Abstract
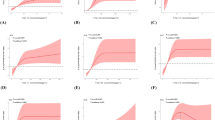
Previous studies on the association between metals and dyslipidemia are not completely consistent. There are few studies investigating the relationship between mixed metal exposure and dyslipidemia as well as the effects of metals on dyslipidemia in community-dwelling elderly. To evaluate the correlations and interaction effect between the urinary concentrations of metals and the risk of dyslipidemia in community-dwelling elderly. We designed a case–control study to assess the correlation between urine metals and dyslipidemia in elderly people in the Yinchuan. The urinary levels of 13 metals, including calcium, vanadium, iron, cobalt, zinc, copper, arsenic, selenium, molybdenum, cadmium, tellurium, and thallium, were measured by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and the blood biochemical analyzer was used to measure the blood lipid levels of 3384 senior individuals from four different areas of Yinchuan city. Logistic regression and restricted cubic splines (RCS) were used to explore the correlation and dose–response relationship between urinary metals and the risk of dyslipidemia. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was used to select metals, and then weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression was used to explore the weight of each metal in mixed metals. Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) was used to explore the interactions between metals on dyslipidemia risk. (1) After selection by LASSO regression, in the multi-metal model, compared with the lowest quartile, the adjusted ORs (95%CI) of the highest quartiles were 0.47 (0.37–0.60) for Fe, 1.43 (1.13–1.83) for Zn, 1.46 (1.11–1.92) for As, 0.59 (0.44–0.80) for Se, 1.53 (1.18–2.00) for Mo, and 1.36 (1.07–1.73) for Te. (2) In the WQS regression model, Fe and Mo accounted for the largest weight in the negative and positive effects of dyslipidemia, respectively. (3) In the BKMR model, there may be a positive interaction between Te and Se on dyslipidemia. Among the mixed metals, Fe, As, Se, Mo, and Te were associated with the prevalence of dyslipidemia, with Fe and Mo contributing the most. There may be certain interactions between Te and Se.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Bobb JF, Claus Henn B, Valeri L, Coull BA (2018) Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ Health 17(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0413-y
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus Henn B, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Godleski JJ, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16(3):493–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxu058
Cakmak S, Mitchell K, Lukina A, Dales R (2023) Do blood metals influence lipid profiles? Findings of a cross-sectional population-based survey. Environ Res 231(Pt 2):116107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116107
Chen L, Ma T, Wang Y, Zheng J (2020) Health risks associated with multiple metal(loid)s in groundwater: a case study at Hetao Plain, northern China. Environ Pollut 263(Pt B):114562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114562
Chen Z, Jiang Y, Lu Y, Li J, Liao S, Liu M (2022) Dyslipidemia prevalence in chinese older adults: a meta-analysis. Chin Gen Pract 25(01):115–121
Dabbagh AJ, Shwaery GT, Keaney JF Jr, Frei B (1997) Effect of iron overload and iron deficiency on atherosclerosis in the hypercholesterolemic rabbit. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17(11):2638–2645. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.17.11.2638
Favé MJ, Lamaze FC, Soave D, Hodgkinson A, Gauvin H, Bruat V, Grenier JC, Gbeha E, Skead K, Smargiassi A, Johnson M, Idaghdour Y, Awadalla P (2018) Gene-by-environment interactions in urban populations modulate risk phenotypes. Nat Commun 9(1):827. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03202-2
Habib A, Finn AV (2014) The role of iron metabolism as a mediator of macrophage inflammation and lipid handling in atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol 5:195. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00195
Haidar Z, Fatema K, Shoily SS, Sajib AA (2023) Disease-associated metabolic pathways affected by heavy metals and metalloid. Toxicol Rep 10:554–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2023.04.010
He L, Zhang Y, Ru D, Xue B, Wen S, Zhou H (2020) Serum iron levels are negatively correlated with serum triglycerides levels in female university students. Ann Palliat Med 9(2):414–419. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm.2020.03.02
He JL, Li GA, Zhu ZY, Hu MJ, Wu HB, Zhu JL, Zhao HH, Zhang HS, Huang F (2021) Associations of exposure to multiple trace elements with the risk of goiter: a case-control study. Environ Pollut 288:117739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117739
Hong KN, Fuster V, Rosenson RS, Rosendorff C, Bhatt DL (2017) How low to go with glucose, cholesterol, and blood pressure in primary prevention of CVD. J Am Coll Cardiol 70(17):2171–2185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.001
Huang X, Jiang D, Zhu Y, Fang Z, Che L, Lin Y, Xu S, Li J, Huang C, Zou Y, Li L, Wu D, Feng B (2017) Chronic high dose zinc supplementation induces visceral adipose tissue hypertrophy without altering body weight in mice. Nutrients 9(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101138
Jiang Q, Xiao Y, Long P, Li W, Yu Y, Liu Y, Liu K, Zhou L, Wang H, Yang H, Li X, He M, Wu T, Yuan Y (2021) Associations of plasma metal concentrations with incident dyslipidemia: prospective findings from the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. Chemosphere 285:131497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131497
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1649
Ju W, Ji M, Li X, Li Z, Wu G, Fu X, Yang X, Gao X (2018) Relationship between higher serum selenium level and adverse blood lipid profile. Clin Nutr 37(5):1512–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2017.08.025
Kang P, Shin HY, Kim KY (2021) Association between dyslipidemia and mercury exposure in adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(2):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020775
Kaur P, Yousuf S, Ansari MA, Ahmad AS, Islam F (2003) Dose- and duration-dependent alterations by tellurium on lipid levels: differential effects in cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem of mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 94(3):259–271. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:94:3:259
Kim SH, Yadav D, Kim SJ, Kim JR, Cho KH (2017) High consumption of iron exacerbates hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, and female sterility in zebrafish via acceleration of glycation and degradation of serum lipoproteins. Nutrients 9(7):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070690
Kim DW, Ock J, Moon KW, Park CH (2022) Association between heavy metal exposure and dyslipidemia among Korean adults: from the Korean National Environmental Health Survey, 2015–2017. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(6):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063181
Lee S, Nam KH, Seong JK, Ryu DY (2018) Molybdate attenuates lipid accumulation in the livers of mice fed a diet deficient in methionine and choline. Biol Pharm Bull 41(8):1203–1210. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b18-00020
Li H, Ge M, Pei Z, He J, Wang C (2022a) Associations of environmental factors with total cholesterol level of middle-aged and elderly people in China. BMC Public Health 22(1):2423. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14922-y
Li X, Hu Y, Lv Y, Gao Y, Yuwen L, Yang W, Weng L, Teng Z, Wang L (2020) Gut microbiota and lipid metabolism alterations in mice induced by oral cadmium telluride quantum dots. J Appl Toxicol 40(8):1131–1140. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3972
Li Z, Kuang H, Li L, Wu M, Liao Z, Zeng K, Ye Y, Fan R (2022b) What adverse health effects will environmental heavy metal co-exposure bring us: based on a biological monitoring study of sanitation workers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24805-9
Liu X, Zhang D, Wu X, Tu J, Gong C, Li Y, Cui W, Chen J, Lu S (2022) Urinary metals as influencing factors of coronary heart disease among a population in Guangzhou. China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241:113746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113746
Luo T, Chen S, Cai J, Liu Q, Gou R, Mo X, Tang X, He K, Xiao S, Wei Y, Lin Y, Huang S, Li T, Chen Z, Li R, Li Y, Zhang Z (2022) Association between combined exposure to plasma heavy metals and dyslipidemia in a chinese population. Lipids Health Dis 21(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-022-01743-6
Mascarenhas P, Furtado JM, Almeida SM, Ferraz ME, Ferraz FP, Oliveira P (2023) Pediatric overweight, fatness and risk for dyslipidemia are related to diet: a cross-sectional study in 9-year-old children. Nutrients 15(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020329
Muthumani M, Prabu SM (2014) Silibinin potentially attenuates arsenic-induced oxidative stress mediated cardiotoxicity and dyslipidemia in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 14(1):83–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-013-9227-x
Papageorgiou M, Merminod F, Ferrari S, Rizzoli R, Biver E (2022) Associations of calcium intake and calcium from various sources with blood lipids in a population of older women and men with high calcium intake. Nutrients 14(6):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061314
Pirillo A, Casula M, Olmastroni E, Norata GD, Catapano AL (2021) Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias. Nat Rev Cardiol 18(10):689–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00541-4
Prasad AS (2014) Zinc: an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: role of zinc in degenerative disorders of aging. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28(4):364–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.07.019
Ranasinghe P, Wathurapatha WS, Ishara MH, Jayawardana R, Galappatthy P, Katulanda P, Constantine GR (2015) Effects of zinc supplementation on serum lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab (lond) 12:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-015-0023-4
Rayman MP (2000) The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet 356(9225):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02490-9
Ruiz-Pesini E, Bayona-Bafaluy MP, Sanclemente T, Puzo J, Montoya J, Pacheu-Grau D (2022) Mitochondrial genetic background may impact statins side effects and atherosclerosis development in familial hypercholesterolemia. Int J Mol Sci 24(1):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010471
Shah AS, Tan L, Long JL, Davidson WS (2013) Proteomic diversity of high density lipoproteins: our emerging understanding of its importance in lipid transport and beyond. J Lipid Res 54(10):2575–2585. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R035725
Shi T, Yang J, Yang B, Cao Y, Ma G (2022) Analysis on selenium content, form and valence in farmland soil of Northern Ningxia. J Ningxia Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 43(01):62–67
Shin SS, Yang EH, Lee HC, Moon SH, Ryoo JH (2022) Association of metabolites of benzene and toluene with lipid profiles in Korean adults: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (2015–2017). BMC Public Health 22(1):1917. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14319-x
Su L, Gao S, Unverzagt FW, Cheng Y, Hake AM, Xin P, Chen C, Liu J, Ma F, Bian J, Li P, Jin Y (2015) Selenium level and dyslipidemia in rural elderly Chinese. PLoS One 10(9):e0136706. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136706
Vavrova S, Struharnanska E, Turna J, Stuchlik S (2021) Tellurium: a rare element with influence on prokaryotic and eukaryotic biological systems. Int J Mol Sci 22(11):5924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115924
Wang Y, Jia XF, Zhang B, Wang ZH, Zhang JG, Huang FF, Su C, Ouyang YF, Zhao J, Du WW, Li L, Jiang HR, Zhang J, Wang HJ (2018) Dietary zinc intake and its association with metabolic syndrome indicators among Chinese adults: an analysis of the China Nutritional Transition Cohort Survey 2015. Nutrients 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050572
Wong SK, Ramli FF, Ali A, Ibrahim N (2022) Genetics of cholesterol-related genes in metabolic syndrome: a review of current evidence. Biomedicines 10(12):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123239
Wu KG, Chang CY, Yen CY, Lai CC (2019) Associations between environmental heavy metal exposure and childhood asthma: a population-based study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 52(2):352–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2018.08.001
Yamauchi H, Aminaka Y, Yoshida K, Sun G, Pi J, Waalkes MP (2004) Evaluation of DNA damage in patients with arsenic poisoning: urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198(3):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2003.10.021
Yu L, Liu W, Wang X, Ye Z, Tan Q, Qiu W, Nie X, Li M, Wang B, Chen W (2022) A review of practical statistical methods used in epidemiological studies to estimate the health effects of multi-pollutant mixture. Environ Pollut 306:119356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119356
Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhang W, Cheng R, Tan A, Shen S, Xiong Y, Zhao L, Lei X (2022) Association between blood lead levels and hyperlipidemiais: results from the NHANES (1999–2018). Front Public Health 10:981749. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.981749
Zhong J, Liu L, Zhang L, Xu Z, Peng L, Zhao X, Yang Q, Yang T, Xu D, Hong F (2022) Association of urinary zinc concentrations with dyslipidemia and its subtypes: baseline data from the Chinese Multi-Ethnic Cohort (CMEC) study. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03454-6
Zhu J, Gao R, Zhao S, Lu G, Zhao D, Li J (2016) Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of dyslipidemia in Adults (2016 Revision ). Chin Circ J 31(10):937–953
Zhu Y, He B, Xiao Y, Chen Y (2019) Iron metabolism and its association with dyslipidemia risk in children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis 18(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-019-0985-8
Zhu X, Fan Y, Sheng J, Gu L, Tao Q, Huang R, Liu K, Yang L, Chen G, Cao H, Li K, Tao F, Wang S (2021) Association between blood heavy metal concentrations and dyslipidemia in the elderly. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(4):1280–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02270-0
Acknowledgements
The authors of this study would like to thank all the participants and staff of this study. The authors of this study would like to thank the editor and reviewers for improving the quality of the manuscript. Thank Siyu Duan for her selfless dedication to the establishment of cohort baseline and the measurement of urinary metals in this study. Thank Dr. Zhang Rui and Dr. Zhao Yi for their support for this project.
Funding
This project was supported by the “Light of the West” Talent Training Plan Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XAB2022YM18), the Natural Science Foundation Project of Ningxia, China (2022AAC05024, 2023AAC02032 and 2022AAC05028), and the Key Research and Development Project of Ningxia (Grant No. 2021BEG02026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhongyuan Zhang: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, data curation. Rui Wang: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft, data curation. Pei He: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data curation. Yuqing Dai: methodology, formal analysis, data curation. Siyu Duan: methodology, formal analysis, data curation. Meiyan Li: investigation. Zhuoheng Shen: investigation. Xiaoyu Li: supervision. Jian Sun: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ningxia Medical University (2021-N0098).
Consent to participate
All the participants signed a free and informed consent form.
Consent for publication
All authors give Environmental Science and Pollution Research permission to publish these research fundings.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhongyuan Zhang, Rui Wang and Pei He contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, R., He, P. et al. Study on the correlation and interaction between metals and dyslipidemia: a case–control study in Chinese community-dwelling elderly. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 105756–105769 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29695-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29695-z