Abstract
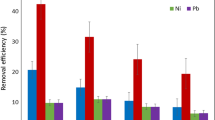
The coexistence of heavy metals and antibiotics in the environment always results in greater toxicity compared to the individual precursors. Therefore, efficient and economic technology for the simultaneous removal of antibiotics and heavy metals is essential. Herein, litchi leaves biochar carbonized at 550 °C (L550) demonstrated high efficiency in co-removal of CTC (1838.1 mmol/kg) and Cu (II) (1212.9 mmol/kg) within wide range of pH (pH 4–7). Ionic strength obviously enhanced the Cu (II) removal but showed no significant effect on CTC removal. Although Al3+ and HPO42− decreased the adsorption capacities of CTC and Cu (II) on L550, the coexistence of Na+, K+, Mg2+, Cl−, NO3−, CO32− and SO42− showed a negligible effect on the simultaneous removal of CTC and Cu (II). Moreover, the adsorption capacities of CTC and Cu (II) on L550 were excellent in the river water, tap water, and lake water. In addition to electrostatic interactions, ion exchange governed Cu (II) adsorption, while surface complexation played a key role in CTC adsorption on L550. Our results demonstrated that litchi leaves biochar could be a promising adsorbent for remediating multi-contaminated environments.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Monaem EM, Ayoup MS, Omer AM, Hammad EN, Eltaweil AS (2023a) Sandwich-like construction of a new aminated chitosan schiff base for efficient removal of congo red. Appl Water Sci 13:67
Abd El-Monaem EM, Eltaweil AS, El-Subruiti GM, Mohy-Eldin MS, Omer AM (2023b) Adsorption of nitrophenol onto a novel Fe3O4-κ-carrageenan/MIL-125(Ti) composite: process optimization, isotherms, kinetics, and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:49301–49313
Ahmad M, Usman ARA, Rafique MI, Al-Wabel MI (2019) Engineered biochar composites with zeolite, silica, and nano-zerovalent iron for the efficient scavenging of chlortetracycline from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:15136–15152
Chen Y-P, Zheng C-H, Huang Y-Y, Chen Y-R (2022a) Removal of chlortetracycline from water using spent tea leaves-based biochar as adsorption-enhanced persulfate activator. Chemosphere 286:131770
Chen Y, Jiang C, Wang Y, Song R, Tan Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z (2022b) Sources, Environmental Fate, and Ecological Risks of Antibiotics in Sediments of Asia’s Longest River: A Whole-Basin Investigation. Environ Sci Technol 56:14439–14451
Chu G, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Sun K, Liu X, Si Y, Pan B, Steinberg CEW (2022) Inherent Minerals Facilitated Bisphenol A Sorption by Biochar: A Key Force by Complexation. ACS ES&T Water 2:184–194
Deng H, Li Q, Huang M, Li A, Zhang J, Li Y, Li S, Kang C, Mo W (2020) Removal of Zn (II), Mn (II) and Cu (II) by adsorption onto banana stalk biochar: adsorption process and mechanisms. Water Sci Technol 82:2962–2974
Du J, Zhang Y, Hu B, Qv M, Ma C, Wei M, Zhang H (2019) Insight into the potentiality of big biochar particle as an amendment in aerobic composting of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 288:121469
Eltaweil AS, Ibrahim K, El-Monaem EM, El-Subruiti GM, Omer AM (2023) Phospate removal by Lanthanum-doped aminated graphene oxide@aminated chitosan microspheres: Insights into the adsorption mechanism. J Clean Prod 385:135640
Fu Y, Jia M, Wang F, Wang Z, Mei Z, Bian Y, Jiang X, Virta M, Tiedje JM (2021) Strategy for Mitigating Antibiotic Resistance by Biochar and Hyperaccumulators in Cadmium and Oxytetracycline Co-contaminated Soil. Environ Sci Technol 55:16369–16378
Graham DW, Olivares-Rieumont S, Knapp CW, Lima L, Werner D, Bowen E (2011) Antibiotic resistance gene abundances associated with waste discharges to the Almendares River near Havana, Cuba. Environ Sci Technol 45:418–424
Han X, Chen J, Li Z, Qiu H (2019) Combustion fabrication of magnetic porous carbon as a novel magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anal Chim Acta 1078:78–89
He M, Xu Z, Hou D, Gao B, Cao X, Ok YS, Rinklebe J, Bolan NS, Tsang DCW (2022) Waste-derived biochar for water pollution control and sustainable development. Nat Rev Earth Env 3:444–460
Hu X-j, Liu Y-g, Zeng G-m, Wang H, You S-h, Hu X, Tan X-f, Chen A-w, Guo F-y (2015) Effects of inorganic electrolyte anions on enrichment of Cu (II) ions with aminated Fe3O4/graphene oxide: Cu (II) speciation prediction and surface charge measurement. Chemosphere 127:35–41
Hu J, Zhou X, Shi Y, Wang X, Li H (2021a) Enhancing biochar sorption properties through self-templating strategy and ultrasonic fore-modified pre-treatment: Characteristic, kinetic and mechanism studies. Sci Total Environ 769:144574
Hu X, Xie Y, He R, Yao L, Ma S, Bai C (2021b) Nano-iron wrapped by graphitic carbon in the carbonaceous matrix for efficient removal of chlortetracycline. Sep Purif Technol 279:119693
Huang B, Liu Y, Li B, Liu S, Zeng G, Zeng Z, Wang X, Ning Q, Zheng B, Yang C (2017) Effect of Cu (II) ions on the enhancement of tetracycline adsorption by Fe3O4@SiO2-Chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Carbohyd Polym 157:576–585
Jiang W, Chen X, Pan B, Zhang Q, Teng L, Chen Y, Liu L (2014) Spherical polystyrene-supported chitosan thin film of fast kinetics and high capacity for copper removal. J Hazard Mater 276:295–301
Li M-f, Liu Y-g, Liu S-b, Shu D, Zeng G-m, Hu X-j, Tan X-f, Jiang L-h, Yan Z-l, Cai X-x (2017) Cu (II)-influenced adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by magnetic graphene oxide/nitrilotriacetic acid nanocomposite: competition and enhancement mechanisms. Chem Eng J 319:219–228
Li Z, Li M, Wang Z, Liu X (2020) Coadsorption of Cu (II) and tylosin/sulfamethoxazole on biochar stabilized by nano-hydroxyapatite in aqueous environment. Chem Eng J 381:122785
Li W, Zhang T, Lv L, Chen Y, Tang W, Tang S (2021) Room-temperature synthesis of MIL-100 (Fe) and its adsorption performance for fluoride removal from water. Colloids Surf A 624:126791
Lian F, Xing B (2017) Black Carbon (Biochar) In Water/Soil Environments: Molecular Structure, Sorption, Stability, and Potential Risk. Environ Sci Technol 51:13517–13532
Liang L, Xi F, Tan W, Meng X, Hu B, Wang X (2021) Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 3:255–281
Martins VV, Zanetti MOB, Pitondo-Silva A, Stehling EG (2014) Aquatic environments polluted with antibiotics and heavy metals: a human health hazard. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5873–5878
Martins AC, Pezoti O, Cazetta AL, Bedin KC, Yamazaki DAS, Bandoch GFG, Asefa T, Visentainer JV, Almeida VC (2015) Removal of tetracycline by NaOH-activated carbon produced from macadamia nut shells: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chem Eng J 260:291–299
Meng Q, Zhang Y, Meng D, Liu X, Zhang Z, Gao P, Lin A, Hou L (2020) Removal of sulfadiazine from aqueous solution by in-situ activated biochar derived from cotton shell. Environ Res 191:110104
Moyo GG, Hu Z, Getahun MD (2020) Decontamination of xenobiotics in water and soil environment through potential application of composite maize stover/rice husk (MS/RH) biochar—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:28679–28694
Omer AM, Elgarhy GS, El-Subruiti GM, El-Monaem EM, Eltaweil AS (2023) Construction of efficient Ni-FeLDH@MWCNT@Cellulose acetate floatable microbeads for Cr(VI) removal: Performance and mechanism. Carbohyd Polym 311:120771
Ou Y, Yao L, Li Y, Bai C, Luque R, Peng G (2020) Magnetically separable Fe-MIL-88B_NH2 carbonaceous nanocomposites for efficient removal of sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 570:163–172
Qin T, Wang Z, Xie X, Xie C, Zhu J, Li Y (2017) A novel biochar derived from cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) roots could remove norfloxacin and chlortetracycline efficiently. Water Sci Technol 76:3307–3318
Qin Q, Wu X, Chen L, Jiang Z, Xu Y (2018) Simultaneous removal of tetracycline and Cu (II) by adsorption and coadsorption using oxidized activated carbon. RSC Adv 8:1744–1752
Qiu Y, Yuan P, Fan C (2016) Effects of tree thinning and heavy pruning on leaf photosynthesis and transpiration in litchi. J Fruit Sci 33:701–708
Qiu W, Chen B, Tang L, Zheng C, Xu B, Liu Z, Magnuson JT, Zhang S, Schlenk D, Xu EG (2022) Antibiotic chlortetracycline causes transgenerational immunosuppression via NF-κB. Environ Sci Technol 56:4251–4261
Ren J, Zhu Z, Qiu Y, Yu F, Zhou T, Ma J, Zhao J (2021) Enhanced adsorption performance of alginate/MXene/CoFe2O4 for antibiotic and heavy metal under rotating magnetic field. Chemosphere 284:131284
Tan G, Sun W, Xu Y, Wang H, Xu N (2016) Sorption of mercury (II) and atrazine by biochar, modified biochars and biochar based activated carbon in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 211:727–735
Tan G, Mao Y, Wang H, Junaid M, Xu N (2019) Comparison of biochar- and activated carbon-supported zerovalent iron for the removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI): influence of pH, ionic strength, and natural organic matter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21609–21618
Tang Y, Chen Q, Li W, Xie X, Zhang W, Zhang X, Chai H, Huang Y (2020) Engineering magnetic N-doped porous carbon with super-high ciprofloxacin adsorption capacity and wide pH adaptability. J Hazard Mater 388:122059
Tao H-y, Ge H, Shi J, Liu X, Guo W, Zhang M, Meng Y, Li X-y (2020) The characteristics of oestrone mobility in water and soil by the addition of Ca-biochar and Fe–Mn-biochar derived from Litchi chinensis Sonn. Environ Geochem Hlth 42:1601–1615
Thompson KA, Shimabuku KK, Kearns JP, Knappe DRU, Summers RS, Cook SM (2016) Environmental comparison of biochar and activated carbon for tertiary wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 50:11253–11262
Wang R-Z, Huang D-L, Liu Y-G, Zhang C, Lai C, Wang X, Zeng G-M, Zhang Q, Gong X-M, Xu P (2020) Synergistic removal of copper and tetracycline from aqueous solution by steam-activated bamboo-derived biochar. J Hazard Mater 384:121470
Wang T, Zhang J, Tao M-t, Xu C-m, Chen M (2021) Quantitative characterization of toxicity interaction within antibiotic-heavy metal mixtures on Chlorella pyrenoidosa by a novel area-concentration ratio method. Sci Total Environ 762:144180
Wu J, Yang J, Feng P, Huang G, Xu C, Lin B (2020) High-efficiency removal of dyes from wastewater by fully recycling litchi peel biochar. Chemosphere 246:125734
Wu Y, Yan H, Zhu X, Liu C, Chu C, Zhu X, Chen B (2022) Biochar Effectively Inhibits the Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes via Restraining the Energy Supply for Conjugative Plasmid Transfer. Environ Sci Technol 56:12573–12583
Xiao X, Chen B, Chen Z, Zhu L, Schnoor JL (2018) Insight into multiple and multilevel structures of biochars and their potential environmental applications: a critical review. Environ Sci Technol 52:5027–5047
Xu N, Zhang B, Tan G, Li J, Wang H (2015) Influence of biochar on sorption, leaching and dissipation of bisphenol A and 17α-ethynylestradiol in soil. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 17:1722–1730
Xu Q, Zhou Q, Pan M, Dai L (2020) Interaction between chlortetracycline and calcium-rich biochar: Enhanced removal by adsorption coupled with flocculation. Chem Eng J 382:122705
Zhao F, Yang L, Chen L, Li S, Sun L (2018) Co-contamination of antibiotics and metals in peri-urban agricultural soils and source identification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34063–34075
Zhao W, Ma J, Liu Q, Dou L, Qu Y, Shi H, Sun Y, Chen H, Tian Y, Wu F (2023) Accurate Prediction of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using an Improved Machine Learning Method: A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci Technol 57:17751–17761
Zhou L, Li N, Owens G, Chen Z (2019) Simultaneous removal of mixed contaminants, copper and norfloxacin, from aqueous solution by ZIF-8. Chem Eng J 362:628–637
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21707037, 52200074), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-32), and the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2021B1212040008).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 21707037, Cuihua Bai, 52200074, Guangcai Tan, China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, CARS-32,Cuihua Bai, Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, 2021B1212040008, Cuihua Bai
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xian Hu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing- original draft; Yifan Qu: Investigation, Validation, Formal analysis; Lixian Yao: Writing -review and editing, Resources; Zhilin Zhang: Investigation; Guangcai Tan, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing-review and editing; Cuihua Bai: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing -review and editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Weiming Zhang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Qu, Y., Yao, L. et al. Boosted simultaneous removal of chlortetracycline and Cu (II) by Litchi Leaves Biochar: Influence of pH, ionic strength, and background electrolyte ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 10430–10442 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31770-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31770-4