Abstract
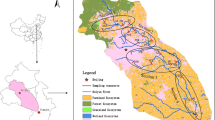
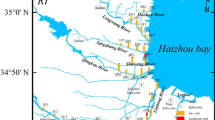
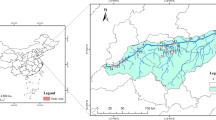
Rural revitalization denotes the gathering of large populations in rural areas and the subsequent gradual urbanization. Rural environments have been deteriorated by heavy metals (HMs) over the last few years. Without the existence of large-scale industries, the accumulation of HMs in sediments due to population aggregation in rural environments needs to be scientifically confirmed. Therefore, in this study we first understand the sediment pollution in rural environments in China and across the globe, and subsequently investigate HMs in sediments in rural micro water. The study area, Sichuan Province, China, was divided into two areas, namely, sparsely populated areas (SPA) and densely populated areas (DPA). Eight typical HMs (As, Zn, Ni, Hg, Cd, Cr, Cu, and Pb) were selected to target in riverine sediments, and the content and spatial distribution characteristics were analyzed. The results indicate that As, Hg, Cd, and Pb concentrations in sediments were higher than background values (BVs), with high concentration sample sites located in the DPA. In addition, the geo-accumulation index (Igeo), pollution load index (PLI) and potential ecological risk index (RI) were used to quantitatively evaluate the pollution characteristics of HMs in sediments, revealing that the sediments exhibited high As and Hg pollution in the DPA (PLI = 1.09). In general, mild (RI = 48.76) and moderate (RI = 154.92) HM pollution was observed in the sediments of the SPA and DPA, respectively, based on the high PLI (> 1.0) and RI (> 150) values. Correlation analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) indicate that the Cd in the sediment generally originated from geogenic sources, while the other elements (Zn, As, Cu, Cr, Hg, Ni and Pb) were primarily linked to anthropogenic sources. Finally, the results demonstrate that population aggregation will lead to the enrichment of HMs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ali AE, Strezov V, Davies PJ, Wright I (2018) River sediment quality assessment using sediment quality indices for the Sydney basin, Australia affected by coal and coal seam gas mining. Sci Total Environ 616:695–702
Argyraki A, Kelepertzis E (2014) Urban soil geochemistry in Athens, Greece: the importance of local geology in controlling the distribution of potentially harmful trace elements. Sci Total Environ 482:366–377
Barkett MO, Akun E (2018) Heavy metal contents of contaminated soils and ecological risk assessment in abandoned copper mine harbor in Yedidalga, Northern Cyprus. Environ Earth Sci 77:378
Bo LJ, Wang DJ, Li TL, Li Y, Zhang G, Wang C, Zhang SQ (2015) Accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic organisms in rural rivers in the Taihu Lake region, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6721–6731
Celis-Hernandez O, Giron-Garcia MP, Ontiveros-Cuadras JF, Canales-Delgadillo JC, Perez-Ceballos RY, Ward RD, Acevedo-Gonzales O, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Merino-Ibarra M (2020) Environmental risk of trace elements in mangrove ecosystems: an assessment of natural vs oil and urban inputs. Sci Total Environ 730:138643
Chaturvedi A, Bhattacharjee S, Singh AK, Kumar V (2018) A new approach for indexing groundwater heavy metal pollution. Ecol Indic 87:323–331
Chen L, Liang S, Liu MD, Yi YJ, Mi ZF, Zhang YX, Li YM, Qi JC, Meng J, Tang X, Zhang HR, Tong YD, Zhang W, Wang XJ, Shu J, Yang ZF (2019) Trans-provincial health impacts of atmospheric mercury emissions in China. Nat Commun 10:1484
Dash S, Borah SS, Kalamdhad AS (2020) Application of positive matrix factorization receptor model and elemental analysis for the assessment of sediment contamination and their source apportionment of Deepor Beel, Assam. Ecol Indic, India, p 114
Franco-Uria A, Lopez-Mateo C, Roca E, Fernandez-Marcos ML (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165:1008–1015
Guo BX, Liu YQ, Zhang F, Hou JZ, Zhang HB, Li CL (2018) Heavy metals in the surface sediments of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3695–3707
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hong AH, Hargan KE, Williams B, Nuangsaeng B, Siriwong S, Tassawad P, Chaiharn C, Los Huertos M (2020) Examining molluscs as bioindicators of shrimp aquaculture effluent contamination in a southeast Asian mangrove. Ecol Indic 115:106365
Huang ZF, Liu CY, Zhao XR, Dong J, Zheng BH (2020) Risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment at the drinking water source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ Sci Eur 32:1–9
Islam MS, Proshad R, Ahmed S (2018) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment of an urban river in Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24:699–720
Jiang YF, Guo X (2019) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of heavy metal pollution from different sources among farmlands in the Poyang Lake region. China J Soils Sediments 19:2472–2484
Jiang YX, Chao SH, Liu JW, Yang Y, Chen YJ, Zhang AC, Cao HB (2017) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 168:1658–1668
Jin YL, O’Connor D, Ok YS, Tsang DCW, Liu A, Hou DY (2019) Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Int 124:320–328
Karimi-Maleh H, Ayati A, Ghanbari S, Orooji Y, Tanhaei B, Karimi F, Alizadeh M, Rouhi J, Fu L, Sillanpaa M (2021) Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: a comprehensive review. J Mol Liq 329:115062
Li HM, Kang XM, Li XM, Li Q, Song JM, Jiao NZ, Zhang YY (2017) Heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China: distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 115:551–558
Li YY, Gao B, Xu DY, Peng WQ, Liu XB, Qu XD, Zhang M (2020) Hydrodynamic impact on trace metals in sediments in the cascade reservoirs, North China. Sci Total Environ 716:136914
Lin Q, Liu EF, Zhang EL, Li K, Shen J (2016) Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena 145:193–203
Liu JL, Li YL, Zhang B, Cao JL, Cao ZG, Domagalski J (2009) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Luan River source water. Ecotoxicology 18:748–758
Maanan M, Saddik M, Maanan M, Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2015) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol Indic 48:616–626
Mendiguchía C, Moreno C, Mánuel-Vez MP, García-Vargas M (2006) Preliminary investigation on the enrichment of heavy metals in marine sediments originated from intensive aquaculture effluents. Aquaculture 254:317–325
Mirzaei M, Hatamimanesh M, Haghshenas A, Moghaddam SM, Ozunu A, Azadi H (2020) Spatial-seasonal variations and ecological risk of heavy metals in Persian gulf coastal region: case study of Iran. J Environ Health Sci 18:91–105
Rodriguez Martin JA, Arias ML, GrauCorbi JM (2006) Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geoestatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex: 1987) 144:1001–12
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments-A case study: Mahanadi basin. India J Hazard Mater 186:1837–1846
Tian K, Wu QM, Liu P, Hu WY, Huang B, Shi B, Zhou YQ, Kwon BO, Choi K, Ryu J, Khim JS, Wang TY (2020) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ Int 136:105512
Tunca E, Aydin M, Sahin UA (2018) An ecological risk investigation of marine sediment from the northern Mediterranean coasts (Aegean Sea) using multiple methods of pollution determination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7487–7503
Wang YZ, Duan XJ, Wang L (2020) Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci Total Environ 710:134953
Xia WT, Wang R, Zhu B, Rudstam LG, Liu YL, Xu YX, Xin W, Chen YS (2020) Heavy metal gradients from rural to urban lakes in central China. Ecol Process 9:1
Xiao R, Bai JH, Huang LB, Zhang HG, Cui BS, Liu XH (2013) Distribution and pollution, toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from urban and rural rivers of the Pearl River delta in southern China. Ecotoxicology 22:1564–1575
Yan CY, Zhuang T, Bai JH, Wen XJ, Lu QQ, Zhang L (2020) Assessment of As, Cd, Zn, Cu and Pb Pollution and Toxicity in River Wetland Sediments and Artificial Wetland Soils Affected by Urbanization in a Chinese Delta. Wetlands 40:2799–2809
Yi YJ, Sun J, Tang CH, Zhang SH (2016) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment in the upper reach of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11002–11013
Zhang ZX, Karimi-Maleh H (2023a) In situ synthesis of label-free electrochemical aptasensor-based sandwich-like AuNPs/PPy/Ti3C2Tx for ultrasensitive detection of lead ions as hazardous pollutants in environmental fluids. Chemosphere 324:138302
Zhang ZX, Karimi-Maleh H (2023b) Label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles/titanium carbide MXene for lead detection with its reduction peak as index signal. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6:68
Zhang C, Shan BQ, Tang WZ, Dong LX, Zhang WQ, Pei YS (2017) Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotox Environ Safe 139:263–271
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Science Foundation of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42107481), the Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Science and Technology (2021YFS0289), and the Research Foundation of Southwest University of Science and Technology (20ZX7150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi Zhou: Writing-original draft, Data curation. Shushu Guo, Wanping Zhang: Investigation, Data curation. Yuankun Yang, Bin Wang, Jingping Zhu: Supervision, Methodology. Shu Chen: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Christian Gagnon
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Guo, S., Zhang, W. et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in riverine sediments of rural area driven by urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 92193–92205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28772-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28772-7