Abstract
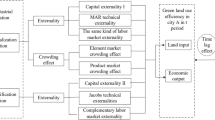
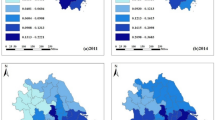
The construction of green and low-carbon circular (GLC) development economic system is conducive to the promotion of “carbon peaking and carbon neutral.” The level of GLC development in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region is related to the realization of the ambitious goal of “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality” in the region. This paper use principal component analysis (PCA) to process GLC development level of 41 cities in the YRD from 2008 to 2020. Then, we constructed panel Tobit model and threshold model from the perspective of industrial co-agglomeration and Internet utilization and empirically tested the influence of the two key variables on GLC development of the YRD. We found that (1) the YRD’s level of GLC development showed a dynamic evolution trend of “fluctuation, convergence, and rise.” The four provincial-level administrative regions of the YRD are in the order of GLC development level: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Anhui. (2) There is an inverted “U” Kuznets curve (KC) between industrial co-agglomeration and the development of GLC of the YRD. In the left segment of KC, the industrial co-agglomeration promotes GLC development of the YRD. In the right segment of KC, the industrial co-agglomeration inhibits GLC development of the YRD. Internet utilization enhances GLC development of the YRD. And the interaction of industrial co-agglomeration and Internet utilization cannot significantly enhance GLC development. (3) Double-threshold effect of opening-up is manifested as follows: industrial co-agglomeration on GLC development of the YRD goes through an insignificant-inhibited-improved evolutionary trajectory. Single-threshold effect of government intervention is manifested as follows: the impact of Internet utilization on GLC development of the YRD shifts from insignificant role to significant enhancement. In addition, there is an inverted-N type KC effect between industrialization and GLC development. Based on the above findings, we proposed suggestions in terms of industrial co-agglomeration, Internet-like digital technology application, anti-monopoly, and rational industrialization.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Añón Higón D, Gholami R, Shirazi F (2017) ICT and environmental sustainability: a global perspective. Telematics Inform 34(4):85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.01.001
Anser MK, Ahmad M, Khan MA, Zaman K, Nassani AA, Askar SE, Abro MMQ, Kabbani A (2021) The role of information and communication technologies in mitigating carbon emissions: evidence from panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(17):21065–21084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12114-y
Avom D, Nkengfack H, Fotio HK, Totouom A (2020) ICT and environmental quality in sub-Saharan Africa: effects and transmission channels. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 155:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120028
Bartolomeo M, dal Maso D, de Jong P, Eder P, Groenewegen P, Hopkinson P, James P, Nijhuis L, Örninge M, Scholl G, Slob A, Zaring O (2003) Eco-efficient producer services—what are they, how do they benefit customers and the environment and how likely are they to develop and be extensively utilised? J Clean Prod 11(8):829–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-6526(02)00157-9
Bastida L, Cohen JJ, Kollmann A, Moya A, Reichl J (2019) Exploring the role of ICT on household behavioural energy efficiency to mitigate global warming. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 103:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.01.004
Boulding KE (1966) The economics of the coming spaceship Earth. In: Environmental quality in a growing economy, 1st edn. Taylor & Francis, New York, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315064147
Cai HY, Xu YZ (2018) Co-agglomeration, trade openness and haze pollution. China Popul, Res Environ 28(06):93–102
Cai ZY, Yang XH, Lin HX, Yang XY, Jiang P (2022) Study on the co-benefits of air pollution control and carbon reduction in the Yellow River Basin: an assessment based on a spatial econometric model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(8):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084537
Chai SG, Li JC (2021) Research on statistical measurement of new driving force of China’s economic growth. J Stat Inf 36(01):47–58
Chen JJ, Liu Y, Zou MM (2016) The improvement of city productivity based on synergy and co-agglomeration of industries: under the background of integrated innovation and conversion of driving force for economic development in China. J Zhejiang Univ (humanit Soc Sci) 46(03):150–163
Cheng Z, Li L, Liu J (2019) The effect of information technology on environmental pollution in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33109–33124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06454-7
Cheng SL, Fan W, Meng FX, Chen JD, Cai BF, Liu GY, Liang S, Song ML, Zhou Y, Yang ZF (2020) Toward low-carbon development: assessing emissions-reduction pressure among Chinese cities. J Environ Manage 271:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111036
Cui TN, Zhang Y (2022) Research on the impact of circular economy on total factor carbon productivity in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(52):78780–78794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21314-7
Danish KN, Baloch MA, Saud S, Fatima T (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22850–22860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2379-2
Dehghan Shabani Z, Shahnazi R (2019) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, information and communications technology, and gross domestic product in Iranian economic sectors: a panel causality analysis. Energy 169:1064–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.062
DTI (2003) Our energy future - creating a low carbon economy. Department for Trade Industry, London
Du XY, Shen LY, Ren YT, Meng CH (2022) A dimensional perspective-based analysis on the practice of low carbon city in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106768
Ellison G, Glaeser EL (1997) Geographic concentration in U.S. manufacturing industries: a dartboard approach. J Polit Econ 105(5):889–927
Erdmann L, Hilty LM (2010) Scenario analysis: exploring the macroeconomic impacts of information and communication technologies on greenhouse gas emissions. J Ind Ecol 14(5):826–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2010.00277.x
Faisal F, Azizullah TT, Pervaiz R (2020) Does ICT lessen CO2 emissions for fast-emerging economies? An application of the heterogeneous panel estimations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(10):10778–10789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07582-w
Fan G, Wang XL, Zhang LW, Zhu HP (2003) Marketization index for China’s provinces. Econ Res J 3:9–18+89
Fan W, Wang F, Liu S, Chen T, Bai X, Zhang Y (2023) How does financial and manufacturing co-agglomeration affect environmental pollution? Evidence from China. J Environ Manage 325:116544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116544
Fang GC, Wang QL, Tian LX (2020) Green development of Yangtze River Delta in China under population-resources-environment-development-satisfaction perspective. Sci Total Environ 727:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138710
Fang Z, Razzaq A, Mohsin M, Irfan M (2022) Spatial spillovers and threshold effects of Internet development and entrepreneurship on green innovation efficiency in China. Technol Soc 68:101844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101844
Fu Y, Ma YH, Liu YJ, Niu WY (2008) Development patterns of low carbon economy. China Popul, Res Environ 3:14–19
Geng Y, Fu J, Sarkis J, Xue B (2012) Towards a national circular economy indicator system in China: an evaluation and critical analysis. J Clean Prod 23(1):216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.07.005
Godil DI, Sharif A, Agha H, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) The dynamic nonlinear influence of ICT, financial development, and institutional quality on CO2 emission in Pakistan: new insights from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(19):24190–24200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08619-1
Granell C, Havlik D, Schade S, Sabeur Z, Delaney C, Pielorz J, Uslander T, Mazzetti P, Schleidt K, Kobernus M, Havlik F, Bodsberg NR, Berre A, Mon JL (2016) Future Internet technologies for environmental applications. Environ Modell Softw 78:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.12.015
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377. https://doi.org/10.2307/2118443
Han X, Dou JM (2022) Can the integration of Yangtze River Delta reshape the spatial distribution of pollution industry? Chin J Environ Manage 14(03):88–96. https://doi.org/10.16868/j.cnki.1674-6252.2022.03.088
Hansen BE (1999) Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: estimation, testing, and inference. J Econometrics 93(2):345–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(99)00025-1
Hao Y, Li Y, Guo YX, Chai JX, Yang CX, Wu HT (2022) Digitalization and electricity consumption: does Internet development contribute to the reduction in electricity intensity in China? Energy Policy 164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112912
Hosseini HM, Kaneko S (2011) Dynamic sustainability assessment of countries at the macro level: a principal component analysis. Ecol Indic 11(3):811–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.10.007
Hu R, Shahzad F, Abbas A, Xu N (2022) Empirical analysis of the impact of industrial Internet development environment on open green innovation of manufacturing enterprises. Front Environ Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.947675
Huang J-T (2018) Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions and government spending on environmental protection in China - evidence from spatial econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 175:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.001
Hui CH, Shen F, Tong L, Zhang JR, Liu B (2022) Fiscal pressure and air pollution in resource-dependent cities: evidence from China. Front Environ Sci 10:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.908490
Ishida H (2015) The effect of ICT development on economic growth and energy consumption in Japan. Telematics Inform 32(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2014.04.003
Khan H, Weili L, Khan I (2022) Examining the effect of information and communication technology, innovations, and renewable energy consumption on CO2 emission: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(31):47696–47712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19283-y
Koutroumpis P (2009) The economic impact of broadband on growth: a simultaneous approach. Telecommun Pol 33(9):471–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2009.07.004
Lange S, Pohl J, Santarius T (2020) Digitalization and energy consumption. Does ICT reduce energy demand? Ecolog Econ 176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106760
Li TX, Li Y, An DF, Han YW, Xu SY, Lu ZM, Crittenden J (2019b) Mining of the association rules between industrialization level and air quality to inform high-quality development in China. J Environ Manage 246:564–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.022
Li TC, Han DR, Feng SS, Liang L (2019a) Can industrial co-agglomeration between producer services and manufacturing reduce carbon intensity in China?. Sustain 11(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11154024
Li SJ, Liu JG, Hu XY (2022) A three-dimensional evaluation model for green development: evidence from Chinese provinces along the belt and road. Environ Devel Sustain: 25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02542-w
Lin BQ, Zhou YC (2021) Does the Internet development affect energy and carbon emission performance? Sustain Prod Consump 28:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.03.016
Liu BL, Zhang Y, Li YS (2022) Influence mechanism of Internet development on urban green innovation: an analysis from the perspective of patents. China Popul, Res Environ 32(06):104–112
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A (2018) How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 178:703–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112
Ozcan B, Apergis N (2018) The impact of Internet use on air pollution: evidence from emerging countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(5):4174–4189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0825-1
Park Y, Meng FC, Baloch MA (2018) The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO2 emissions: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(30):30708–30719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3108-6
Peng C, Elahi E, Fan BB, Li ZH (2022) Effect of high-tech manufacturing co-agglomeration and producer service industry on regional innovation efficiency. Front Environ Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.942057
Plepys A (2002) The grey side of ICT. Environ Impact Assess Rev 22(5):509–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0195-9255(02)00025-2
Prieto-Sandoval V, Jaca C, Ormazabal M (2018) Towards a consensus on the circular economy. J Clean Prod 179:605–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.224
Qian Y, Liu J, Cheng ZH, Forrest JYL (2021) Does the smart city policy promote the green growth of the urban economy? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(47):66709–66723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15120-w
Raheem ID, Tiwari AK, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2020) The role of ICT and financial development in CO2 emissions and economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2):1912–1922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06590-0
Ren SM, Li LQ, Han YQ, Hao Y, Wu HT (2022) The emerging driving force of inclusive green growth: does digital economy agglomeration work? Bus Strateg Environ 31(4):1656–1678. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2975
Ren SY, Hao Y, Xu L, Wu HT, Ba N (2021) Digitalization and energy: how does Internet development affect China’s energy consumption? Energy Econ 98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105220
Röller L-H, Waverman L (2001) Telecommunications infrastructure and economic development: a simultaneous approach. Amer Econ Rev 91(4):909–923
Sadorsky P (2012) Information communication technology and electricity consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 48:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.04.064
Salahuddin M, Alam K (2016) Information and communication technology, electricity consumption and economic growth in OECD countries: a panel data analysis. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 76:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.11.005
Shaheen F, Zaman K, Lodhi MS, Nassani AA, Haffar M, Abro MMQ (2022) Do affluent nations value a clean environment and preserve it? Evaluating the N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(31):47267–47285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19104-2
Shahnazi R, Dehghan Shabani Z (2019) The effects of spatial spillover information and communications technology on carbon dioxide emissions in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):24198–24212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05636-7
Shi BF, Yang HF, Wang J, Zhao JX (2016) City green economy evaluation: empirical evidence from 15 sub-provincial cities in China. Sustain 8(6):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060551
Shi LY, Xiang XQ, Zhu W, Gao LJ (2018) Standardization of the evaluation index system for low-carbon cities in china: a case study of Xiamen. Sustainability 10(10):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103751
Smith A (1776) The wealth of nations. The Commercial Press, Beijing
Stankovic JJ, Jankovic-Milic V, Marjanovic I, Janjic J (2021) An integrated approach of PCA and PROMETHEE in spatial assessment of circular economy indicators. Waste Manag 128:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.04.057
Sun W, Huang CC (2020) How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evid China J Clean Prod 272:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122828
Tang JH, Tong MH, Sun YH, Du JT, Liu NN (2020) A spatio-temporal perspective of China’s industrial circular economy development. Sci Total Environ 706:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135754
Tang C, Xu Y, Hao Y, Wu H, Xue Y (2021) What is the role of telecommunications infrastructure construction in green technology innovation? A firm-level analysis for China. Energy Econ 103:105576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105576
Tang Y, Chen W, Chen S, Sohail MT (2022) Examining the potential role of ICT diffusion on green growth: does financial development matter in BRICS economies? Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24894-6
Tian X, Bai FL, Jia JH, Liu Y, Shi F (2019) Realizing low-carbon development in a developing and industrializing region: impacts of industrial structure change on CO2 emissions in southwest China. J Environ Manage 233:728–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.078
Tobin J (1958) Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 26(1):24–36. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907382
UNEP (2011) Towards a green economy: pathways to sustainable development and poverty eradication. www.unep.org/greeneconomy
Wang MX, Zhao HH, Cui JX, Fan D, Lv B, Wang G, Li ZH, Zhou GJ (2018) Evaluating green development level of nine cities within the Pearl River Delta, China. J Clean Prod 174:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.328
Wang H, Huang JJ, Zhou H, Deng CB, Fang CL (2020) Analysis of sustainable utilization of water resources based on the improved water resources ecological footprint model: a case study of Hubei Province. China J Environ Manage 262:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110331
Wang KY, Zhang YF, Hong YX (2021) Research on monopoly of China’s Internet platform market: formation logic, behavior definition and government regulation. Finance Econ 10:56–69
Wang JL, Wang WL, Ran QY, Irfan M, Ren SY, Yang XD, Wu HT, Ahmad M (2022) Analysis of the mechanism of the impact of Internet development on green economic growth: evidence from 269 prefecture cities in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):9990–10004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16381-1
Wang X, Tian N, Wang S (2023) The impact of information and communication technology industrial co-agglomeration on carbon productivity with the background of the digital economy: empirical evidence from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010316
World Bank 2012 Inclusive Green Growth: the Pathway to Sustainable Developmenthttps://doi.org/10.1596/978-0-8213-9551-6
Wu XF (2018) Have producer services and manufacturing industry co-agglomeration promoted total factor productivity. Collect Essays Finance Econ 12:13–20. https://doi.org/10.13762/j.cnki.cjlc.20180409.002
Wu HT, Xue Y, Hao Y, Ren SY (2021) How does Internet development affect energy-saving and emission reduction? Evidence from China. Energy Econ 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105577
Xie TT, Zhao Y (2017) Technology innovation, financial development and industrial structure upgrading - based on bayesian quantile regression. Sci Technol Manage Res 37(05):1–8
Xiong HR (2019) Platform monopoly in the development of digital economy in China and its governance strategies. Reform(07): 52–61
Xu S-C, Li Y-W, Miao Y-M, Gao C, He Z-X, Shen W-X, Long R-Y, Chen H, Zhao B, Wang S-X (2019) Regional differences in nonlinear impacts of economic growth, export and FDI on air pollutants in China based on provincial panel data. J Clean Prod 228:455–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.327
Yang TL, Zhu YM, Liu MH, Zhou B (2020) Industrial co-agglomeration, marketization and environmental pollution in resource-based cities. Ind Econ Res 6:15–27. https://doi.org/10.13269/j.cnki.ier.2020.06.002
Yang HC, Zhang FM, He YX (2021a) Exploring the effect of producer services and manufacturing industrial co-agglomeration on the ecological environment pollution control in China. Environ Devel Sustain 23(11):16119–16144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01339-7
Yang XD, Wu HT, Ren SY, Ran QY, Zhang JN (2021b) Does the development of the Internet contribute to air pollution control in China? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 56:207–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2020.12.001
Yang HC, Xu XZ, Zhang FM (2022) Industrial co-agglomeration, green technological innovation, and total factor energy efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(41):62475–62494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20078-4
Ye YL, Ye S, Yu HC (2021) Can industrial collaborative agglomeration reduce haze pollution? City-level empirical evidence from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041566
Ye PH, Li J, Ma WJ, Zhang HR (2022) Impact of collaborative agglomeration of manufacturing and producer services on air quality: evidence from the emission reduction of PM2.5, NOx and SO2 in China. Atmosphere 13(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060966
Yu BB (2022) The impact of the Internet on industrial green productivity: evidence from China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 177:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121527
Yusuf S, Nabeshima K (2005) Creative industries in East Asia. Cities 22(2):109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2005.01.001
Zeng WP, Lin L, Huang Y (2021) Industrial collaborative agglomeration, marketization, and green innovation: evidence from China’s provincial panel data. J Clean Prod 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123598
Zhang YG, Dou RY, Bai YJ (2020) Measurement on China’s green low-carbon circular developing economic system construction. J Quant Technol Econ 37(08):83–102. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2020.08.005
Zhao J, Shahbaz M, Dong KY (2022a) How does energy poverty eradication promote green growth in China? The role of technological innovation. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 175:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121384
Zhao S, Hafeez M, Faisal CMN (2022b) Does ICT diffusion lead to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in emerging Asian economies? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(8):12198–12207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16560-0
Zhu XY, Zhang YQ, Yang WZ (2022) Corporate co-agglomeration and green economy efficiency in China. Front Psychol 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.890214
Zhuang RL, Mi KA, Feng ZW (2021) Industrial co-agglomeration and air pollution reduction: an empirical evidence based on provincial panel data. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212097
Funding
This work was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (22BJY106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shizhong Tian: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, writing — review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition. Yukai Meng: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing — original draft. Xiaoyue Li: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing — review and editing. Li Si: writing — review and editing. Yuhong Yin: writing — review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research did not involve human participants, human data, or human tissues. This study was based on the published materials.
Consent for publication
This research does not contain any individual person’s data in the form of individual details, images, or videos. This work is based on the published literature.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, S., Meng, Y., Li, X. et al. Industrial co-agglomeration, Internet utilization, and the development of green and low-carbon cycle — based on the empirical study of 41 cities in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 66867–66896 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27012-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27012-2