Abstract
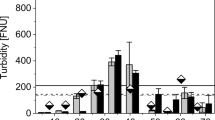
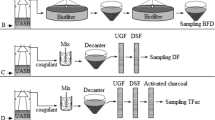
This study investigated the performance of a granular filtration system (GFS) composed of a rock filter (RF), a rapid sand filter (RSF), and an activated carbon filter (ACF), applied to the post-treatment of an anaerobic reactor effluent. Four filtration rates (FR) were applied to the GFS (in m3·m−2·d−1): 100–60-60, 100–90-90, 200–120-120, and 200–160-160, for RF-RSF-ACF, respectively. A clarified final effluent with low turbidity (~ 10 NTU), solids (~ 6.5 mg TSS.L−1), and organic matter content (~ 40 mg COD.L−1) was obtained when the GFS worked with FR up to 100–90-90 m3·m−2·d−1. For higher FR, the effluent quality was a little poorer. Principal component analysis showed when the RSF operated at 120 or 160 m3·m−2·d−1, it presented an effluent with higher turbidity which did not affect negatively the ACF performance. The hydraulic load limits in the RSF were reached in periods of 45, 30, and 24.5 h for the FR of 60, 120, and 160 m3·m−2·d−1, respectively, and head loss analysis depicted a more distributed solid retention through the sand depth with the lower FR. Thus, the results revealed that the RF-RSF-ACS system is a promising alternative for effluent polishing of anaerobic reactor, especially when the FR is set at 90 m3·m−2·d−1 or even higher.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data were generated at the Federal University of Pernambuco and are available at https://repositorio.ufpe.br/handle/123456789/29106. Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author [Wanderli Rogério Moreira Leite].
Abbreviations
- ACF :
-
activated carbon filter
- ACF1, 2, 3, 4 :
-
activated carbon filter under operational condition 1, 2, 3, 4
- EColi :
-
Escherichia coli
- FR :
-
filtration rate
- FR1, 2, 3, 4 :
-
Filtration rates applied to each filter under operational condition 1, 2, 3, 4
- GFS :
-
granular filtration system
- GFS1, 2, 3, 4 :
-
granular filtration system under operational condition 1, 2, 3, 4
- GAC :
-
granular activated carbon
- HL :
-
head loss
- MPN :
-
most probable number
- PCA :
-
principal component analysis
- PC1, 2, 3 :
-
principal component 1, 2, 3
- p-value :
-
descriptive level of probability test
- P1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 :
-
piezometer 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
- PVC :
-
polyvinyl chloride
- R 2 :
-
coefficient of linear regression fit
- RF :
-
rock filter
- RHL :
-
relative head loss
- RSF :
-
rapid sand filter
- RSF1, 2, 3, 4 :
-
rapid sand filter under operational condition 1, 2, 3, 4
- RSF-ACF :
-
rapid sand filter and activated carbon filter set
- SCOD :
-
soluble chemical oxygen demand
- TCOD :
-
total chemical oxygen demand
- TColi :
-
total coliforms
- TSS :
-
total suspended solids
- TURB :
-
turbidity
- UASB :
-
upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor
References
Altman J, Rehfeld D, Träder K, Sperlich A, Jekel M (2016) Combination of granular activated carbon adsorption and deep-bed filtration as a single advanced wastewater treatment step for organic micropollutant and phosphorus removal. Water Res 92:131–139
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd ed. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Bai R, Tien C (1997) Particle detachment in deep bed filtration. J Colloid Interface Sci 186(2):307–317
Banejad H, Pirtaj Hamedany R, Daneshi N (2010) Evaluate of head loss, sediment value and iron removal in rapid sand filter. J Am Sci 6(12):1218–1226
Bombardelli WW, Camargo APD, Frizzone JA, Lavanholi R, Rocha HSD (2019) Local head loss caused in connections used in micro-irrigation systems. Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambient 23(7):492–498
BRASIL (2005) Resolução CONAMA (Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente). Resolution Nº. 357 of March 17, 2005. Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil, Brasilia. 2005 (in Portuguese)
Bressani-Ribeiro T, Brandt EMF, Gutierrez KG, Díaz CA, Garcia GB, Chernicharo CAL (2017) Potential of resource recovery in UASB/trickling filter systems treating domestic sewage in developing countries. Water Sci Technol 75(7):1659–1666
Butkovskyi A, Sevenou L, Meulepas RJW, Hernandez Leal L, Zeeman G, Rijnaarts HHM (2018) Micropollutant removal from black water and grey water sludge in a UASB-GAC reactor. Water Sci Technol 77(4):1137–1148
Camper AK, LeChevallier MW, Broadaway SC, McFeters GA (1985) Growth and persistence of pathogens on granular activated carbon filters. Appl Environ Microbiol 50(6):1378–1382
Cavallini GS, Sousa Vidal CM, Souza JB, Campos SX (2016) Post-treatment of anaerobic reactor effluent using coagulation/oxidation followed by double filtration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(7):6244–6252
Crittenden JC, Trussell RR, Hand DW, Howe KJ, Tchobanoglous G (2012) MWH’s water treatment: principles and design, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, p 1920
Cruz LMO, Gomes BGLA, Tonetti AL, Figueiredo ICS (2019) Using coconut husks in a full-scale decentralized wastewater treatment system: the influence of an anaerobic filter on maintenance and operational conditions of a sand filter. Ecol Eng 127:454–459
Dorji U, Tenzin U, Dorji P, Pathak N, Johir MA, Volpin F, Dorji C, Chernicharo CAL, Tijing L, Shon H, Phuntsho S (2021) Exploring shredded waste PET bottles as a biofilter media for improved on-site sanitation. Process Saf Environ Prot 148:370–381
Elbana M, Cartagena FR, Puig-Bargués J (2012) Effectiveness of sand media filters for removing turbidity and recovering dissolved oxygen from a reclaimed effluent used for micro-irrigation. Agric Water Manage 111:27–33
Florencio L, Kato MT, Morais JC (2001) Domestic sewage treatment in full-scale UASB plant at Mangueira, Recife. Pernambuco Water Sci Technol 44(4):71–77
Florencio L, Bastos RKX, Aisse MM (2006) Treatment and use of domestic sewage. PROSAB, Rio de Janeiro - RJ, ABES, p 427 (in Portuguese)
Foresti E, Zaiat M, Vallero M (2006) Anaerobic processes as the core technology for sustainable domestic wastewater treatment: consolidated applications, new trends, perspectives, and challenges. Rev Environ Sci Bio/technol 5(1):3–19
Gaur RZ, Khan AA, Lew B, Diamantis V, Kazmi AA (2017) Performance of full-scale UASB reactors treating low or medium strength municipal wastewater. Environ Processes 4(1):137–146
George JP, Chen Z, Shaw P (2009) Fault detection of drinking water treatment process using PCA and Hotelling’s T2 chart. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 50:970–975
Hamoda MF, Al-Ghusain I, Al-Mutairi NZ (2004) Sand filtration of wastewater for tertiary treatment and water reuse. Desalination 164(3):203–211
Hoslett J, Massara TM, Malamis S, Ahmad D, van den Boogaert I, Katsou E, Ahmad B, Ghazal H, Simons S, Wrobel L, Jouhara H (2018) Surface water filtration using granular media and membranes: a review. Sci Total Environ 639:1268–1282
Jackson DA (1993) Stopping rules in principal components analysis: a comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology 74:2204–2214
Jusoh A, Rajiah MNA, Nora’aini A, Azizah E (2011) Determination of head loss progress in dual-media BOPS-sand filter using numerical modeling incorporated with matrix approach. Desalin. Water Treat. 32(1–3):33–41
Kawamura S (1999) Design and operation of high-rate filters. J Am Water Works Assoc 91(12):77–90
Khan AA, Gaur RZ, Tyagi VK, Khursheed A, Lew B, Mehrotra I, Kazmi AA (2011) Sustainable options of post treatment of UASB effluent treating sewage: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(12):1232–1251
Kharel S, Stapf M, Miehe U, Ekblad M, Cimbritz M, Falås P, Nilsson J, Sehlén R, Bregendahl J, Bester K (2021) Removal of pharmaceutical metabolites in wastewater ozonation including their fate in different post-treatments. Sci Total Environ 759:143989
Koivunen J, Siitonen A, Heinonen-Tanski H (2003) Elimination of enteric bacteria in biological–chemical wastewater treatment and tertiary filtration units. Water Res 37(3):690–698
Kumar P, Rehab H, Hegde K, Brar SK, Cledon M, Kermanshahi-Pour A, Duy SV, Sauvé S, Surampalli RY (2020) Physical and biological removal of microcystin-LR and other water contaminants in a biofilter using manganese dioxide coated sand and graphene sand composites. Sci Total Environ 703:135052
Leite WRM, Belli Filho P, Gottardo M, Pavan P, Bolzonella D (2018) Monitoring and control improvement of single and two stage thermophilic sludge digestion through multivariate analysis. Waste Biomass Valorization 9(6):985–994
Linhares BD (2017) Granular filters (sand and activated carbon) for post-treatment of anaerobic effluent. Master’s dissertation, Postgraduate Program in Civil Engineering, Federal University of Pernambuco (in Portuguese)
Mahanna H, Fouad M, Radwan K, Elgamal H (2015) Predicting of effluent turbidity from deep bed sand filters used in water treatment. Int J Sci Eng Res 6(9):621–626
Mauclaire L, Schürmann A, Thullner M, Zeyer J, Gammeter S (2004) Sand filtration in a water treatment plant: biological parameters responsible for clogging. J Water Supply: Res Technology-Aqua 53(2):93–108
Melo ARB (2014) Post-treatment of UASB reactor effluent by sand filtration and activated carbon. Master’s dissertation, Postgraduate Program in Civil Engineering, Federal University of Pernambuco (in Portuguese)
Mesquita M, Testezlaf R, Ramirez JS (2012) The effect of media bed characteristics and internal auxiliary elements on sand filter head loss. Agric Water Manage 115:178–185
Moussavi G, Kazembeigi F, Farzadkia M (2010) Performance of a pilot scale up-flow septic tank for on-site decentralized treatment of residential wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 88(1):47–52
Ncube P, Pidou M, Stephenson T, Jefferson B, Jarvis P (2018) Consequences of pH change on wastewater depth filtration using a multimedia filter. Water Res 128:111–119
Paredes L, Fernandez-Fontaina E, Lema JM, Omil F, Carballa M (2016) Understanding the fate of organic micropollutants in sand and granular activated carbon biofiltration systems. Sci Total Environ 551–552:640–648
Racar M, Dolar D, Špehar A, Košutić K (2017) Application of UF/NF/RO membranes for treatment and reuse of rendering plant wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 105:386–392
Rajala RL, Pulkkanen M, Pessi M, Heinonen-Tanski H (2003) Removal of microbes from municipal wastewater effluent by rapid sand filtration and subsequent UV irradiation. Water Sci Technol 47(3):157–162
Salcedo JC, Testezlaf R, Mesquita M (2011) Backwash process in sand filters used in localized irrigation. Eng Agric 31(6):1226–1237 ((in Portuguese))
Saliba PD, Von Sperling M (2017) Performance evaluation of a large sewage treatment plant in Brazil, consisting of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor followed by activated sludge. Water Sci Technol 76(8):2003–2014
Santos MVAD, Morais JCD, Veras STS, Leite WRM, Gavazza S, Florencio L, Kato MT (2021) Hybrid anaerobic and aerobic reactors for organic matter and nitrogen removal in diluted domestic sewage. Eng Sanit Ambiental 26(3):591–600
Sbardella L, Comas J, Fenu A, Rodriguez-Roda I, Weemaes M (2018) Advanced biological activated carbon filter for removing pharmaceutically active compounds from treated wastewater. Sci Total Environ 636:519–529
Scardina P, Edwards M (2002) Practical implications of bubble formation in conventional treatment. J Am Water Works Assoc 94(8):85–94
Silva CP, Campos SX (2022) The effects of anaerobic reactor post-treatments by rapid filtration systems and conventional techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(41):61870–61880
Silva CP, Pedroso CR, Zarpellon DI, Machado Filho JG, Vidal CMS, Zimmermann CM, Campos SX (2019) Post-treatment of anaerobic reactor effluent for reuse using a triple filtration system. J Environ Manage 233:76–82
Silva MJM (2006) Use of slow filtration and disinfection techniques to adapt sanitary sewage to discharge and reuse standards. Doctoral thesis, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture and Urbanism, State University of Campinas
Stevik TK, Aa K, Ausland G, Hanssen JF (2004) Retention and removal of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater percolating through porous media: a review. Water Res 38(6):1355–1367
Tonetti AL, Couracci Filho B, Nicolau CE, Barbosa M, Tonon D (2012) Sewage treatment and reuse water production using sand filters. Eng Sanit Ambiental 17(3):287–294 ((in Portuguese))
Tonon D, Tonetti AL, Coraucci Filho B, Bueno DAC (2015) Wastewater treatment by anaerobic filter and sand filter: hydraulic loading rates for removing organic matter, phosphorus, pathogens and nitrogen in tropical countries. Ecol Eng 82:583–589
Tyagi VK, Khan AA, Kazmi AA, Mehrotra I, Chopra AK (2009) Slow sand filtration of UASB reactor effluent: a promising post treatment technique. Desalination 249(2):571–576
Verma S, Daverey A, Sharma A (2017) Slow sand filtration for water and wastewater treatment–a review. Environ Technol Rev 6(1):47–58
Von Sperling M, Chernicharo CAL (2002) Urban wastewater treatment technologies and the implementation of discharge standards in developing countries. Urban Water 4(1):105–114
Vries D, Bertelkamp C, Kegel FS, Hofs B, Dusseldorp J, Bruins JH, de Vet W, Van den Akker B (2017) Iron and manganese removal: recent advances in modelling treatment efficiency by rapid sand filtration. Water Res 109:35–45
Weber W Jr, Pirbazari M, Melson G (1978) Biological growth on activated carbon: an investigation by scanning electron microscopy. Environ Sci Technol 12(7):817–819
WHO - World Health Organization (1989) Health guidelines for the use of wastewater in agriculture and aquaculture. WHO, Geneva, p 74
Young-Rojanschi C, Madramootoo C (2014) Intermittent versus continuous operation of biosand filters. Water Res 49:1–10
Yu J, Zhang D, Ren W, Liu B (2019) Transport of Enterococcus faecalis in granular activated carbon column: potential energy, migration, and release. Colloids Surf B 183:110415
Acknowledgements
The authors want to acknowledge the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the Foundation for the Support of Science and Technology of Pernambuco Sate (FACEPE) for the financial support (PRONEX/NUTREL project) and to the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for granting scholarships. The authors also express their gratitude to the Agency of Financing Studies and Projects (FINEP) for supporting the project National Network of Decentralized Sewage Treatment (RENTED), Fibra Ambiental Enegnharia for the cession and support in the operation of pilot reactors and filters, and Pernambuco Sanitation Company (COMPESA) and BRK Ambiental for supporting the experimental work and sample collection at the Rio Formoso and the Mangueira STP.
Funding
This work received support from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), the Foundation for the Support of Science and Technology of Pernambuco Sate (FACEPE), and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES). The authors also express their gratitude to the Agency of Financing Studies and Projects (FINEP) (Reference number 1859/10), for supporting the project National Network of Decentralized Sewage Treatment (RENTED).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wanderli Rogério Moreira Leite: software, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. Bruno Delvaz Linhares: data acquisition, methodology, writing—original draft preparation. Juliana Cardoso de Morais: methodology, formal analysis. Sávia Gavazza: methodology, writing—reviewing and editing. Lourdinha Florencio: methodology, writing—original draft. Mario Takayuki Kato: funding acquisition, project administration, resources, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authors confirm that accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct have been followed. Authors have included sources of funding, potential conflicts of interest, and informed consent to participate in the Statements and Declarations section. Authors also declare that the manuscript does not involve animals.
Consent to participate
The authors declare that the manuscript does not involve human subjects, does not describe human transplantation studies, and does not report on studies involving vulnerable groups.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to the publication of their work in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Leite, W.R.M., Linhares, B.D., de Morais, J.C. et al. Effect of filtration rates on the performance and head loss development in granular filters during the post-treatment of anaerobic reactor effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 84023–84034 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28335-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28335-w