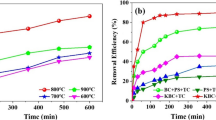
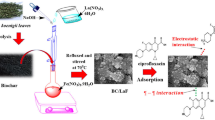
Abstract
Antibiotics pollution is an urgent public health issue. Biochar is a kind of promising composite for removal antibiotic in aqueous environment. In this study, a novel magnetic graphoxide/biochar composite (mGO/TBC) was synthesized by simple impregnation method and used as an efficient and recyclable persulfate (PS) activator for degradation and removal of sulfonamides (SAs) and quinolones (QNs) antibiotics. Based on the synergism pre-adsorption and degradation between graphoxide and biochar, the removal rates of mGO/TBC on sarafloxacin hydrochloride, sulfadimethoxine, sulfapyridine, sulfadoxine, sulfamonomethoxine, sulfachloropyridazine, enrofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin were increased above 95%. Moreover, the mGO/TBC could be reused at least seven times after degradation-recovery cycles. Quenching experiment and ESR analysis proved that 1O2, •OH, and SO4•− from mGO/TBC/PS system were the primary oxidation active species to degrade SAs and QNs. It is a promising substrate for antibiotic bioremediation with good application prospects.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad M, Teel AL, Watts RJ (2013) Mechanism of Persulfate Activation by Phenols. Environ Sci Technol 47:5864–5871. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400728c
Akbari S, Ghanbari F, Moradi M (2016) Bisphenol A degradation in aqueous solutions by electrogenerated ferrous ion activated ozone, hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: Applying low current density for oxidation mechanism. Chem Eng J 294:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.106
Akiyama George, Matsuda Ryotaro, Sato Hiroshi, Takata Masaki, Kitagawa Susumu (2011) Cellulose Hydrolysis by a New Porous Coordination Polymer Decorated with Sulfonic Acid Functional Groups. Adv Mater 23:3294–3297. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201101356
Aup-Ngoen Kamonwan, Noipitak Mai (2020) Effect of carbon-rich biochar on mechanical properties of PLA-biochar composites. Sustain Chem Pharm 15:100204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.100204
Bu Yushan, Guo Feng, Li Kejiang, Liang Zeng, Zhang Jianliang, Jiang Chunhe, Bi Zhisheng (2022) High-temperature pyrolysis behavior and structural evolution mechanism of graphene oxide: A ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation. Appl Surf Sci 593:153451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153451
Cao S, Chen J, Lai G, Xi C, Li X, Zhang L, Wang G, Chen Z (2019) A high efficient adsorbent for plant growth regulators based on ionic liquid and beta-cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic graphene oxide. Talanta 194:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.013
Chen H, Gao B, Li H (2015) Removal of sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide. J Hazard Mater 282:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.063
Chen Feng, Xi-Lin Wu, Yang Liu, Chen Chaofa, Lin Hongjun, Chen Jianrong (2020) Efficient degradation and mineralization of antibiotics via heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by using graphene supported single-atom Cu catalyst. Chem Eng J 394:124904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124904
Chen Yi-Ping, Zheng Chao-Hong, Huang Yao-Yi, Chen Yi-Ren (2022) Removal of chlortetracycline from water using spent tea leaves-based biochar as adsorption-enhanced persulfate activator. Chemosphere 286:131770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131770
Cheng X, Guo H, Zhang Y, Xiao Wu, Liu Y (2017) Non-photochemical production of singlet oxygen via activation of persulfate by carbon nanotubes. Water Res 113:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.016
Chia CH, Downie A, Munroe P (2015) Characteristics of Biochar: Physical and Structural Properties.
Dai X-H, Fan H-X, Yi C-Y, Dong B, Yuan S-J (2019) Solvent-free synthesis of a 2D biochar stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron composite for the oxidative degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 7:6849–6858. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta11661j
Deng F, Olvera-Vargas H, Garcia-Rodriguez O, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Qiu S, Yang J (2019) Waste-wood-derived biochar cathode and its application in electro-Fenton for sulfathiazole treatment at alkaline pH with pyrophosphate electrolyte. J Hazard Mater 377:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.077
Dong Fu-Xin, Yan Liu, Huang Shi-Ting, Liang Jing-Yi, Zhang Wen-Xuan, Yao Xiao-Wen, Chen Xie, Qian Wei, Guo Peng-Ran, Kong Ling-Jun, Chu Wei, Diao Zeng-Hui (2022) Removal of antibiotics sulfadiazine by a biochar based material activated persulfate oxidation system: Performance, products and mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 157:411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.11.045
Feng Dongdong, Dawei Guo Yu, Zhang Shaozeng Sun, Zhao Yijun, Shang Qi, Sun Hongliang, Jiangquan Wu, Tan Heping (2021) Functionalized construction of biochar with hierarchical pore structures and surface O-/N-containing groups for phenol adsorption. Chem Eng J 410:127707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127707
Fu Haichao, Zhao Peng, Shengjun Xu, Cheng Gong, Li Zhuoqian, Li Yi, Li Kai, Ma Shuanglong (2019) Fabrication of Fe3O4 and graphitized porous biochar composites for activating peroxymonosulfate to degrade p-hydroxybenzoic acid: Insights on the mechanism. Chem Eng J 375:121980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121980
Furman OS, Teel AL, Watts RJ (2010) Mechanism of Base Activation of Persulfate. Environ Sci Technol 44:6423–6428. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1013714
Ge Y, Li Z (2018) Application of Lignin and Its Derivatives in Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions in Water: A Review. Acs Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 6:7181–7192. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01345
Gholami Peyman, Dinpazhoh Laleh, Khataee Alireza, Hassani Aydin, Bhatnagar Amit (2020) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of novel Fe-Cu layered double hydroxide/biochar nanocomposite with enhanced sonocatalytic activity for degradation of cefazolin sodium. J Hazard Mater 381:120742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120742
Ho YS, Ng JCY, McKay G (2000) Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: Review. Sep Purif Methods 29:189–232. https://doi.org/10.1081/spm-100100009
Ho S-H, Chen Y-d, Li R, Zhang C, Ge Y, Cao G, Ma M, Duan X, Wang S, Ren N-q (2019) N-doped graphitic biochars from C-phycocyanin extracted Spirulina residue for catalytic persulfate activation toward nonradical disinfection and organic oxidation. Water Res 159:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.008
Huang Danlian, Wang Xi, Zhang Chen, Zeng Guangming, Peng Zhiwei, Zhou Jin, Cheng Min, Wang Rongzhong, Zhengxun Hu, Qin Xiang (2017) Sorptive removal of ionizable antibiotic sulfamethazine from aqueous solution by graphene oxide-coated biochar nanocomposites: Influencing factors and mechanism. Chemosphere 186:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.154
Jia Jia, Cheng Mengqian, Xue Xue, Guan Yongjing, Wang Zaizhao (2020) Characterization of tetracycline effects on microbial community, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas spp. in gut of goldfish Carassius auratus Linnaeus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110182
Jiang X, Guo Y, Zhang L, Jiang W, Xie R (2018) Catalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by persulfate activated with nano Fe-0 immobilized mesoporous carbon. Chem Eng J 341:392–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.034
Khan FSA, Mubarak NM, Khalid M, Walvekar R, Abdullah EC, Mazari SA, Nizamuddin S, Karri RR (2020) Magnetic nanoadsorbents’ potential route for heavy metals removal-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:24342–24356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08711-6
Langbehn Rayane Kunert, Michels Camila, Soares Hugo Moreira (2021) Antibiotics in wastewater: From its occurrence to the biological removal by environmentally conscious technologies. Environ Pollut 275:116603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116603
Lapworth DJ, Baran N, Stuart ME, Ward RS (2012) Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environ Pollut 163:287–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.034
Li, Pu, Yuru Wang, Bi Huang, Shengqi Guan, Tiangang Luan, Ge Lin, and Ke Yuan (2022) Antibiotics in wastewater of Guangdong, China: distribution patterns, and their environmental risk due to incomplete removal. Sci Total Environ 849:157889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157889
Liang C, Lin Y-T, Shin W-H (2009) Persulfate regeneration of trichloroethylene spent activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 168:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.006
Liang H, Zhu C, Ji S, Kannan P, Chen Fu (2022a) Magnetic Fe2O3/biochar composite prepared in a molten salt medium for antibiotic removal in water. Biochar 4:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-021-00130-1
Liang Lan, Chen Guanyi, Li Ning, Liu Hengxin, Yan Beibei, Wang Yanshan, Duan Xiaoguang, Hou Li’an, Wang Shaobin (2022b) Active sites decoration on sewage sludge-red mud complex biochar for persulfate activation to degrade sulfanilamide. J Colloid Interface Sci 608:1983–1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.150
Liu S, Huang B, Chai L, Liu Y, Zeng G, Wang X, Zeng W, Shang M, Deng J, Zhou Z (2017) Enhancement of As(V) adsorption from aqueous solution by a magnetic chitosan/biochar composite. RSC Adv 7:10891–10900. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra27341f
Liu Junguang, Jiang Shaojun, Chen Dongdong, Dai Guangling, Wei Dongyang, Shu Yuehong (2020a) Activation of persulfate with biochar for degradation of bisphenol A in soil. Chem Eng J 381:122637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122637
Liu Yongde, Li Jinsong, Lairong Wu, Shi Yahui, He Qiaochong, Chen Jing, Wan Dongjin (2020b) Magnetic spent bleaching earth carbon (Mag-SBE@C) for efficient adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride: Response surface methodology for optimization and mechanism of action. Sci Total Environ 722:137817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137817
Liu Tianqi, Lawluvy Yelly, Shi Yang, Ighalo Joshua O, He Yide, Zhang Yongjun, Yap Pow-Seng (2022) Adsorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution using modified biochar: A review. J Environ Chem Eng 10:106502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106502
Luo Jiayi, Yi Yunqiang, Ying Guangguo, Fang Zhanqiang, Zhang Yifeng (2022) Activation of persulfate for highly efficient degradation of metronidazole using Fe(II)-rich potassium doped magnetic biochar. Sci Total Environ 819:152089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152089
Ma W, Wang Na, Yunchen Du, Ping Xu, Sun B, Zhang L, Lin K-Y (2019) Human-Hair-Derived N, S-Doped Porous Carbon: An Enrichment and Degradation System for Wastewater Remediation in the Presence of Peroxymonosulfate. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 7:2718–2727. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05801
Olmez-Hanci T, Arslan-Alaton I, Genc B (2013) Bisphenol A treatment by the hot persulfate process: Oxidation products and acute toxicity. J Hazard Mater 263:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.032
Patel Anil Kumar, Katiyar Ravi, Chen Chiu-Wen, Singhania Reeta Rani, Awasthi Mukesh Kumar, Bhatia Shashikant, Bhaskar Thallada, Dong Cheng-Di (2022) Antibiotic bioremediation by new generation biochar: Recent updates. Bioresour Technol 358:127384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127384
Petrie Bruce, Barden Ruth, Kasprzyk-Hordern Barbara (2015) A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res 72:3–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.053
Qian L, Chen B (2014) Interactions of Aluminum with Biochars and Oxidized Biochars: Implications for the Biochar Aging Process. J Agric Food Chem 62:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404624h
Qu Jianhua, Dong Min, Wei Shuqi, Meng Qingjuan, Limin Hu, Qi Hu, Wang Lei, Han Wei, Zhang Ying (2020) Microwave-assisted one pot synthesis of β-cyclodextrin modified biochar for concurrent removal of Pb(II) and bisphenol a in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 250:117003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117003
Reguyal F, Sarmah AK (2018) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole by magnetic biochar: Effects of pH, ionic strength, natural organic matter and 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol. Sci Total Environ 628–629:722–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.323
Rong Xing, Xie Meng, Kong Lingshuai, Natarajan Vinothkumar, Ma Long, Zhan Jinhua (2019) The magnetic biochar derived from banana peels as a persulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. Chem Eng J 372:294–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.135
Rostamian R, Behnejad H (2016) A comparative adsorption study of sulfamethoxazole onto graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets through equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic modeling. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.12.011
Singhania RR, Agarwal RA, Kumar RP, Sukumaran RK (2018) Energy, Environment, and Sustainability] Waste to Wealth II Land Applications of Biochar: An Emerging Area. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7431-8:171-197
Soni K, Jyoti K, Chandra H, Chandra R (2022) Bacterial antibiotic resistance in municipal wastewater treatment plant; mechanism and its impacts on human health and economy. Bioresource Technology Reports 101080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101080
Sun XM, Li YD (2004) Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 43:597–601. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200352386
Sun H, Peng X, Zhang S, Liu S, Xiong Ya, Tian S, Fang J (2017) Activation of peroxymonosulfate by nitrogen-functionalized sludge carbon for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water. Bioresour Technol 241:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.102
Tang J, Bin Mu, Zheng M, Wang A (2015) One-Step Calcination of the Spent Bleaching Earth for the Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Acs Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 3:1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00040
Tang HZ, Wang YH, Li S, Wu J, Li JW, Zhou HY, Gao ZX (2019) Graphene oxide composites for magnetic solid-phase extraction of twelve quinolones in water samples followed by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:7039–7049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02081-w
Tucureanu V, Matei A, Avram AM (2016) FTIR Spectroscopy for Carbon Family Study. Crit Rev Anal Chem 46:502–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2016.1157013
Vicente F, Santos A, Romero A, Rodriguez S (2011) Kinetic study of diuron oxidation and mineralization by persulphate: Effects of temperature, oxidant concentration and iron dosage method. Chem Eng J 170:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.042
Wang Jialin, Zhang Chong, Xiong Ling, Song Guangdong, Liu Fei (2022) Changes of antibiotic occurrence and hydrochemistry in groundwater under the influence of the South-to-North Water Diversion (the Hutuo River, China). Sci Total Environ 832:154779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154779
Xu Ximeng, Chen Weiming, Shaoyan Zong Xu, Ren, and Dan Liu, (2019) Atrazine degradation using Fe3O4-sepiolite catalyzed persulfate: Reactivity, mechanism and stability. J Hazard Mater 377:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.029
Yu J, Tang L, Pang Ya, Zeng G, Wang J, Deng Y, Liu Y, Feng H, Chen S, Ren X (2019) Magnetic nitrogen-doped sludge-derived biochar catalysts for persulfate activation: Internal electron transfer mechanism. Chem Eng J 364:146–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.163
Yu Jiangfang, Tang Lin, Pang Ya, Zeng Guangming, Feng Haopeng, Zou Jiajing, Wang Jingjing, Chengyang Feng Xu, Zhu Xilian Ouyang, Tan Jisui (2020) Hierarchical porous biochar from shrimp shell for persulfate activation: A two-electron transfer path and key impact factors. Appl Catal B Environ 260:118160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118160
Zbair M, Ahsaine HA, Anfar Z (2018) Porous carbon by microwave assisted pyrolysis: An effective and low-cost adsorbent for sulfamethoxazole adsorption and optimization using response surface methodology. J Clean Prod 202:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.155
Zhang Runyuan, Zheng Xiaoxian, Zhang Dongqing, Niu Xiaojun, Ma Jinlin, Lin Zhang, Mingli Fu, Zhou Shaoqi (2021) Insight into the roles of endogenous minerals in the activation of persulfate by graphitized biochar for tetracycline removal. Sci Total Environ 768:144281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144281
Zhou Y, Cao S, Xi C, Lai G, Li X, Zhang L, Wang G, Chen Z (2018) Controllable synthesis of magnetic nanoporous carbon with tunable porosity for the efficient cleanup of vegetable samples. Anal Chim Acta 1041:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.040
Zhou Yue, Cao Shurui, Xi Cunxian, Li Xianliang, Zhang Lei, Wang Guomin, Chen Zhiqiong (2019) A novel Fe3O4/graphene oxide/citrus peel-derived bio-char based nanocomposite with enhanced adsorption affinity and sensitivity of ciprofloxacin and sparfloxacin. Bioresour Technol 292:121951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121951
Zhu D, An XL, Chen QL, Yang XR, Christie P, Ke X, Wu LH, Zhu YG (2018) Antibiotics Disturb the Microbiome and Increase the Incidence of Resistance Genes in the Gut of a Common Soil Collembolan. Environ Sci Technol 52:3081–3090. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04292
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFC1601101) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773482).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Pang: conceptualization, data curation, writing—original draft. Yonghui Wang: methodology, investigation. Shuang Li: validation. Yuanyuan Luo: investigation. Jian Hou: formal analysis. Guanyu Wang: resources. Tie Han: supervision. Qingbin Guo: conceptualization, writing—reviewing, and editing. Huanying Zhou: writing—review and editing, Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition. Zhixian Gao: Conceptualization, Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, W., Wang, Y., Li, S. et al. Novel magnetic graphoxide/biochar composite derived from tea for multiple SAs and QNs antibiotics removal in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43215–43228 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25298-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25298-w