Abstract
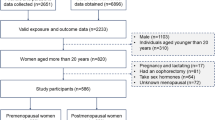
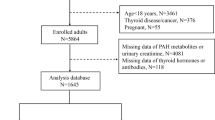
We examined the relationships between exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) metabolites and sex hormones in pre- and postmenopausal women from the 2013–2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The study comprised 648 premenopausal and 370 postmenopausal women (aged 20 years or older) with comprehensive data on PAH metabolites and sex steroid hormones. To evaluate the correlations between individual or mixture of the PAH metabolites and sex hormones stratified by menopausal status, we used linear regression and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR). After controlling for confounders, 1-Hydroxynaphthalene (1-NAP) was inversely associated with total testosterone (TT), and 1-NAP, 3-Hydroxyfluorene (3-FLU), and 2-Hydroxyfluorene (2-FLU) were inversely associated with estradiol (E2). 3-FLU was positively associated with sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and TT/E2, whereas 1-NAP and 2-FLU were inversely associated with free androgen index (FAI). In the BKMR analyses, chemical combination concentrations at or above the 55th percentile were inversely connected to E2, TT, and FAI values but positively correlated with SHBG when compared with the matching 50th percentile. In addition, we only found that mixed exposure to PAHs was positively associated with TT and SHBG in premenopausal women. Exposure to PAH metabolites, either alone or as a mixture, was negatively associated with E2, TT, FAI, and TT/E2 but positively associated with SHBG. These associations were stronger among postmenopausal women.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adeniran JA, Abdulraheem MO, Ameen HA, Odediran ET, Yusuf MO (2021) Source identification and health risk assessments of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in settled dusts from different population density areas of Ilorin Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 193(12):777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09566-1
Agarwal P, Singh L, Anand M, Taneja A (2018) Association between placental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS), oxidative stress, and preterm delivery: a case-control study. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74(2):218–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0455-0
Baird GL, Archer-Chicko C, Barr RG, Bluemke DA, Foderaro AE, Fritz JS, Hill NS, Kawut SM, Klinger JR, Lima JAC, Mullin CJ, Ouyang P, Palevsky HI, Palmisicano AJ, Pinder D, Preston IR, Roberts KE, Smith KA, Walsh T, Whittenhall M, Ventetuolo CE (2018) Lower DHEA-S levels predict disease and worse outcomes in post-menopausal women with idiopathic, connective tissue disease- and congenital heart disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 51(6):1800467. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00467-2018
Bobb JF, Claus Henn B, Valeri L, Coull BA (2018) Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ Health 17(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0413-y
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus Henn B, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Godleski JJ, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16(3):493–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxu058
Cathey AL, Watkins DJ, Rosario ZY, Vélez Vega CM, Loch-Caruso R, Alshawabkeh AN, Cordero JF, Meeker JD (2020) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure results in altered CRH, reproductive, and thyroid hormone concentrations during human pregnancy. Sci Total Environ 749:141581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Health and Nutrition Examination Laboratory Procedure Manual. Sex Hormone-binding Globulin. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Hyatttsville, MD, 2018a.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Health and Nutrition Examination Laboratory Procedure Manual. Total Estradiol and Total Testosterone. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Hyatttsville, MD, 2018b.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Yu Z, Guan Y, Chen R, Wang C (2021) Early-life phenanthrene exposure inhibits reproductive ability in adult zebrafish and the mechanism of action. Chemosphere 272:129635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129635.
Deswal R, Yadav A, Dang AS (2018) Sex hormone binding globulin - an important biomarker for predicting PCOS risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Biol Reprod Med 64(1):12–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/19396368.2017.1410591
Edwards BJ, Li J (2013) Endocrinology of menopause. Periodontol 2000 61(1):177-94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2011.00407.x
El Khoudary SR, Thurston RC (2018) Cardiovascular implications of the menopause transition: endogenous sex hormones and vasomotor symptoms. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 45(4):641–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogc.2018.07.006
Ekpe OD, Sim W, Choi S, Choo G, Oh JE (2021) Assessment of exposure of Korean firefighters to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via their measurement in serum and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites in urine. Environ Sci Technol 55(20):14015–14025. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c02554
Ferguson KK, Peterson KE, Lee JM, Mercado-García A, Blank-Goldenberg C, Téllez-Rojo MM (2014) Meeker JD (2014) Prenatal and peripubertal phthalates and bisphenol A in relation to sex hormones and puberty in boys. Reprod Toxicol 47:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.06.002
Gao D, Lin J, Ou K, Chen Y, Li H, Dai Q, Yu Z, Zuo Z, Wang C (2018a) Embryonic exposure to benzo(a)pyrene inhibits reproductive capability in adult female zebrafish and correlation with DNA methylation. Environ Pollut 240:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.139
Gao P, da Silva E, Hou L, Denslow ND, Xiang P, Ma LQ (2018b) Human exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: metabolomics perspective. Environ Int 119:466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.07.017
Gozgit JM, Nestor KM, Fasco MJ, Pentecost BT, Arcaro KF (2004) Differential action of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on endogenous estrogen-responsive genes and on a transfected estrogen-responsive reporter in MCF-7 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.003
Güdücü N, Görmüş U, Kutay SS, Kavak ZN, Telatar B (2013) Endogenous sex hormones and their associations with cardiovascular risk factors in post-menopausal women. J Endocrinol Invest 36(8):588–592. https://doi.org/10.3275/8881
Guo J, Huang J, Zhang L, Li C, Qin Y, Liu W, Li J, Huang G (2020) Benzo[b]fluoranthene impairs mouse oocyte maturation via inducing the apoptosis. Front Pharmacol 11:1226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01226
Hall JE (2015) Endocrinology of the menopause. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 44(3):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2015.05.010
Honour JW (2018) Biochemistry of the menopause. Ann Clin Biochem 55(1):18–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004563217739930
Hýžd’alová M, Pivnicka J, Zapletal O, Vázquez-Gómez G, Matthews J, Neca J, Pencíková K, Machala M, Vondrácek J (2018) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent metabolism plays a significant role in estrogen-like effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on cell proliferation. Toxicol Sci 165(2):447–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy153
Huang Y, Guo J, Lv N et al (2018) Associations of urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with age at natural menopause in US women aged 35–65, NHANES 2003–2012. Environ Pollut 243:1878–1886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.109
Jaspers L, Dhana K, Muka T, Meun C, Kiefte-de Jong JC, Hofman A, Laven JS, Franco OH, Kavousi M (2016) Sex steroids, sex hormone-binding globulin and cardiovascular health in men and postmenopausal women: the Rotterdam study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(7):2844–2852. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-1435
Johnson CL DS, Burt VL, Mohadjer LK (2014) National health and nutrition examination survey: sample design. 2011–2014. Available: Https://www.Cdc.Gov/nchs/data/series/sr_02/sr02_162.Pdf [accessed 03/13 2020].
Johnson CL, Paulose-Ram R, Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kruszon-Moran D, Dohrmann SM, Curtin LR (2013) National health and nutrition examination survey: analytic guidelines, 1999–2010. Vital Health Stat 2. 2013;(161):1–24.
Li F, Wu H, Li L, Li X, Zhao J, Peijnenburg WJ (2012) Docking and QSAR study on the binding interactions between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and estrogen receptor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.03.009
Li H, Lai Z, Zeng Y, Gao Y, Yang W, Mai Y, Wang C (2021) Occurrence, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Pearl River Delta, China. Mar Pollut Bull 170:112666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112666.
Li J, Fan H, Liu K, Li X, Fan D, Lu X, Xia Y, Cao Y, Xiao C (2020) Associations of urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with albuminuria in U.S. adults, NHANES 2003–2014. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 195:110445. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110445.
Liu B, Xue Z, Zhu X, Jia C (2017) Long-term trends (1990–2014), health risks, and sources of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the U.S. Environ Pollut 220(Pt B):1171–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.018.
Luderer U, Christensen F, Johnson WO et al (2017) Associations between urinary biomarkers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and reproductive function during menstrual cycles in women. Environ Int 100:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.021
Luo K, Liu J, Wang Y, Aimuzi R, Luo F, Ao J, Zhang J (2020) Associations between organophosphate esters and sex hormones among 6–19-year old children and adolescents in NHANES 2013–2014. Environ Int. 2020;136:105461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105461.
Malloy K W, Hart S, Burke K et al (2022) Circulating androgens are lower in PAH patients compared to controls and stable over time[M]//B54. Pacific heights: biomarkers and quality of life in pulmonary hypertension. American Thoracic Society A3067-A3067.
Maggio M, Ceda GP, Lauretani F, Bandinelli S, Corsi AM, Giallauria F, Guralnik JM, Zuliani G, Cattabiani C, Parrino S, Ablondi F, Dall’aglio E, Ceresini G, Basaria S (2011) Ferrucci L (2011) SHBG, sex hormones, and inflammatory markers in older women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(4):1053–1059. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-1902
Matikainen T, Perez GI, Jurisicova A et al (2001) Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor-driven Bax gene expression is required for premature ovarian failure caused by biohazardous environmental chemicals. Nat Genet 28(4):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng575
Mustieles V, Fernández MF, Martin-Olmedo P, González-Alzaga B, Fontalba-Navas A, Hauser R, Olea N, Arrebola JP (2017) Human adipose tissue levels of persistent organic pollutants and metabolic syndrome components: combining a cross-sectional with a 10-year longitudinal study using a multi-pollutant approach. Environ Int 104:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.04.002
Netter A, Siri E, Tassitro V, Resseguier N, Beauval N, Sari-Minodier I, Courbiere B, Perrin J (2020) Influence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure on IVF: now is the time to focus on women. Reprod Biomed Online 41(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2020.03.022
NCHS. Laboratory Procedure Manual for Serum Sex Hormone Binding Globulin. National Center for Environmental Health; 2013-2014a. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/TST_H_MET_Sex_Hormone_Binding_Globulin.pdf.
NCHS. Laboratory Procedure Manual for Serum Total Estradiol and Total Testosterone. National Center for Environmental Health; 2013-2014b. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/TST_H_MET_Total_Estradiol_and_Total_Testosterone.pdf.
NCHS. Laboratory Procedure Manual for Serum Sex Hormone Binding Globulin. National Center for Environmental Health; 2015-2016a. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/TST_H_MET_Sex_Hormone_Binding_Globulin.pdf.
NCHS. Laboratory Procedure Manual for Serum Total Estradiol and Total Testosterone. National Center for Environmental Health; 2015-2016b. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/TST_H_MET_Total_Estradiol_and_Total_Testosterone.pdf.
Ouidir M, Buck Louis GM, Kanner J, Grantz KL, Zhang C, Sundaram R, Rahman ML, Lee S, Kannan K, Tekola-Ayele F, Mendola P (2020) Association of maternal exposure to persistent organic pollutants in early pregnancy with fetal growth. JAMA Pediatr 174(2):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5104
Perel E, Wilkins D, Killinger DW (1980) The conversion of androstenedione to estrone, estradiol, and testosterone in breast tissue. J Steroid Biochem 13(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4731(80)90117-x
Ramachandran S, Hackett GI, Strange RC (2019) Sex hormone binding globulin: a review of its interactions with testosterone and age, and its impact on mortality in men with type 2 diabetes. Sex Med Rev 7(4):669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.06.006
Sahay D, Lloyd SE, Rivera JA, Jezioro J, McDonald JD, Pitiranggon M, Yan B, Szabolcs M, Terry MB, Miller RL (2021) Prenatal polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, altered ERα pathway-related methylation and expression, and mammary epithelial cell proliferation in offspring and grandoffspring adult mice. Environ Res 196:110961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110961.
Sievers CK, Shanle EK, Bradfield CA, Xu W (2013) Differential action of monohydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with estrogen receptors α and β. Toxicol Sci 132(2):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs287
Simó R, Sáez-López C, Barbosa-Desongles A, Hernández C, Selva DM (2015) Novel insights in SHBG regulation and clinical implications. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26(7):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.05.001
Stogiannidis E, Laane R (2015) Source characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by using their molecular indices: an overview of possibilities. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 234:49–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10638-0_2
Takahashi TA, Johnson KM (2015) Menopause. Med Clin North Am 99(3):521–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2015.01.006
Tao C, Fan Y, Niu R, Li Z, Qian H, Yu H, Xu Q, Xu Q, Lu C (2021) Urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sex hormones in children and adolescents: evidence from NHANES. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 216:112215. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112215.
Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM (1999) A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(10):3666–3672. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.10.6079
Wang M, Jia S, Lee SH, Chow A, Fang M (2021) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in indoor environments are still imposing carcinogenic risk. J Hazard Mater 409:124531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124531.
Wilke TJ, Utley DJ (1987) Total testosterone, free-androgen index, calculated free testosterone, and free testosterone by analog RIA compared in hirsute women and in otherwise-normal women with altered binding of sex-hormone-binding globulin. Clin Chem 33(8):1372–1375
Yang P, Sun H, Gong YJ, Wang YX, Liu C, Chen YJ, Sun L, Huang LL, Ai SH, Lu WQ, Zeng Q (2017) Repeated measures of urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites in relation to altered reproductive hormones: a cross-sectional study in China. Int J Hyg Environ Health 20(8):1340–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2017.09.004
Yang Z, Guo C, Li Q, Zhong Y, Ma S, Zhou J, Li X, Huang R, Yu Y (2021) Human health risks estimations from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in serum and their hydroxylated metabolites in paired urine samples. Environ Pollut 290:117975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117975.
Ye X, Pan W, Li C, Ma X, Yin S, Zhou J, Liu J (2020) Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and risk for premature ovarian failure and reproductive hormones imbalance. J Environ Sci (china) 91:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.12.015
Yin S, Tang M, Chen F, Li T, Liu W (2017) Environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): the correlation with and impact on reproductive hormones in umbilical cord serum. Environ Pollut 220(Pt B):1429–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.090
Zajda K, Gregoraszczuk EL (2020) Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons mixture, in human blood levels, decreased oestradiol secretion by granulosa cells via ESR1 and GPER1 but not ESR2 receptor. Hum Exp Toxicol 39(3):276–289. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119886027
Zhang Y, Dong S, Wang H, Tao S, Kiyama R (2016) Biological impact of environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (ePAHs) as endocrine disruptors. Environ Pollut 213:809–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.050
Zhao D, Guallar E, Ouyang P, Subramanya V, Vaidya D, Ndumele CE, Lima JA, Allison MA, Shah SJ, Bertoni AG, Budoff MJ, Post WS (2018) Michos ED (2018) Endogenous sex hormones and incident cardiovascular disease in post-menopausal women. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(22):2555–2566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.01.083
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Shijiazhuang Science and Technology Research and Development Plan Project (NO.201461173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhan Liu: project development, data collection, management and analysis, manuscript writing. Xihui Zhu, Yancen Meng: project development, data management and analysis, manuscript writing and editing. Yaru Ju, Yanjing Yang: data collection, management and analysis. Su’e Zhang, Liye Miao: data analysis, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The protocol of NHANES was approved by the institutional review board of the National Center for Health Statistics, CDC. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before participation in this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Brief synopsis: Exposure to PAH metabolites, either alone or as a mixture, was associated with sex hormone indicators especially in postmenopausal women.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Meng, Y., Ju, Y. et al. Association of the urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with sex hormones stratified by menopausal status older than 20 years: a mixture analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 57717–57727 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26099-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26099-x