Abstract
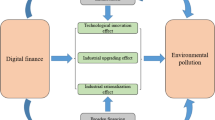
Due to people’s insufficient anticipation of the negative impact of highly developed industries and the lack of prevention, global environmental pollution has occurred. These pollutants include air pollution, water pollutants, and land pollution, which not only cause direct damage and impact the ecosystem but also endanger the health of urban residents and economic development. Therefore, researching environmental pollution management is necessary to help solve these imminent environmental problems. In addition, digital finance, based on digital technology, can identify bottlenecks in environmental pollution management, formulate more effective governance strategies, and reduce environmental pollution at the source. In this context, this study uses the environmental pollution data of 287 cities in China from 2011 to 2021. It uses the fixed-effects and mediation effect models to analyze digital finance’s role in environmental pollution management. The research shows that digital finance can promote environmental pollution management and play a promoting role through two channels of influence: green technology innovation and government green subsidies. At the same time, the effect of this promotion is more significant in cities in the Midwest and in resource-based cities. The research results propose strategies for government organizations in environmental pollution management, and alleviate current resource and environmental problems, in addition to realizing sustainable urban development.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data related to the paper can be obtained from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Azam M, Alam MM, Hafeez MH (2018) Effect of tourism on environmental pollution: further evidence from Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand. J Clean Prod 190:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.168
Başar S, Tosun B (2021) Environmental Pollution Index and economic growth: evidence from OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:36870–36879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13225-w
Brink E, Aalders T, Ádám D, Feller R et al (2016) Cascades of green: a review of ecosystem-based adaptation in urban areas. Glob Environ Chang 36:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.11.003
Chen S, Zhang H (2021) Does digital finance promote manufacturing servitization: micro evidence from China. Int Rev Econ Financ 76:856–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iref.2021.07.018
Chu H, Yu H, Chong Y, Li L (2023) Does the development of digital finance curb carbon emissions? Evidence from county data in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(17):49237–49254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25659-5
Du M, Hou Y, Zhou Q, Ren S (2022) Going green in China: how does digital finance affect environmental pollution? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(60):89996–90010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21909-0
Feng S, Zhang R, Li G (2022) Environmental decentralization, digital finance and green technology innovation. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 61:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2022.02.008
Feng T, Du H, Lin Z, Zuo J (2020) Spatial spillover effects of environmental regulations on air pollution: evidence from urban agglomerations in China. J Environ Manag 272:110998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110998
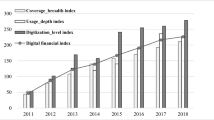
Guo F, Wang JY, Wang F, Kong T, Zhang X, Cheng ZY (2020) Measure China’s digital financial inclusion: Index compilation and spatial characteristics. China Economic Quarterly 19(4):1401–1418. https://doi.org/10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2020.03.12
Han X, Zhang H, Zhu W (2023) The impact of digital finance on women’s bargaining power: evidence from China. China Econ Rev:102007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2023.102007
Hou G, Zou Z, Zhang T, Meng Y (2019) Analysis of the effect of industrial transformation of resource-based cities in Northeast China. Economies 7(2):40 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Hou H, Zhu YB, Wang J, Zhang ML (2022) Will green financial policy help improve China’s environmental quality? the role of digital finance and green technology innovation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(4):10527–10539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22887-z
Hu D, Zhai C, Zhao S (2023) Does digital finance promote household consumption upgrading? An analysis based on data from the China family panel studies. Econ Model 125:106377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2023.106377
Huang L, Lei Z (2021) How environmental regulation affect corporate green investment: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 279:123560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123560
Hussain J, Lee CC, Chen Y (2022) Optimal green technology investment and emission reduction in emissions generating companies under the support of green bond and subsidy. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 183:121952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121952
Lan J, Kakinaka M, Huang X (2012) Foreign direct investment, human capital and environmental pollution in China. Environ Resour Econ 51:255–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-011-9498-2
Lee CC, Wang F (2022) How does digital inclusive finance affect carbon intensity? J Econ Anal Policy 75:174–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.05.010
Lei T, Luo X, Jiang J, Zou K (2023) Emission reduction effect of digital finance: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(22):62032–62050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26424-4
Li J, Wu Y, Xiao JJ (2020) The impact of digital finance on household consumption: evidence from China. Econ Model 86:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2019.09.027
Li Z, Liao G, Wang Z, Huang Z (2018) Green loan and subsidy for promoting clean production innovation. J Clean Prod 187:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.066
Liang L, Wang Z, Li J (2019) The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J Clean Prod 237:117649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117649
Liao B, Li L (2022) Spatial division of labor, specialization of green technology innovation process and urban coordinated green development: evidence from China. Sustain Cities Soc 80:103778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103778
Liao G, Li Z, Wang M, Albitar K (2022) Measuring China’s urban digital finance. Quant Financ Econ 6:385–404 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Liu K, Lin B (2019) Research on influencing factors of environmental pollution in China: a spatial econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 206:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.194
Ma Q, Tariq M, Mahmood H, Khan Z (2022) The nexus between digital economy and carbon dioxide emissions in China: the moderating role of investments in research and development. Technol Soc 68:101910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101910
Müller A, Österlund H, Marsalek J, Viklander M (2020) The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: a review of sources. Sci Total Environ 709:136125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136125
Ozili PK (2018) Impact of digital finance on financial inclusion and stability. Borsa Istanbul Rev 18(4):329–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bir.2017.12.003
Qiu S, Wang Z, Liu S (2021) The policy outcomes of low-carbon city construction on urban green development: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment conducted in China. Sustain Cities Soc 66:102699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102699
Razzaq A, Sharif A, Ozturk I, Skare M (2023) Asymmetric influence of digital finance, and renewable energy technology innovation on green growth in China. Renew Energy 202:310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.11.082
Ren S, Hao Y, Wu H (2022) How does green investment affect environmental pollution? Evidence from China. Environ Resour Econ 81:25–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-021-00615-4
Ren X, Zeng G, Gozgor G (2023) How does digital finance affect industrial structure upgrading? Evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. J Environ Manag 330:117125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117125
Sapkota P, Bastola U (2017) Foreign direct investment, income, and environmental pollution in developing countries: panel data analysis of Latin America. Energy Econ 64:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.04.001
Sohail MT, Ullah S, Majeed MT, Usman A (2021) Pakistan management of green transportation and environmental pollution: a nonlinear ARDL analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:29046–29055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12654-x
Sun Y, Tang X (2022) The impact of digital inclusive finance on sustainable economic growth in China. Financ Res Lett 50:103234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2022.103234
Wang H, Guo J (2022) Impacts of digital inclusive finance on CO2 emissions from a spatial perspective: evidence from 272 cities in China. J Clean Prod 355:131618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131618
Wang J (2023) Digital inclusive finance and rural revitalization. Financ Res Lett 57:104157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.104157
Wang KL, Zhu RR, Cheng YH (2022) Does the development of digital finance contribute to haze pollution control? Evidence from China. Energies 15(7):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072660
Wen ZL, Y BJ, (2014) Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv Methods Pract Psychol Sci 22(5):731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Xie X, Shen Y, Zhang H, Guo F (2018) Can digital finance promote entrepreneurship? Evidence from China. China Econ Q 17(4):1557–1580. https://doi.org/10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2018.03.12
Yue P, Korkmaz AG, Yin Z, Zhou H (2022) The rise of digital finance: financial inclusion or debt trap? Financ Res Lett 47:102604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2021.102604
Zhengning PU, Jinhua FEI (2022) The impact of digital finance on residential carbon emissions: evidence from China. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 63:515–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2022.07.006
Zhong K (2022) Does the digital finance revolution validate the Environmental Kuznets Curve? Empirical findings from China. PLoS One 17(1):e0257498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257498
Addendum
Due to space limitations, we can only show the results of environmental pollution management calculations for 31 provincial capital cities in the “Appendix” section. The environmental pollution management data of the remaining cities can be obtained from our author.
Funding
This article is funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19BTJ056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the research. Zhe Zhang is responsible for material preparation and data collection. The data analysis was done by Zheming Dong, and the first draft was written by Shujun Yao and Zheming Dong. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Measurement results of environmental pollution management levels in 31 provincial capital cities in China
2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Beijing | 0.8380 | 0.8282 | 0.8271 | 0.8291 | 0.8344 | 0.8486 | 0.8505 | 0.8652 | 0.8587 | 0.8799 | 0.8722 |
Tianjin | 0.5431 | 0.5459 | 0.5342 | 0.5426 | 0.5415 | 0.5733 | 0.5558 | 0.5888 | 0.5889 | 0.6278 | 0.6204 |
Shanghai | 0.5873 | 0.5217 | 0.5563 | 0.5317 | 0.5420 | 0.5227 | 0.6249 | 0.7046 | 0.7001 | 0.7064 | 0.7033 |
Chongqing | 0.1088 | 0.1172 | 0.1089 | 0.1034 | 0.1012 | 0.1007 | 0.1218 | 0.0847 | 0.0867 | 0.0737 | 0.1021 |
Lanzhou | 0.8957 | 0.9090 | 0.9100 | 0.9140 | 0.9183 | 0.9196 | 0.9085 | 0.9126 | 0.9225 | 0.8618 | 0.8635 |
Xining | 0.8421 | 0.8383 | 0.8379 | 0.8412 | 0.8435 | 0.8020 | 0.8032 | 0.8026 | 0.8162 | 0.6863 | 0.6680 |
Xi’an | 0.8454 | 0.8498 | 0.8612 | 0.8700 | 0.8826 | 0.9105 | 0.9045 | 0.9084 | 0.9058 | 0.9158 | 0.9147 |
Zhengzhou | 0.6554 | 0.6601 | 0.6787 | 0.6592 | 0.6399 | 0.7122 | 0.7113 | 0.7098 | 0.7093 | 0.7412 | 0.7338 |
Jinan | 0.8272 | 0.8266 | 0.8288 | 0.8334 | 0.8311 | 0.8333 | 0.8437 | 0.8480 | 0.8446 | 0.8020 | 0.8144 |
Taiyuan | 0.7706 | 0.7860 | 0.8031 | 0.8200 | 0.8389 | 0.8679 | 0.8798 | 0.8843 | 0.8882 | 0.8591 | 0.8668 |
Hefei | 0.9063 | 0.9036 | 0.9038 | 0.8972 | 0.9021 | 0.9136 | 0.9084 | 0.9169 | 0.9166 | 0.9036 | 0.9026 |
Changsha | 0.8702 | 0.8618 | 0.8592 | 0.8577 | 0.8545 | 0.8758 | 0.8760 | 0.8702 | 0.8619 | 0.8788 | 0.8797 |
Wuhan | 0.8703 | 0.8838 | 0.9044 | 0.8941 | 0.9015 | 0.9065 | 0.9027 | 0.9506 | 0.9513 | 0.8973 | 0.9010 |
Nanjing | 0.6901 | 0.6639 | 0.6538 | 0.6584 | 0.6457 | 0.6780 | 0.7074 | 0.7322 | 0.7260 | 0.7150 | 0.6944 |
Chengdu | 0.8090 | 0.7988 | 0.8012 | 0.7995 | 0.7959 | 0.8145 | 0.8142 | 0.8290 | 0.8216 | 0.8275 | 0.8295 |
Guiyang | 0.8861 | 0.8953 | 0.8923 | 0.8903 | 0.8942 | 0.8510 | 0.8067 | 0.8825 | 0.8761 | 0.8172 | 0.8340 |
Kunming | 0.7267 | 0.8897 | 0.8954 | 0.9142 | 0.9062 | 0.7873 | 0.8311 | 0.8371 | 0.8813 | 0.7534 | 0.7953 |
Harbin | 0.8501 | 0.8823 | 0.9099 | 0.9169 | 0.9259 | 0.9074 | 0.9220 | 0.9332 | 0.9400 | 0.8943 | 0.9153 |
Changchun | 0.4536 | 0.4236 | 0.4214 | 0.4263 | 0.4292 | 0.5287 | 0.5265 | 0.4215 | 0.3854 | 0.4004 | 0.4034 |
Shenyang | 0.6277 | 0.6198 | 0.6096 | 0.6160 | 0.6354 | 0.6803 | 0.6890 | 0.6654 | 0.6620 | 0.6825 | 0.6850 |
Shijiazhuang | 0.6687 | 0.6466 | 0.6483 | 0.6597 | 0.6772 | 0.6329 | 0.7241 | 0.7376 | 0.7439 | 0.7442 | 0.7358 |
Hangzhou | 0.6842 | 0.6564 | 0.6542 | 0.6476 | 0.6524 | 0.6541 | 0.6636 | 0.7464 | 0.7585 | 0.7840 | 0.7774 |
Nanchang | 0.9358 | 0.9258 | 0.9279 | 0.9328 | 0.9293 | 0.9153 | 0.9279 | 0.9651 | 0.9654 | 0.9377 | 0.9385 |
Guangzhou | 0.8477 | 0.8288 | 0.8275 | 0.8292 | 0.8313 | 0.8167 | 0.8244 | 0.8975 | 0.8951 | 0.9015 | 0.8940 |
Fuzhou | 0.8916 | 0.8973 | 0.8965 | 0.9011 | 0.8989 | 0.8613 | 0.8511 | 0.8560 | 0.8427 | 0.8241 | 0.8282 |
Haikou | 0.9973 | 0.9961 | 0.9960 | 0.9957 | 0.9957 | 0.9965 | 0.9956 | 0.9983 | 0.9983 | 0.9950 | 0.9963 |
Nanning | 0.8279 | 0.8195 | 0.8236 | 0.8230 | 0.8285 | 0.8638 | 0.8555 | 0.8446 | 0.8391 | 0.8291 | 0.8545 |
Lasa | 0.9268 | 0.9233 | 0.9224 | 0.9229 | 0.9233 | 0.9381 | 0.9341 | 0.9196 | 0.9148 | 0.8997 | 0.9286 |
Yinchuan | 0.9062 | 0.8906 | 0.8988 | 0.9053 | 0.9101 | 0.9007 | 0.9226 | 0.9235 | 0.9290 | 0.8748 | 0.8729 |
Urumqi | 0.7440 | 0.7385 | 0.7501 | 0.7491 | 0.7536 | 0.7397 | 0.7297 | 0.7414 | 0.7341 | 0.7455 | 0.7500 |
Hohhot | 0.8505 | 0.8476 | 0.8453 | 0.8267 | 0.8489 | 0.8035 | 0.8294 | 0.8296 | 0.8329 | 0.7756 | 0.8131 |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, S., Dong, Z. & Zhang, Z. How digital finance affects environmental pollution management: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 105231–105246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29787-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29787-w