Abstract
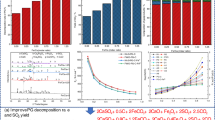
Phosphogypsum (PG), which has great environmental harm and restricts the sustainable development of phosphorus chemical industry, is a solid waste produced in phosphoric acid production. Thermal decomposition of PG is an extensive way to reutilization of resource, and the key point is to establish an appropriate decomposition path and catalyst system of PG. In the work, the strategy for low-temperature and highly-efficient decomposition of PG is established based on the thermodynamic analysis and the experimental research by metal ions to reduce the decomposition temperature. Meanwhile, SEM(Scanning Electron Microscope) is used to characterize the composition and morphology of PG in the various conditions, also the decomposition temperature is analyzed by TGA(Thermogravimetric Analysis). Then, the decomposition ratio via Fe3+/Co2+/Ni2+ unitary/ternary catalyst is obtained by precipitation method. Through kinetic analysis combined with XRF(X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer) and EDX(Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy) results, it is found that there is a reaction competition in the decomposition process by Fe3+/Co2+/Ni2+ ternary catalyst. Further the mechanism of catalytic system on PG is derived. The present work can be concluded that Fe3+/Co2+/Ni2+ can effectively reduce the decomposition temperature of PG, and the effect of ternary metal is more obvious than that of unitary metal. Finally, pomelo peel is used instead of coke to successfully decompose PG at low temperature by one step method. The establishment of low temperature decomposition system of PG has potential application in phosphorus chemical industry and is in line with sustainable development.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Apaydin-Varol E, Uzun BB, Önal E, Pütüna AE (2014) Synthetic fuel production from cottonseed: Fast pyrolysis and a TGA/FT-IR/MS study. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 105:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2013.10.006
Canut MM, Jacomino VM, Bråtveit K, Gomes AM, Yoshida MI (2008) Microstructural analyses of phosphogypsum generated by Brazilian fertilizer industries. Mater Charact 59(4):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2007.02.001
Chen QJ, Ding WJ, Sun HJ, Peng TJ, Ma GH (2020) Utilization of phosphogypsum to prepare high-purity CaCO3 in the NH4Cl-NH4OH-CO2 system. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(31):11649–11657. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c03070
Coats AW, Redfern JP (1964) Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 201(4914):68–69
Di ZC, Yang FL, Cao Y, Zhang K, Guo YX, Gao SL, Cheng FQ (2019) The transformation pathways on the catalytic and stability-promoted CaSO4 reduction in CLC process using Fe2O3 supported. Fuel 253:327–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.141
Ding WJ, Chen QJ, Sun HJ, Peng TJ (2019) Modified mineral carbonation of phosphogysum for CO2 sequestration. J CO2 Utilization 34:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2019.08.002
Du BX, Huang K (2013) The Research on Comprehensive Utilization of Phosphogypsum. Adv Mater Res 850–851:1368–1371. https://doi.org/10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMR.850-851.1368
Gan ZX, Cui Z, Yue HR, Tang SY, Liu CJ, Li C, Liang B, Xie HP (2016) An efficient methodology for utilization of K-feldspar and phosphogypsum with reduced energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Chin J Chem Eng 24(11):1541–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2016.04.001
Gong S, Li XL, Song FX, Lu DH, Chen QL (2020) Preparation and Application in HDPE of Nano-CaSO4 from Phosphogypsum. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(11):4511–4520. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07632
Han XY, Chen HK, Li BQ (2000) Thermogravimetric study on the reductive decomposition of calcium sulfate with pure H2 at high temperature. Coal Convers 23:72. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2000.02.014
He HW, Hao LF, Fan CG, Li SG, Lin WG (2022) A two-step approach to phosphogypsum decomposition: Oxidation of CaS with CO2. Thermochim Acta 708:179122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2021.179122
Joseph HF, Leo AW (1966) A quick direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polym Lett 4:322–328
Kais A, Mohamed J (2018) A thermogravimetric study into the effects of additives and water vapor on the reduction of gypsum and Tunisian phosphogypsum with graphite or coke in a nitrogen atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim 132(1):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6871-6
Khaghanikavkani E, Farid MM (2011) Thermal pyrolysis of polyethylene: kinetic study. Energy Sci Technol 2(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3968/j.est.1923847920110201.597
Lü L, Li C, Zhang GQ, Hu XW, Liang B (2018) Decomposition behavior of CaSO4 during potassium extraction from a potash feldspar-CaSO4 binary system by calcination. Chin J Chem Eng 26(4):838–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.10.001
Lu DH, Chen QL, Li CQ, Gong S (2021) Effect of potassium feldspar on the decomposition rate of phosphogypsum. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 96:374–383. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6549
Lutskiy D, Litvinova T, Ignatovich A, Fialkovskiy I (2018) Complex processing of phosphogypsum-a way of recycling of dumps with reception of commodity production of wide application. J Eco Eng 19(2):221–225. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/83562
Ma GF, Yang PF (2018) Analysis on Comprehensive Treatment Approaches of Phosphorus Gypsum. Chem Fertilizer Design 56(03):42–45
Ma LP, Ning P, Zheng SC, Niu XK, Zhang W, Du YL (2010) Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Analysis of the Decomposition of Phosphogypsum via a Solid-State Reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:3597–3602. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie901950y
Ma LP, Niu XK, Hou J, Zheng DL, Xu WJ (2011) Reaction mechanism and influence factors analysis for calcium sulfide generation in the process of phosphogypsum decomposition. Thermochim Acta 526(1/2):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2011.09.013
Ma LP, Du YL, Niu XK, Zheng SC, Zhang W (2012) Thermal and Kinetic Analysis of the Process of Thermochemical Decomposition of Phosphogypsum with CO and Additives. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(19):6680–6685. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2029859
Merwea EM, Strydoma CA, Potgieter JH (1999) Thermogravimetric analysis of the reaction between carbon and CaSO4⋅2H2O, gypsum and phosphogypsum in an inert atmosphere. Thermochim Acta 340–341:431–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(99)00287-7
Motaung SR, Zvimba JN, Maree JP, Kolesnikov AV (2015) Thermochemical reduction of pelletized gypsum mixed with carbonaceous reductants. Water SA 41(3):369–374. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v41i3.08
Ozawa T (1965) A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 38:1881–1886
Ozawa T (1986) Application of friedman plot. J Therm Anal 31(3):547–551
Ozawa T (1992) Estimation of activation energy by isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta 203(1):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(92)85192-x
Pérez-López R, Macías F, Cánovas CR, Sarmiento AM, Pérez-Moreno SM (2016) Pollutant flows from a phosphogypsum disposal area to an estuarine environment: an insight from geochemical signatures. Sci Total Environ 553:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.070
Pilawka R, Maka H (2014) Kinetics of thermal decomposition of isocyanate-epoxy materials crosslinked in the presence of 1-ethylimidazole accelerator. Polimery 59(5):409–145. https://doi.org/10.14314/polimery.2014.409
Sbirrazzuoli N, Vincent L, Vyazovkin S (2000) Comparison of several computational procedures for evaluating the kinetics of thermally simulated condensed phase reactions. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 54:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(00)00103-9
Shafiee M, Foroutan R, Fouladi K, Ahmadlouydarab M, Ramavandi B, Sahebi S (2018) Application of oak powder/Fe3O4 magnetic composite in toxic metals removal from aqueous solutions. Adv Powder Technol S0921883118305806-. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.12.006
Szekely JL, Evans JW, Sohn HY (1976) Gas-solid reactions. Academic Press, New York
Tan HB, Dong FQ, Liu JF, Wang J, He XC (2018) Effects of impurities from phosphogypsum on the crystal growth of calcium sulfate hemihydrates. Mater Technol 52(5):633–637. https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2018.082
Tayibi H, Choura M, López FA, Alguacil FJ, López-Delgado A (2009) Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J Environ Manag 90(8):2377–2386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.03.007
Vyazovkin S, Wight CA (1999) Model-free and model-fitting approaches to kinetic analysis of isothermal and nonisothermal data. Thermochim Acta 340–341:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(99)00253-1
Wang XX, Ran XL, Liu SW, Wu YX (2010) Experimental study on the analytical method for calcium sulfate in phosphogysum. J Wuhan Inst Tech 32(05):41–44. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2010.05.012
Wu FH, Chen BJ, Qu GF, Liu S, Zhao CY, Ren YC, Liu XX (2022) Harmless treatment technology of phosphogypsum: directional stabilization of toxic and harmful substances. J Environ Manag 311:114827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114827
Xiao HP, Zhou JH, Cao XY (2005) Experiments and model of the decomposition of CaSO4 under CO atmosphere. J Fuel Chem Technol 33:150. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.02.005
Yan B, Ma LP, Xie LG, Ma J, Zi ZC, Yan XD (2013) Reaction Mechanism for Iron Catalyst in the Process of Phosphogypsum Decomposition. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(49):17383–17389. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie403321w
Yan B, Ma LP, Ma J (2014) Mechanism Analysis of Ca, S Transformation in Phosphogypsum Decomposition with Fe Catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(18):7648–7654. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie501159y
Yang J, Wei Y, Yang J, Xiang HP, Ma LP, Zhang W, Wang LC, Peng YH, Liu HP (2019a) Syngas production by chemical looping gasification using Fe supported on phosphogypsum compound oxygen carrier. Energy 168(Feb.1):126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.106
Yang J, Zhu B, Ma LP, Liu HP (2019b) Investigation of Al2O3 and Fe2O3 transmission and transformation during the decomposition of phosphogypsum. Chin J Chem Eng 27(5):1125–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.09.023
Zhang J, Wei C, Ran JY, Li Y, Chen JJ (2022) Properties of polymer composite with large dosage of phosphogypsum and it’s application in pipeline. Polym Test 116:107742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2022.107742
Zheng SC, Ning P, Ma LP, Niu XK, Zhang W, Chen YH (2011) Reductive decomposition of phosphogypsum with high-sulfur-concentration coal to SO2 in an inert atmosphere. Chem Eng Res Des 89(12):2736–2741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2011.03.016
Zheng DL, Ma LP, Wang RM, Yang J, Dai QX (2018) Research on thermal decomposing properties of phosphogypsum with Fe addition under multi-atmosphere control. Thermochim. Acta 66159–66166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.01.011
Acknowledgements
The authors sincere thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions to improve the article quality.
Funding
This work was supported by Post-doctoral Scientific Research Station of Wengfu (Group) Co., Ltd, National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Mineral Salt Deep Utilization and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant numbers [YF(2020)022], [SF201906] and [2023YFS0359, 23ZDYF1088]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qin Luo proposed the idea of the research and engaged in experimental research, data analysis, manuscript preparation and revision. Weijun Wang and Boli Zeng mainly engaged in raw material preparation, research and analysis. Qiulin Deng mainly engaged in research idea, manuscript editing, revision work. Huiwei Liao, Hongbin Tan and Faqin Dong conducted the research guidance and revisions. Chenli Luo, Junhong Tu and Liangxian Wu mainly engaged in revision work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Author disclosure statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Q., Deng, Q., Liao, H. et al. Low temperature and highly-efficient one-step decomposition of phosphogypsum via biochar by Fe3+/Co2+/Ni2+ unitary/ternary catalyst. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 90787–90798 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28754-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28754-9