Abstract
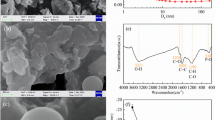
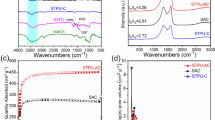
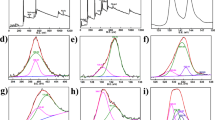
Sycamore leaf biochar (PSAC) was prepared by a two-step phosphoric acid-assisted hydrothermal carbonization combined with a short-time activation method. The characterization results showed that the introduction of phosphoric acid molecules and thermal activation resulted in a substantial increase in the specific surface area (994.21 m2/g) and microporous capacity (0.307 cm3/g) of PSAC. The batch adsorption results showed that the adsorption process of PSAC on bisphenol A (BPA) was best described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Sips isothermal model, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 247.42 mg/g. The adsorption of BPA onto PSAC was determined to be a spontaneous endothermic process. The equilibrium adsorption capacity of PSAC exhibited an upward trend with increasing initial BPA concentration and temperature while decreasing with higher adsorbent dosage and pH value. Coexisting cations and humic acids in water have little impact on the adsorption performance of PSAC for BPA. The adsorption mechanism of BPA by PSAC was mainly governed by pore filling and hydrogen bonding interactions, π-π interactions, and intraparticle diffusion. Furthermore, PSAC demonstrated good reusability by its sustained adsorption capacity of BPA, which remained at 82.6% of the initial adsorption capacity even after four adsorption–desorption cycles. These findings highlight the potential of utilizing low-cost sycamore leaf biochar as an effective adsorbent for the removal of the endocrine disruptor BPA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data flies are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Adebisi GA, Chowdhury ZZ, Abd Hamid SB, Ali E (2016) Hydrothermally treated banana empty fruit bunch fiber activated carbon for Pb(II) and Zn(II) removal. BioResources 11:9686–9709. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.4.9686-9709
Amalina F, Razak ASA, Krishnan S et al (2022) Biochar production techniques utilizing biomass waste-derived materials and environmental applications – a review. J Hazard Mater Adv 7:100134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100134
Cao L, Yu IKM, Tsang DCW et al (2018) Phosphoric acid-activated wood biochar for catalytic conversion of starch-rich food waste into glucose and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Bioresour Technol 267:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.048
Chandrasekar R, Rajendran HK, Priyan VV, Narayanasamy S (2022) Valorization of sawdust by mineral acid assisted hydrothermal carbonization for the adsorptive removal of bisphenol A: a greener approach. Chemosphere 303:135171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135171
Chatir EM, El Hadrami A, Ojala S, Brahmi R (2022) Production of activated carbon with tunable porosity and surface chemistry via chemical activation of hydrochar with phosphoric acid under oxidizing atmosphere. Surf Interfaces 30:101849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101849
Dai L, Lu Q, Zhou H et al (2021) Tuning oxygenated functional groups on biochar for water pollution control: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 420:126547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126547
Ding H, Zhang Z, Li Y et al (2022) Fabrication of novel Fe/Mn/N co-doped biochar and its enhanced adsorption for bisphenol a based on π–π electron donor–acceptor interaction. Bioresour Technol 364:128018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128018
Dos Santos KJL, Dos Santos GEDS, De Sá ÍMGL et al (2019) Wodyetia bifurcata biochar for methylene blue removal from aqueous matrix. Bioresour Technol 293:122093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122093
Fang Z, Hu Y, Wu X et al (2018) A novel magnesium ascorbyl phosphate graphene-based monolith and its superior adsorption capability for bisphenol A. Chem Eng J 334:948–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.067
Hacıosmanoğlu GG, Doğruel T, Genç S et al (2019) Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using phosphonated levan. J Hazard Mater 374:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.015
Han Q, Wang M, Sun F et al (2023) Effectiveness and degradation pathways of bisphenol A (BPA) initiated by hydroxyl radicals and sulfate radicals in water: initial reaction sites based on DFT prediction. Environ Res 216:114601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114601
Hernández-Abreu AB, Álvarez-Torrellas S, Rocha RP et al (2021) Effective adsorption of the endocrine disruptor compound bisphenol A from water on surface-modified carbon materials. Appl Surf Sci 552:149513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149513
Hoslett J, Ghazal H, Katsou E, Jouhara H (2021) The removal of tetracycline from water using biochar produced from agricultural discarded material. Sci Total Environ 751:141755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141755
Hou S, Yang P (2022) BPA biodegradation driven by isolated strain SQ-2 and its metabolism mechanism elucidation. Biochem Eng J 185:108540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2022.108540
Hu Q, Lan R, He L et al (2023) A critical review of adsorption isotherm models for aqueous contaminants: curve characteristics, site energy distribution and common controversies. J Environ Manage 329:117104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117104
Huang R, Liu X, Qi F et al (2022) Efficient preparation of carbon nanospheres-anchored porous carbon materials and the investigation on pretreatment methods. Bioresour Technol 344:126235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126235
Jagtoyen M, Derbyshire F (1998) Activated carbons from yellow poplar and white oak by H3PO4 activation. Carbon 36:1085–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00082-7
Jin Q, Zhang S, Wen T et al (2018) Simultaneous adsorption and oxidative degradation of bisphenol A by zero-valent iron/iron carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped carbon matrix. Environ Pollut 243:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.061
Karthikeyan P, Banu HAT, Meenakshi S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of metal loaded chitosan-alginate biopolymeric hybrid beads for the efficient removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 130:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.059
Kazak O, Tor A (2020) In situ preparation of magnetic hydrochar by co-hydrothermal treatment of waste vinasse with red mud and its adsorption property for Pb(II) in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 393:122391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122391
Králik M (2014) Adsorption, chemisorption, and catalysis. Chem Pap 68. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0624-9
Lachos-Perez D, César Torres-Mayanga P, Abaide ER et al (2022) Hydrothermal carbonization and liquefaction: differences, progress, challenges, and opportunities. Bioresour Technol 343:126084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126084
Le TD, Nguyen DT, Nguyen QL et al (2023) Adsorptive removal of dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) using novel nanoparticles based on cationic surfactant-coated titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:42367–42377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25312-1
Lee MY, Ahmed I, Yu K et al (2021) Aqueous adsorption of bisphenol A over a porphyrinic porous organic polymer. Chemosphere 265:129161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129161
Li J, Zhou B, Liu Y et al (2008) Influence of the coexisting contaminants on bisphenol A sorption and desorption in soil. J Hazard Mater 151:389–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.001
Li S, Gong Y, Yang Y et al (2015) Recyclable CNTs/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites as adsorbents to remove bisphenol A from water and their regeneration. Chem Eng J 260:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.032
Li Y, Meas A, Shan S et al (2018) Hydrochars from bamboo sawdust through acid assisted and two-stage hydrothermal carbonization for removal of two organics from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 261:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.108
Li K, Ma S, Xu S et al (2021) The mechanism changes during bisphenol A degradation in three iron functionalized biochar/peroxymonosulfate systems: the crucial roles of iron contents and graphitized carbon layers. J Hazard Mater 404:124145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124145
Li Z, Hu C, Hu Z et al (2022) Facile synthesis of novel multifunctional β-cyclodextrin microporous organic network and application in efficient removal of bisphenol A from water. Carbohydr Polym 276:118786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118786
Libbrecht W, Vandaele K, De Buysser K et al (2015) Tuning the pore geometry of ordered mesoporous carbons for enhanced adsorption of bisphenol-A. Materials 8:1652–1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8041652
Liu H, Xu G, Li G (2020) The characteristics of pharmaceutical sludge-derived biochar and its application for the adsorption of tetracycline. Sci Total Environ 747:141492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141492
Liu L, Cai W, Dang C et al (2020) One-step vapor-phase assisted hydrothermal synthesis of functionalized carbons: effects of surface groups on their physicochemical properties and adsorption performance for Cr(VI). Appl Surf Sci 528:146984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146984
Liu Q, Li D, Cheng H et al (2021) High mesoporosity phosphorus-containing biochar fabricated from Camellia oleifera shells: impressive tetracycline adsorption performance and promotion of pyrophosphate-like surface functional groups (C-O-P bond). Bioresour Technol 329:124922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124922
Lv B-W, Xu H, Guo J-Z et al (2022) Efficient adsorption of methylene blue on carboxylate-rich hydrochar prepared by one-step hydrothermal carbonization of bamboo and acrylic acid with ammonium persulphate. J Hazard Mater 421:126741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126741
Ma Y, Yang L, Wu L et al (2020) Carbon nanotube supported sludge biochar as an efficient adsorbent for low concentrations of sulfamethoxazole removal. Sci Total Environ 718:137299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137299
Ma Y, Qi Y, Yang L et al (2021) Adsorptive removal of imidacloprid by potassium hydroxide activated magnetic sugarcane bagasse biochar: adsorption efficiency, mechanism and regeneration. J Clean Prod 292:126005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126005
Madhavarao M, Ramesh A, Purnachandrarao G, Seshaiah K (2006) Removal of copper and cadmium from the aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Ceiba pentandra hulls. J Hazard Mater 129:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.018
Nguyen V-T, Nguyen T-B, Chen C-W et al (2019) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons production and tetracycline adsorption behavior of biochar derived from spent coffee ground. Bioresour Technol 284:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.096
Nguyen T-B, Truong Q-M, Chen C-W et al (2022) Mesoporous and adsorption behavior of algal biochar prepared via sequential hydrothermal carbonization and ZnCl2 activation. Bioresour Technol 346:126351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126351
Nguyen TH, Nguyen TTL, Nguyen TC et al (2023) Adsorption behavior of cationic surfactant onto aluminum hydroxide nanoparticles and application in lindane removal. Mater Today Commun 34:105266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105266
Olivares-Marín M, Fernández-González C, Macías-García A, Gómez-Serrano V (2006) Thermal behaviour of lignocellulosic material in the presence of phosphoric acid. Influence of the acid content in the initial solution. Carbon 44:2347–2350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2006.04.004
Puziy AM, Poddubnaya OI, Gawdzik B, Tascón JMD (2020) Phosphorus-containing carbons: preparation, properties and utilization. Carbon 157:796–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.018
Qu J, Bi F, Hu Q et al (2023) A novel PEI-grafted N-doping magnetic hydrochar for enhanced scavenging of BPA and Cr(VI) from aqueous phase. Environ Pollut 321:121142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121142
Regkouzas P, Diamadopoulos E (2019) Adsorption of selected organic micro-pollutants on sewage sludge biochar. Chemosphere 224:840–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.165
Shi W, Wang H, Yan J et al (2022) Wheat straw derived biochar with hierarchically porous structure for bisphenol A removal: preparation, characterization, and adsorption properties. Sep Purif Technol 289:120796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120796
Srivastav AL, Pham TD, Izah SC et al (2022) Biochar adsorbents for arsenic removal from water environment: a review. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108:616–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03374-6
Sun Z, Zhao L, Liu C et al (2020) Fast adsorption of BPA with high capacity based on π-π electron donor-acceptor and hydrophobicity mechanism using an in-situ sp2 C dominant N-doped carbon. Chem Eng J 381:122510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122510
Tan KL, Hameed BH (2017) Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.024
Tian W, Qiu J, Li N et al (2021) Efficient piezocatalytic removal of BPA and Cr(VI) with SnS2/CNFs membrane by harvesting vibration energy. Nano Energy 86:106036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106036
Wang J, Wang S (2019) Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: a review. J Clean Prod 227:1002–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.282
Wang Y, Wei X, Qi Y, Huang H (2021) Efficient removal of bisphenol-A from water and wastewater by Fe2O3-modified graphene oxide. Chemosphere 263:127563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127563
Wei J, Tu C, Yuan G et al (2019) Carbon-coated montmorillonite nanocomposite for the removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 368:541–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.080
Wu Z, Chen Z, Tang J et al (2023) Efficient adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) in water using one-step H3PO4-assisted prepared Leersia hexandra Swartz hydrochar. Mater Today Sustain 21:100260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100260
Xiang Y, Xu Z, Wei Y et al (2019) Carbon-based materials as adsorbent for antibiotics removal: mechanisms and influencing factors. J Environ Manage 237:128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.068
Xu L, Bai T, Yi X et al (2023) Polypropylene fiber grafted calcium alginate with mesoporous silica for adsorption of bisphenol A and Pb2+. Int J Biol Macromol 238:124131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124131
Yang H, Hu S, Zhao H et al (2021) High-performance Fe-doped ZIF-8 adsorbent for capturing tetracycline from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 416:126046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126046
Zhao X, Li M, Zhai F et al (2021) Phosphate modified hydrochars produced via phytic acid-assisted hydrothermal carbonization for efficient removal of U(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). J Environ Manage 298:113487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113487
Zhou F, Li K, Hang F et al (2022) Efficient removal of methylene blue by activated hydrochar prepared by hydrothermal carbonization and NaOH activation of sugarcane bagasse and phosphoric acid. RSC Adv 12:1885–1896. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA08325B
Zhu M, Kong L, Xie M et al (2021) Carbon aerogel from forestry biomass as a peroxymonosulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. J Hazard Mater 413:125438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125438
Funding
This work was supported by the Wuhan Science and Technology Planning Project (Grant No. 2020020601012274).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Li: methodology, investigation, data curation, writing original draft. Xiangyi Gong: conceptualization, methodology, writing original draft. Dekang Meng: methodology, supervision, writing–review and editing. Fengying Wu: writing–review and editing. Dajun Ren: supervision, writing–review and editing, funding acquisition. Jiaquan Zhang: funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors of the article consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Gong, X., Meng, D. et al. Effective adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution using phosphoric acid-assisted hydrochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 123083–123097 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30951-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30951-5