal of Arsenic(III) from water using magnetite precipitated onto Douglas fir biochar. J Environ Manag 250:109429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109429
Pan B, Qiu H, Pan B, Nie G, Xiao L, Lv L, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Zheng S (2010) Highly efficient removal of heavy metals by polymer-supported nanosized hydrated Fe(III) oxides: Behavior and XPS study. Water Res 44:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.10.027
Qiao Y, Wu J, Xu Y, Fang Z, Zheng L, Cheng W, Tsang EP, Fang J, Zhao D (2017) Remediation of cadmium in soil by biochar-supported iron phosphate nanoparticles. Ecol Eng 106:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.06.023
Qin L, He L, Yang W, Lin A (2020) Preparation of a novel iron-based biochar composite for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9214–9226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06954-6
Qiu YB, Ren LF, Shao JH, Xia L, Zhao Y (2022) An integrated separation technology for high fluoride-containing wastewater treatment: fluoride removal, membrane fouling behavior and control. J Cleaner Prod 349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131225
Qu JH, Wang YX, Tian X, Jiang Z, Deng FX, Tao Y, Jiang Q, Wang L, Zhang Y (2021) KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) and naphthalene from water: affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J Hazard Mater 401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123292
Qu J, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Tao Y, Jiang Z, Yu H, Dong M, Zhang Y (2022) Stabilization of lead and cadmium in soil by sulfur-iron functionalized biochar: performance, mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J Hazard Mater 425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127876
Renu, Agarwal M, Singh K (2017) Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: a review. J Water Reuse Desal 7:387–419. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.104
Singh P, Pal P, Mondal P, Saravanan G, Nagababu P, Majumdar S, Labhsetwar N, Bhowmick S (2021) Kinetics and mechanism of arsenic removal using sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chem Eng J 412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128667
Tian S, Gong Y, Ji H, Duan J, Zhao D (2020) Efficient removal and long-term sequestration of cadmium from aqueous solution using ferrous sulfide nanoparticles: Performance, mechanisms, and long-term stability. Sci Total Environ 704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135402
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Wan X, Li C, Parikh SJ (2020) Simultaneous removal of arsenic, cadmium, and lead from soil by iron-modified magnetic biochar. Environ Pollut 261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114157
Wang JL, Guo X (2020) Adsorption kinetic models: physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J Hazard Mater 390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122156
Wang Y, Wu X, Wang SF, Xiao F, Zhang DN, Yao SH, Jia YF (2018) The adsorption behavior of thioarsenite on magnetite and ferrous sulfide. Chem Geol 492:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.030
Wang Y, Zhu X, Feng D, Hodge AK, Hu L, Lü J, Li J (2019) Biochar-supported FeS/Fe3O4 composite for catalyzed fenton-type degradation of ciprofloxacin. Catalysts 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9121062
Wang G, Peng C, Tariq M, Lin S, Wan J, Liang W, Zhang W, Zhang L (2022a) Mechanistic insight and bifunctional study of a sulfide Fe3O4 coated biochar composite for efficient As(III) and Pb(II) immobilization in soils. Environ Pollut 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118587
Wang G, Peng C, Tariq M, Lin S, Wan J, Liang W, Zhang W, Zhang L (2022b) Mechanistic insight and bifunctional study of a sulfide Fe3O4 coated biochar composite for efficient As(III) and Pb(II) immobilization in soils. Environ Pollut 293:118587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118587
Wilson SC, Lockwood PV, Ashley PM, Tighe M (2010) The chemistry and behaviour of antimony in the soil environment with comparisons to arsenic: a critical review. Environ Pollut 158:1169–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.045
Wu S, He H, Inthapanya X, Yang C, Lu L, Zeng G, Han Z (2017) Role of biochar on composting of organic wastes and remediation of contaminated soils-a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 24:16560–16577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9168-1
Wu J, Huang D, Liu X, Meng J, Tang C, Xu J (2018) Remediation of As(III) and Cd(II) co-contamination and its mechanism in aqueous systems by a novel calcium-based magnetic biochar. J Hazard Mater 348:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.011
Wu C, Shi LZ, Xue SG, Li WC, Jiang XX, Rajendran M, Qian ZY (2019) Effect of sulfur-iron modified biochar on the available cadmium and bacterial community structure in contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 647:1158–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.087
Yang R, Wang Y, Li M, Hong YJ (2014) A new carbon/ferrous sulfide/iron composite prepared by an in situ carbonization reduction method from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) stems and its Cr(VI) removal ability. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 2:1270–1279. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500092z
Yang X, Zhang X, Wang Z, Li S, Zhao J, Liang G, Xie X (2019) Mechanistic insights into removal of norfloxacin from water using different natural iron ore–biochar composites: more rich free radicals derived from natural pyrite-biochar composites than hematite-biochar composites. Appl Catalysis B-Environ 255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117752
Yang D, Wang L, Li Z, Tang X, He M, Yang S, Liu X, Xu J (2020) Simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II) and As(III) by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Sci Total Environ 708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134823
Yang T, Xu Y, Huang Q, Sun Y, Liang X, Wang L, Qin X, Zhao L (2021a) Adsorption characteristics and the removal mechanism of two novel Fe-Zn composite modified biochar for Cd(II) in water. Bioresour Technol 333:125078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125078
Yang Y, Zhang YH, Wang GY, Yang ZBA, Xian JR, Yang YX, Li T, Pu YL, Jia YX, Li Y, Cheng Z, Zhang SR, Xu XX (2021b) Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) by a novel nanoscale FeS/chitosan/biochar composite from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105407
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, Wang P, Liu Y, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2016) Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Sci Technol 50:7290–7304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01897
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42007123 and 42007316), Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (2020GXNSFBA159026), Special Project of Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent (Guike AD19245181), Research funds of The Guangxi Key Laboratory of Theory and Technology for Environmental Pollution Control (1801K005), and Foundation of Guilin University of Technology (GLUTQD2017139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yuxi Lu: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing original draft. Hua Lin: formal analysis, investigation. Yanpeng Liang: formal analysis, investigation, resources. Mi Feng and Zijian Zhou: writing review and editing. Zihao Liang and Huawei Li: investigation, resources. Honghu Zeng and Gongning Chen: writing review and editing, conceptualization, resources, funding acquisition, supervision. And all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, ., Zeng, H., Lin, H. et al. Synergistic removal performance and mechanism of Cd(II) and As(III) from irrigation water by iron sulfide-based porous biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 11591–11604 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31932-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31932-y