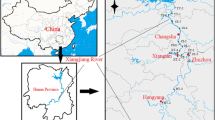
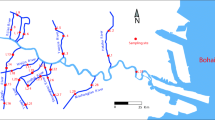
Abstract
The Haizhou Bay in eastern China, for a long time, is seriously polluted with heavy metals (HMs) due to intensive anthropic pressure. The river runoff is the dominant pathway of HM transport in the coastal region. However, the information on HM pollution in coastal rivers flowing into Haizhou Bay was still limited, and potential risks and possible sources raised by HMs in this area were neglected up to now. To fully understand the distribution and ecological risks of sediments in seven rivers along the bay, surface sediments were collected and seven HMs (Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb) were investigated. The results showed that HM concentrations generally met the primary standard criteria of China (marine sediment quality), except for Cu and Zn. On the other hand, Zn and Cu tended to exhibit probable adverse biological effects in the Shawang River comparison with some sediment quality guidelines (SQGs). Moreover, the enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index demonstrated that there was no or slight contamination to be found for Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb and moderate pollution for Cd. The contamination factor (Cfi), integrated contamination degree (CF), modified degree of contamination (mCd), and modified pollution index (MPI) revealed individual metal contamination in localized areas. In these river sediments, the potential ecological risk (RI) was low to moderate, except Cd posted a considerable ecological risk because of its high enrichment. Furthermore, the Shawang River and Linhong River were seriously polluted with HMs among seven rivers. These results provided a new direction for controlling HM pollution in Haizhou Bay which suggested substantial measures should be implemented to alleviate the potential risk of HMs, to these rivers sediments.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
References
Arnason JG, Fletcher BA (2003) A 40+ year record of Cd, Hg, Pb, and U deposition in sediments of Patroon Reservoir, Albany County, NY, USA. Environ Pollut 123:383–391
Birch GF, Apostolatos C (2013) Use of sedimentary metals to predict metal concentrations in black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) tissue and risk to human health (Sydney estuary, Australia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5481–5491
Brady JP, Ayoko GA, Martens WN, Goonetilleke A (2014) Enrichment, distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediments of Deception Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 81:248–255
Brady JP, Ayoko GA, Martens WN, Goonetilleke A (2015) Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–14
Burton JGA (2002) Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 3:65–76
Chen BB, Hu RQ, Chen MD (1985) The natural background-values of environmental elements in the beach soils of Jiangsu province. (in Chinese). J Nanjing Agric Univ 3:54–60
Chi QH, Yan MC (2007) Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry (in Chinese). Geological Publishing House, Beijing
China State Bureau of Technical Supervision (2002) GB18668-2002 marine sediment quality. Standards Press of China, Beijing
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37:4311–4330
Duan X, Li Y (2017) Distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24753–24764
Farkas A, Erratico C, Vigano L (2007) Assessment of the environmental significance of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments of the River Po. Chemosphere 68:761–768
Feng ZH, Zhang T, Li Y, He XR, Wang R, Xu JT, Gao G (2019) The accumulation of microplastics in fish from an important fish farm and mariculture area, Haizhou Bay, China. Sci Total Environ 696:133948
Gan H, Lin J, Liang K, Xia Z (2013) Selected trace metals (As, Cd and Hg) distribution and contamination in the coastal wetland sediment of the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 66:252–258
Gao S, Luo TC, Zhang BR, Zhang HF, Han YW, Zhao ZD, Hu YK (1998) Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:1959–1975
Garrels RM, Mackenzie FT (1971) Evolution of sedimentary rocks. Norton, New York, p 450
Godarzi NM, Shahbazi K, Grigoryan K (2012) The study of mercury pollution distribution around a chlor-alkali petrochemical complex, Bandar Imam, southern Iran. Environ Earth Sci 67:1485–1492
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control — a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Han D, Cheng J, Hu X, Jiang Z, Mo L, Xu H, Ma Y, Chen X, Wang H (2017) Spatial distribution, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 115:141–148
Han B, Lin FX, Ding Y, Zheng L (2018) Distribution characteristics, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Haizhou Bay, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24:847–858
He XR, Wang J (2008) The evaluation of heavy pollution of surface layer deposit in the river of Lianyun Port City with geological accumulated index. (in Chinese). Inner Mongol Environ Sci 20:80–84
He XR, Fu YS, Liu R (2007) Pollution of heavy metals and their potential ecological risk in surface sediments from rivers in Lianyungang. (in Chinese). J Huaihai Inst Technol (Nat Sci Ed) 01:47–50
Li Y, Li HG (2017) Historical records of trace metals in core sediments from the Lianyungang coastal sea, Jiangsu, China. Mar Pollut Bull 116:56–63
Li Y, Feng ZH, Li GQ, Yan BL (2010) The estimation of source of heavy metal contamination and assessment in marine sediments in Lianyungang area. (in Chinese). Oceanol Limnol Sin 41:829–833
Li Y, Li HG, Liu FC (2017) Pollution in the urban soils of Lianyungang, China, evaluated using a pollution index, mobility of heavy metals, and enzymatic activities. Environ Monit Assess 189:34
Li Y, Liu FC (2015) Heavy metal concentrations and enzymatic activities in the functional zone sediments of Haizhou Bay, Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China. Environ Monit Assess 187:660
Liaghati T, Preda M, Cox M (2004) Heavy metal distribution and controlling factors within coastal plain sediments, Bells Creek catchment, southeast Queensland, Australia. Environ Int 29:935–948
Linkov I, von Stackelberg KE, Burmistrov D, Bridges TS (2001) Uncertainty and variability in risk from trophic transfer of contaminants in dredged sediments. Sci Total Environ 274:255–269
Liu B, Wang J, Xu M, Zhao L, Wang Z (2019a) Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Haizhou Bay national ocean park, China. Mar Pollut Bull 149:110651
Liu QX, Jia ZZ, Li SY, Hu JT (2019b) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and quantitative source apportionment in surface sediments along a partially mixed estuary (Modaomen, China). Chemosphere 225:829–838
Liu BQ, Xu M, Wang J, Wang ZF, Zhao L (2021) Ecological risk assessment and heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 163:111954
Luo LL, Mei K, Qua LY, Zhang C, Chen H, Wang SY, Di D, Huang H, Wang ZF, Xia F, Dahlgren RA, Zhang MH (2019) Assessment of the Geographical Detector Method for investigating heavy metal source apportionment in an urban watershed of Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 653:714–722
Macdonald DD, Carr RS, Calder FD, Long ER, Ingersoll CG (1996) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 5:253–278
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Dvelopment and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Martin J-M, Meybeck M (1979) Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar Chem 7:173–206
Milliman JD, Farnsworth KL (2011) River discharge to the coastal ocean: a global synthesis. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 392
Mucha AP, Vasconcelos MTSD, Bordalo AA (2003) Macrobenthic community in the Douro estuary: relations with trace metals and natural sediment characteristics. Environ Pollut 121:169–180
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Naser HA (2013) Assessment and management of heavy metal pollution in the marine environment of the Arabian Gulf: A review. Mar Pollut Bull 72:6–13
Nguyen BT, Do DD, Nguyen TX, Nguyen VN, Phuc Nguyen DT, Nguyen MH, Thi Truong HT, Dong HP, Le AH, Bach QV (2019) Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River, Vietnam. Environ Pollut 256:113412
Ramesh R, Chen Z, Cummins V, Day J, D’Elia C, Dennison B, Forbes DL, Glaeser B, Glaser M, Glavovic B, Kremer H, Lange M, Larsen JN, Le Tissier M, Newton A, Pelling M, Purvaja R, Wolanski E (2015) Land–ocean interactions in the coastal zone: Past, present & future. Anthropocene 12:85–98
Rubio B, Nombela MA, Vilas F (2000) Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain): An assessment of metal pollution. Mar Pollut Bull 40:968–980
Sarkar SK, Mondal P, Biswas JK, Kwon EE, Ok YS, Rinklebe J (2017) Trace elements in surface sediments of the Hooghly (Ganges) estuary: distribution and contamination risk assessment. Environ Geochem Health 39:1245–1258
Shi YJ, Xu XB, Li QF, Zhang M, Li J, Lu YL, Liang LY, Zheng XQ, Shao XQ (2018) Integrated regional ecological risk assessment of multiple metals in the soils: a case in the region around the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ Pollut 242:288–297
Sun X, Fan D, Liu M, Tian Y, Pang Y, Liao H (2018) Source identification, geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ Pollut 241:938–949
Sun L, Wang J, Zhang HF, Xu M (2020) The characteristics and mechanism of changes in the marine environmental capacity of the estuaries of Haizhou Bay in northern Jiangsu from 2006 to 2016. J Mar Sci Eng 8:787
Teng YG, Yang J, Zuo R, Wang JS (2011) Impact of urbanization and industrialization upon surface water quality: a pilot study of Panzhihua mining town. J Earth Sci China 22:658–668
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang SL, Xu XR, Sun YX, Liu JL, Li HB (2013) Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 76:7–15
Wang Y, Duan X, Wang L (2020a) Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci Total Environ 710:134953
Wang X, Fu R, Li H, Zhang Y, Lu M, Xiao K, Zhang X, Zheng C, Xiong Y (2020b) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments: a comprehensive, large-scale evaluation for the Bohai Sea, China. Environ Pollut 260:113986
Wang X, Liu B, Zhang W (2020c) Distribution and risk analysis of heavy metals in sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:10802–10810
Yang SL, Li L, Chen LG, Chen LQ, Shen ZP (2018) Improving ASTER GDEM accuracy using land use-based linear regression methods: a case study of Lianyungang, East China. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 4:145
Ye Z, Chen J, Gao L, Liang Z, Li S, Li R, Jin G, Shimizu Y, Onodera S-I, Saito M, Gopalakrishnan G (2020) 210Pb dating to investigate the historical variations and identification of different sources of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 150:110670
Zhang M, Sun X, Xu J (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the East China Sea: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111473
Zhang R, Guan ML, Shu YJ, Shen LY, Chen XX, Zhang F, Li TG (2016) Historical record of lead accumulation and source in the tidal flat of Haizhou Bay, Yellow Sea: insights from lead isotopes. Mar Pollut Bull 106:383–387
Zhang R, Zhang F, Zhang TC (2013a) Sedimentary records of PAHs in a sediment core from tidal flat of Haizhou Bay, China. Sci Total Environ 450:280–288
Zhang R, Zhang F, Ding Y, Gao J, Chen J, Zhou L (2013b) Historical trends in the anthropogenic heavy metal levels in the tidal flat sediments of Lianyungang, China. J Environ Sci 25:1458–1468
Zhang R, Zhang F, Zhang TC, Yan HQ, Shao W, Zhou L, Tong HB (2014) Historical sediment record and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from tidal flats of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 89:487–493
Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhang F, Ding Y, Gao J, Chen J, Yan H, Shao W (2013c) Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 74:403–412
Zhao G, Ye S, Yuan H, Ding X, Wang J (2017) Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2966–2979
Zhao WJ, Zhu XD, Sun X, Shu YQ, Li YF (2015) Water quality changes in response to urban expansion: spatially varying relations and determinants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16997–17011
Zhang YM, Wang J, Meng K, Qiu YF (2019) Changes of heavy metal content in sediments at Haizhou bay and risk assessment. Ecol Environ Res 17:11327–11339
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Marine Special Program of Jiangsu Province in China (JSZRHYKJ202007), the National Natural Science Foundation (U1901215), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41771218; 41271228), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST (No. 2020r047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Longjiang Mao;
Methodology: Zhihai Tan, Wanzhu Feng;
Formal analysis and investigation: Xiaoqian Deng, Longjiang Mao, …;
Writing — original draft preparation: Xiaoqian Deng;
Writing — review and editing: Longjiang Mao, Yuling Wu;
Funding acquisition: Longjiang Mao;
Resources: Longjiang Mao, Yuanzhi Zhang;
Supervision: Longjiang Mao, Yuling Wu, Yuanzhi Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V. V. S. S. Sarma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, X., Mao, L., Wu, Y. et al. Pollution, risks, and sources of heavy metals in sediments from the urban rivers flowing into Haizhou Bay, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 38054–38065 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18151-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18151-5