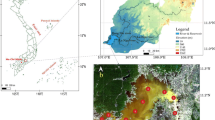
Abstract
Safe drinking water sources are crucial for human health. Consequently, water quality management, including continuous monitoring of water quality and algae at sources, is critical to ensure the availability of safe water for local residents. This study aimed to construct statistical prediction models considering probability distributions relevant to cyanophyte cell counts and compare their prediction performance. In this study, water quality parameters at Juam Lake and Tamjin Lake, representative water sources in the Yeongsan and Seomjin rivers, South Korea, were investigated. We used a water quality monitoring network, algae alert system, and hydraulic and hydrological data measured every 7 days from January 2017 to December 2022 from the Water Environment Information System of the National Institute of Environmental Research. Using data for 2017–2021 as a training set and data for 2022 as a test set, the performances of seven models were compared for predicting cyanophyte cell counts. Environmental factors associated with algae in water sources were observed based on the monitoring data, and a prediction model appropriate for the cyanophyte distribution was generated, which also included the risk of toxicity. The extreme gradient boosting with the random forest model had the best predictive performance for cyanophyte cell counts. The study results are expected to facilitate water quality management in various water systems, including water sources.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdellatif D, El Moutaouakil K, Satori K (2018) Clustering and Jarque-Bera normality test to face recognition. Procedia Comput Sci 127:246–255
Ajiferuke I, Famoye F (2015) Modelling count response variables in informetric studies: comparison among count, linear, and lognormal regression models. J Informet 9:499–513
Angelov PP, Soares EA, Jiang R, Arnold NI, Atkinson PM (2021) Explainable artificial intelligence: an analytical review. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Know Discov 11:e1424
Capblancq T, Forester BR (2021) Redundancy analysis: a Swiss Army Knife for landscape genomics. Methods Ecol Evol 12:2298–2309
Casella G, Berger RL (2021) Statistical inference. Cengage Learning, Boston, Massachusetts
Cavanaugh JE, Neath AA (2019) The Akaike information criterion: background, derivation, properties, application, interpretation, and refinements. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat 11:e1460
Choi DH, Jung JW, Lee KS, Choi YJ, Yoon KS, Cho SH et al (2012) Estimation of pollutant load delivery ratio for flow duration using LQ equation from the Oenam-cheon watershed in Juam Lake. J Environ Sci Int 21:31–39
Cohen P, West SG, Aiken LS (2014) Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. Routledge, Abingdon, UK
Das KR, Imon AHMR (2016) A brief review of tests for normality. Am J Theor Appl Stat 5:5–12
Dobson AJ, Barnett AG (2018) An introduction to generalized linear models. Chapman and Hall/CRC press, Boca Raton, Florida
Đorić D, Nikolić-Đorić E, Jevremović V, Mališić J (2009) On measuring skewness and kurtosis. Qual Quant 43:481–493
Environment Information System of the National Institute of Environmental Research website, last modified March 30, 2023. http://water.nier.go.kr. Accessed 23 Apr 2023
Falconer IR, Humpage AR (2005) Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2:43–50
Górecki T, Hörmann S, Horváth L, Kokoszka P (2018) Testing normality of functional time series. J Time Ser Anal 39:471–487
Hastie TJ (2017) Generalized additive models. Statistical models in S, 1st edn. Routledge, Oxfordshire, pp 249–307
He J, Hou XL, Wang WC (2022) Study of water quality pollution index, land-use and socio-economic factors in Yingkou Irrigation District of China based on redundancy analysis. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 21:297–302
Kaur P, Stoltzfus J, Yellapu V (2018) Descriptive statistics. Int J Acad Med 4:60
Kim SG (2017) Green algae and algae warning system. Water for Future 50:22–26
Ku CS, Yang Y, Park Y, Lee J (2013) Health benefits of blue-green algae: prevention of cardiovascular disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Med Food 16(2):103–111
Lee KL, Choi JS, Lee JH, Jung KY, Kim HS (2021) Response of epilithic diatom assemblages to weir construction on the Nakdong River, Republic of Korea. Ecol Indic 126:107711
Lim JC, Kim TS (2018) Analysis of biodiversity and ecological characteristics on Tamjin-river estuarine ecosytem. J Wet Res 20:181–189
Loeys T, Moerkerke B, De Smet O, Buysse A (2012) The analysis of zero-inflated count data: beyond zero-inflated Poisson regression. Br J Math Stat Psychol 65:163–180
Mahmood T, Xie M (2019) Models and monitoring of zero-inflated processes: the past and current trends. Quality and Reliability Engin Int 35(8):2540–2557
Martinez WL, Martinez AR, Solka J (2017) Exploratory data analysis with MATLAB. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Mukhopadhyay N (2020) Probability and statistical inference. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Ramosaj B, Pauly M (2019) Consistent estimation of residual variance with random forest Out-Of-Bag errors. Stat Probab Lett 151:49–57
Rebekić A, Lončarić Z, Petrović S, Marić S (2015) Pearson’s or Spearman’s correlation coefficient-which one to use? Poljoprivreda 21:47–54
Rigatti SJ (2017) Random forest. J Insur Med 47:31–39
Sakizadeh M, Zhang C (2021) Source identification and contribution of land uses to the observed values of heavy metals in soil samples of the border between the Northern Ireland and Republic of Ireland by receptor models and redundancy analysis. Geoderma 404:115313
Seo KA, Jung SJ, Park JH, Hwang KS, Lim BJ (2013) Relationships between the characteristics of algae occurrence and environmental factors in Lake Juam, Korea. J Korean Soc Water Environ 29:317–328
Seo MJ, Lee HJ, Kim YS (2019) Relationship between coliform bacteria and water quality factors at weir stations in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water 11:1171
Shim YJ, Cha JY, Park YS, Lee DJ, Seo YH, Hong JP et al (2014) A study on the land purchase priority measurement of the riparian areas in Yeongsan and Seomjin River basin-focusing on the riparian areas of the Juam Lake. J Korean Soc Environ Restor Technol 17:173–184
SigmaPlot (2014) SigmaPlot for windows. https://systatsoftware.com/sigmaplot/. Accessed 10 Apr 2023
Singh AP, Dhadse K, Ahalawat J (2019) Managing water quality of a river using an integrated geographically weighted regression technique with fuzzy decision-making model. Environ Monit Assess 191:1–17
ter Braak CJ, Šmilauer P (2018) Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination (version 5.10). Biometris, Wageningen University & Research
Water Resources Management Information System website, last modified March 30, 2023. http://www.wamis.go.kr. Accessed 23 Apr 2023
Winter B (2019) Statistics for linguists: an introduction using R. Routledge, New York
Yu JJ, Lee HJ, Lee KL, Lyu HS, Whang JW, Shin LY et al (2014) Relationship between distribution of the dominant phytoplankton species and water temperature in the Nakdong River, Korea. Korean J Ecol Environ 47:247–257
Yusuf OB, Bello T, Gureje O (2017) Zero inflated Poisson and zero inflated negative binomial models with application to number of falls in the elderly. Biostat Biom Open Access J 1:69–75
Zhang W, Wu C, Zhong H, Li Y, Wang L (2021) Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on Bayesian optimization. Geosci Front 12:469–477
Zhang X, Yi N (2020) Fast zero-inflated negative binomial mixed modeling approach for analyzing longitudinal metagenomics data. Bioinformatics 36:2345–2351
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the water quality team and algae team of the Yeongsan River Environment Research Center at the National Institute of Environmental Research for their assistance with sampling and analysis and Editage (http://www.editage.co.kr) for their English language editing service.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute of Environment Research (NIER), funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea (grant number [NIER-2022-01-01-044]). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Seong-Yun Hwang and Kang-Young Jung; data curation, Seong-Yun Hwang and Kang-Young Jung; formal analysis, Seong-Yun Hwang and Kyung-Lak Lee; funding acquisition, Jong-Hwan Park and Dong-Seok Shin; investigation, Hyeon-Su Chung, Mi-Sun Son, and Don-Woo Ha; methodology, Seong-Yun Hwang; project administration, Seong-Yun Hwang, Won-Seok Lee, and Dong-Seok Shin; resources, Byung-Woong Choi; software, Kyung-Lak Lee, Seong-Yun Hwang, and Kang-Young Jung; Supervision, Jong-Hwan Park, Won-Seok Lee, and Dong-Seok Shin; validation, Seong-Yun Hwang, Byung-Woong choi, and Kang-Young Jung; visualization, Kyung-Lak Lee, Seong-Yun Hwang, and Kang-Young Jung; roles/writings—original draft, Seong-Yun Hwang; writing—review and editing, Seong-Yun Hwang and Kang-Young Jung. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Seong-Yun Hwang is the first author of this study.
Highlights
- Statistical distribution of variables predicting water quality or algae-related variables warrant consideration
- Redundancy analysis can investigate seasonal or environmental distributions of algae
- Water quality management is enhanced by predicting cyanophyte cell counts
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, SY., Choi, BW., Park, JH. et al. Evaluation of algal species distributions and prediction of cyanophyte cell counts using statistical techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 117143–117164 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30077-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30077-8