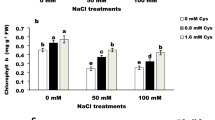
Abstract
Copper (Cu), an essential micronutrient, can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) at its supra-optimal level in living cells as a transition metal, thus producing oxidative stress in plants. Therefore, protecting plants from Cu-induced oxidative stress via the exogenous application of chemical substances, particularly L-glutamic acid (L-Glu), could be a viable strategy for mitigating the toxicity of Cu. The aim of our present study was to investigate how ʟ-Glu protects lentil seedlings from oxidative stress produced by toxic Cu and allows them to survive under Cu toxicity. The results exhibited that when lentil seedlings were exposed to excessive Cu, their growth was inhibited and their biomass decreased due to an increase in Cu accumulation and translocation to the root, shoot, and leaves. Exposure to toxic Cu also depleted photosynthetic pigments, imbalanced water content, and other essential nutrients, increased oxidative stress, and reduced enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants. However, pre-treatment of ʟ-Glu improved the phenotypic appearance of lentil seedlings, which was distinctly evidenced by higher biomass production, maintenance of water balance, and an increase in photosynthetic pigments when exposed to toxic Cu. ʟ-Glu also protected the seedlings from Cu-induced oxidative stress by reducing the oxidative stress marker, specifically by the efficient action of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, particularly ascorbate, catalase, monodehydroascorbate, and glutathione peroxidase and maintaining redox balance. Furthermore, ʟ-Glu assisted in maintaining the homeostasis of Cu and other nutrient in the roots, shoots, and leaves of lentil. Collectively, our results provide evidence of the mechanism of ʟ-Glu-mediated protective role in lentil against Cu toxicity, thus proposed as a potential chemical for managing Cu toxicity not only in lentil but also other plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdulmajeed AM, Alnusairi GS, Alharbi MH, Almushhin A, Hasan MM, Soliman MH (2021) Alleviation of copper phytotoxicity by acetylsalicylic acid and nitric oxide application in mung bean involves the up-regulation of antioxidants, osmolytes and glyoxalase system. J Plant Interact 16:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2021.1922771
Abogadallah GM (2010) Insights into the significance of antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.4.10873
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4496-5
Anjum NA, Ahmad I, Mohmood I, Pacheco M, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Umar S, Ahmad A, Khan NA, Iqbal M, Prasad MN (2012) Modulation of glutathione and its related enzymes in plants’ responses to toxic metals and metalloids—a review. Environ Exp Bot 75:307–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.07.002
Anjum NA, Gill SS, Gill R, Hasanuzzaman M, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Ahmad I, Tuteja R, Tuteja N (2014) Metal/metalloid stress tolerance in plants: role of ascorbate, its redox couple, and associated enzymes. Protoplasma 251:1265–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0636-x
Ballabio C, Panagos P, Lugato E, Huang J-H, Orgiazzi A, Jones A, Fernández-Ugalde O, Borrelli P, Montanarella L (2018) Copper distribution in European topsoils: an assessment based on LUCAS soil survey. Sci Total Environ 636:282–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.268
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brunetto G, de Melo GW, Terzano R, Del Buono D, Astolfi S, Tomasi N, Pii Y, Mimmo T, Cesco S (2016) Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity. Chemosphere 162:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.104
Cavalcanti Luna MA, Rodrigues Vieira E, Okada K, Campos-Takaki GM, do Nascimento AE (2015) Copper-induced adaptation, oxidative stress and its tolerance in Aspergillus niger UCP1261. Electron j Biotech 18:418–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2015.09.006
Cheng Y, Zhang X, Sun T, Tian Q, Zhang WH (2018) Glutamate receptor homolog3. 4 is involved in regulation of seed germination under salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 59:978–988. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy034
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112301
Clune S, Crossin E, Verghese K (2017) Systematic review of greenhouse gas emissions for different fresh food categories. J Clean Prod 140:766–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.082
Das K, Roychoudhury A (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2:53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00025-9
Drążkiewicz M, Skórzyńska-Polit E, Krupa Z (2003) Response of the ascorbate–glutathione cycle to excess copper in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.). Plant Sci 164:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00383-7
Fardus J, Hossain M, Fujita M (2021) Modulation of the antioxidant defense system by exogenous l-glutamic acid application enhances salt tolerance in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.). Biomolecules 11:587. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040587
Fardus J, Hossain MS, Fujita M (2021b) Potential role of L-glutamic acid in mitigating cadmium toxicity in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) through modulating the antioxidant defense system and nutrient homeostasis. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj Napoca 49:12485–12485
Feng X, Xu J, Liang Y, Chen G-L, Fan X-W, Li Y-Z (2017) A proteomic-based investigation of potential copper-responsive biomarkers: proteins, conceptual networks, and metabolic pathways featuring Penicillium janthinellum from a heavy metal-polluted ecological niche. Microbiol Open 00:e485. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.485
Forde BG (2014) Glutamate signaling in roots. J Exp Bot 65:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert335
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2011) Ascorbate and glutathione: the heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol 155:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.167569
Gaetke LM, Chow-Johnson HS, Chow CK (2014) Copper: toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 88:1929–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1355-y
Gaur S, Kumar J, Prasad SM, Sharma S, Bhat JA, Sahi S, Singh VP, Tripathi DK, Chauhan DK (2021) Silicon and nitric oxide interplay alleviates copper induced toxicity in mung bean seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.08.011
Ghori Z, Iftikhar H, Bhatti MF, Nasar um M, Sharma I, Kazi AG, Ahmad P (2016) Chap. 15 - phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soil. In: Ahmad P (ed) Plant Metal Interaction. Elsevier, 385–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803158-2.00015-1
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Halliwell B, Gutteridge J (1984) Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem J 219:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2190001
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hossain MS, Abdelrahman M, Tran CD, Nguyen KH, Chu HD, Watanabe Y, Hasanuzzaman M, Mohsin SM, Fujita M, Tran LSP (2020) Insights into acetate-mediated copper homeostasis and antioxidant defense in lentil under excessive copper stress. Environ Pollut 258:113544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113544
Huang WL, Wu FL, Huang HY, Huang WT, Deng CL, Yang LT, Huang ZR, Chen LS (2020) Excess copper-induced alterations of protein profiles and related physiological parameters in citrus leaves. Plants 9:291. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030291
Iqbal MZ, Nayab S, Shafiq M (2018) Effects of copper on seed germination and seedling growth performance of lens culinaris medik. J Plant Develop 25:85. https://doi.org/10.33628/jpd.2018.25.1.85
Islam F, Yasmeen T, Ali Q, Mubin M, Ali S, Arif MS, Hussain S, Riaz M, Abbas F (2016) Copper-resistant bacteria reduces oxidative stress and uptake of copper in lentil plants: potential for bacterial bioremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:220–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5354-1
Juang KW, Lo YC, Chen TH, Chen BC (2019) Effects of copper on root morphology, cations accumulation, and oxidative stress of grapevine seedlings. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:873–879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02616-y
Kan CC, Chung TY, Wu HY, Juo YA, Hsieh MH (2017) Exogenous glutamate rapidly induces the expression of genes involved in metabolism and defense responses in rice roots. BMC Genom 18:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3588-7
Karimi P, Khavari-Nejad R, Niknam V, Ghahremaninejad F, Najafi F (2012) The effects of excess copper on antioxidative enzymes, lipid peroxidation, proline, chlorophyll, and concentration of Mn, Fe, and Cu in Astragalus neo-mobayenii. Sci World J 2012:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/615670
Kaur H, Goyal N (2022) Biochemical adaptations in plants under heavy metal stress: a revisit to antioxidant defense network. In Metals Metalloids Soil Plant Water Systems. Academic Press, 51–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91675-2.00001-9
Keramat B, Kalantari KM, Arvin MJ (2010) Effects of methyl jasmonate treatment on alleviation of cadmium damages in soybean. J Plant Nutr 33:1016–1025. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904161003728685
Khazaei H, Subedi M, Nickerson M, Martínez-Villaluenga C, Frias J, Vandenberg A (2019) Seed protein of lentils: current status, progress, and food applications. Foods 391:47–56. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090391
Kong D, Ju C, Parihar A, Kim S, Cho D, Kwak JM (2015) Arabidopsis glutamate receptor homolog3.5 modulates cytosolic Ca2+ level to counteract effect of abscisic acid in seed germination. Plant Physiol 167:1630–1642. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.251298
Kumar V, Pandita S, Sidhu GPS, Sharma A, Khanna K, Kaur P, Bali AS, Setia R (2020) Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 127810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127810
Kumar S, Pandey G (2020) Biofortification of pulses and legumes to enhance nutrition. Heliyon 6(3):e03682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03682
Kumar S, Trivedi PK (2018) Glutathione S-transferases: role in combating abiotic stresses including arsenic detoxification in plants. Front Plant Sci 9:751. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00751
Küpper H, Andresen E (2016) Mechanisms of metal toxicity in plants. Metallomics 8:269–285. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MT00244C
La VH, Lee BR, Islam MT et al (2020) Characterization of glutamate-mediated hormonal regulatory pathway of the drought responses in relation to proline metabolism in Brassica napus L. Plants 9:512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040512
Li ZG, Ye XY, Qiu XM (2019) Glutamate signaling enhances the heat tolerance of maize seedlings by plant glutamate receptor-like channels mediated calcium signaling. Protoplasma 256:1165–1169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-019-01351-9
Lin YF, Aarts MG (2012) The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3187–3206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1089-z
Liu J, Wang J, Lee S, Wen R (2018) Copper-caused oxidative stress triggers the activation of antioxidant enzymes via ZmMPK3 in maize leaves. PLoS ONE 13:e0203612. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203612
LS (2021) Silicon in mitigation of abiotic stress-induced oxidative damage in plants. Crit Rev Biotechnol 41:918–934. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2021.1892582
Moravcova S, Tuma J, Ducaiova ZK et al (2018) Influence of salicylic acid pretreatment on seeds germination and some defence mechanisms of Zea mays plants under copper stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 122:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.11.007
Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 22:959–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1073-x
Mostofa MG, Hossain MA, Fujita M, Tran LS (2015) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms associated with trehalose-induced copper-stress tolerance in rice. Sci Rep 5:11433. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11433
Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Rahman A, Alam MM, Mahmud JA, Suzuki T, Fujita M (2016) Polyamines confer salt tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) by reducing sodium uptake, improving nutrient homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01104
Naidu R, Bolan NS (2008) Contaminant chemistry in soils: key concepts and bioavailability. In: Naidu R et al (eds) Developments in soil science, vol 32. Elsevier BV, Amsterdam, pp 9–37
Nair PMG, Chung IM (2015) Study on the correlation between copper oxide nanoparticles induced growth suppression and enhanced lignification in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 113:302–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.013
Nazir F, Hussain A, Fariduddin Q (2019) Hydrogen peroxide modulate photosynthesis and antioxidant systems in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants under copper stress. Chemosphere 230:544–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.001
Nephali L, Piater LA, Dubery IA, Patterson V, Huyser J, Burgess K, Tugizimana F (2020) Biostimulants for plant growth and mitigation of abiotic stresses: a metabolomics perspective. Metabolites 10:505. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120505
Nguyen HC, Lin KH, Ho SL, Chiang CM, Yang CM (2018) Enhancing the abiotic stress tolerance of plants: from chemical treatment to biotechnological approaches. Physiol Plant 164:452–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12812
Noctor G, Mhamdi A, Foyer CH (2016) Oxidative stress and antioxidative systems: recipes for successful data collection and interpretation. Plant Cell Environ 39:1140–1160. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12726
Noreen S, Akhter MS, Yaamin T, Arfan M (2018) The ameliorative effects of exogenously applied proline on physiological and biochemical parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) crop under copper stress condition. J Plant Interact 13:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1437480
Ortega P, Sánchez E, Gil E, Matamoros V (2022) Use of cover crops in vineyards to prevent groundwater pollution by copper and organic fungicides. Chemosphere 303:134975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134975
Peña N, Antón A, Kamilaris A, Fantke P (2018) Modeling ecotoxicity impacts in vineyard production: addressing spatial differentiation for copper fungicides. Sci Total Environ 616:796–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.243
Pető A, Lehotai N, Feigl G, Tugyi N, Ördög A, Gémes K, Tari I, Erdei L, Kolbert Z (2013) Nitric oxide contributes to copper tolerance by influencing ROS metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 32:1913–1923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1503-5
Poggere G, Gasparin A, Barbosa JZ, Melo GW, Corrêa RS, Motta ACV (2023) Soil contamination by copper: sources, ecological risks, and mitigation strategies in Brazil. J Trace Elem Med Biol 4:100059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemin.2023.100059
Pulido P, Cazalis R, Cejudo FJ (2009) An antioxidant redox system in the nucleus of wheat seed cells suffering oxidative stress. Plant J 57:132–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03675.x
Rahman A, Hossain MS, Mahmud JA, Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2016) Manganese-induced salt stress tolerance in rice seedlings: regulation of ion homeostasis, antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 22:291–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0371-1
Rai S, Singh PK, Mankotia S, Swain J, Satbhai SB (2021) Iron homeostasis in plants and its crosstalk with copper, zinc, and manganese. Plant Stress 1:100008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2021.100008
Romano A, Gallo V, Ferranti P, Masi P (2021) Lentil flour: nutritional and technological properties, in vitro digestibility and perspectives for use in the food industry. Curr Opin Food Sci 40:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2021.04.003
Sadak MSH, Abdelhamid MT, Schmidhalter U (2015) Effect of foliar application of amino acids on plant yield and some physiological parameters in bean plants irrigated with seawater. Acta Biol Colom 20:141–152. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v20n1.42865
Savvides A, Ali S, Tester M, Fotopoulos V (2016) Chemical priming of plants against multiple abiotic stresses: mission possible? Trends Plant Sci 21:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.11.003
Schutzendubel A, Polle A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53:1351–1365. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1351
Sharma P, Sirhindi G, Singh AK, Kaur H, Mushtaq R (2017) Consequences of copper treatment on pigeon pea photosynthesis, osmolytes and antioxidants defense. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:809–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0461-8
Sharma R, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK, Al-Huqail AA, Siddiqui MH, Ahmad P (2019) Oxidative stress mitigation and initiation of antioxidant and osmoprotectant responses mediated by ascorbic acid in Brassica juncea L. subjected to copper (II) stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 182:109436–109445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109436
Shoaib A, Javaid, A (2021) Oxidative stress in plants exposed to heavy metals. In Organic Solutes, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidant Enzymes Under Abiotic Stressors. CRC Press, 133–152.
Sytar O, Kumar A, Latowski D et al (2013) Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35:985–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1169-6
Tahjib-Ul-Arif M, Sohag AAM, Mostofa MG, Polash MAS, Mahamud AGMSU, Afrin S, Hossain MA, Hossain MA, Murata Y, Tran LP (2021) Comparative effects of ascobin and glutathione on copper homeostasis and oxidative stress metabolism in mitigation of copper toxicity in rice. Plant Biol (stuttg) 23(Suppl 1):162–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13222
Taiz L, Zeiger E, Møller IM, Murphy A (2015) Plant physiology and development, 6th edn. Sinauer Associates Inc., Publishers, Sunderland
Tegenaw A, Sorial GA, Sahle-Demessie E, Han C (2019) Characterization of colloid-size copper-based pesticide and its potential ecological implications. Environ Pollut 253:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.036
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.01.006
Toyota M, Spencer D, Sawai-Toyota S, Jiaqi W, Zhang T, Koo AJ, Howe GA, Gilroy S (2018) Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Sci 361:1112–1115. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat7744
Vázquez-Blanco R, Arias-Estévez M, Bååth E, Fernández-Calviño D (2021) Comparing the effect of Cu-based fungicides and pure Cu salts on microbial biomass, microbial community structure and bacterial community tolerance to Cu. J Hazard Mater 409:124960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124960
Vieira-Filho LO, Monteiro FA (2022) Silicon improves photosynthetic activity and induces antioxidant enzyme activity in Tanzania Guinea grass under copper toxicity. Plant Stress 3:100045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2021.100045
Vivancos PD, Dong Y, Ziegler K, Markovic J, Pallardó FV, Pellny TK, Verrier PJ, Foyer CH (2010) Recruitment of glutathione into the nucleus during cell proliferation adjusts whole-cell redox homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana and lowers the oxidative defence shield. Plant J 64:825–838. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04371.x
Wei L, Luo C, Li X, Shen Z (2008) Copper accumulation and tolerance in Chrysanthemum coronarium L. and Sorghum sudanense L. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-007-9114-1
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81192-2
Yang SH, Wang LJ, Li SH (2007) Ultraviolet-B irradiation-induced freeing tolerance in relation to antioxidant system in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves. Environ Exp Bot 60:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.12.003
Zheng Y, Luo L, Wei J, Chen Q, Yang Y, Hu X, Kong X (2018) The glutamate receptors AtGLR1.2 and AtGLR1.3 increase cold tolerance by regulating jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, in Press 506:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.153
Zhou T, Zheng LP, Yuan HY, Yuan YF, Wang JW (2012) The nitric oxide production and NADPH-diaphorase activity in root tips of Vicia faba L. under copper toxicity. Plant Omics J 5:115–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jannatul Ferdus and Md. Shahadat Hossain; formal analysis: Md. Shahadat Hossain and Md. Mahfuzur Rob; supervision: Masayuki Fujita; writing—original draft: Jannatul Fardus; writing—review and editing: Md. Shahadat Hossain, Md. Mahfuzur Rob, and Masayuki Fujita. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable (this finding does not contain any individual person’s data).
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed with the publication of this paper in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fardus, J., Hossain, S., Rob, M.M. et al. ʟ-glutamic acid modulates antioxidant defense systems and nutrient homeostasis in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) under copper toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 78507–78520 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27993-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27993-0