Abstract
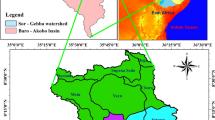
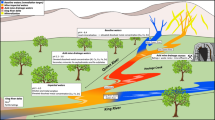
Many subsidence lakes have formed in eastern China as a result of underground coal mining. These coal mining–related subsidence lakes vary in their formation time and connectivity with rivers. These factors may influence the water chemistry and hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope characteristics of the lake water. This study collected and tested subsidence lake water, atmospheric precipitation, river water, and shallow groundwater in the study area. The results showed that the water chemical types of the subsidence lake water and river water are Cl-Na and HCO3·Cl-Na and that the water chemical types of the shallow groundwater are mainly HCO3·Cl-Na and HCO3·Cl-Ca. There are no significant differences in the water chemical characteristics of subsidence lakes with different subsidence ages and types. The major ions in each water body mainly come from evaporite dissolution and silicate weathering, and ion exchange occurs. Reverse ion exchange occurs in some shallow groundwater samples. The stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in the subsidence lake water, river water, and shallow groundwater are distributed along a straight line with a slope less than that of the LMWL, indicating that these water bodies have a common source, namely, precipitation. With increases in the formation time of the subsidence lakes, the heavy isotopes in the lake water gradually become depleted, and the d value gradually increases, mainly driven by precipitation dilution, weakening evaporation, river recharge, and groundwater recharge. The isotopic values of different types of lakes with the same subsidence time differ little. The research results may provide scientific guidance for the rational development and utilization of water resources in coal mining subsidence areas, enrich the study of the hydrological cycle in the area, and are of great significance for the protection of the local water balance and water environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adimalla N, Qian H, Li P (2019) Entropy water quality index and probabilistic health risk assessment from geochemistry of groundwaters in hard rock terrain of Nanganur County, South India. Geochem 80:125544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125544
An SK, Jiang CL, Zhang WX, Chen X, Zheng LG (2020) Influencing factors of the hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and shallow groundwater in the subsidence area of the Huainan Coalfield Influencing factors of the hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and shallow groundwater in the subsidence area of the Huainan Coalfield. Arab J Geosci 13:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5140-3
Azizi F, AsghariMoghaddam A, Nazemi A (2018) Introducing an novel method in evaluation of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics, GWQISI index: case study-Malekan Aquifer. Northwest of Iran Arab J Geosci 44(2):86–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4360-x
Benettin P, Volkmann THM, Freyberg JV, Jana F (2018) Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:2881–2890. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-2881-2018-40
Bhat MA, Zhong J, Dar T, Kumar A, Li S-L (2022) Spatial distribution of stable isotopes in surface water on the upper Indus River basin (UIRB): implications for moisture source and paleo elevation reconstruction. Appl Geochem 136:105137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105137
Chen XM, Gan YQ, Liu YD, Li XQ, Yu TT (2011) Spatial distribution characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in the main stream of the Yangtze River. Geol Sci Technol Bull 30:10–114. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.05.018
Chen YC, Yuan L, Xu C (2016) Investigation on using mining subsidence area to build a reservoir in Huainan Coal Mining Area. J China Coal Soc 41:2830–2835. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.0135
Chen BY, Liu GJ, Wu D, Sun RY (2018) The elemental geochemical characteristics of aluminous argillites in Taiyuan Formation from Huainan coalfield. Coal Geol Explor 46(03):21–27
Chen X, Jiang CL, Zheng LG, Zhang LQ, Hu J (2021) Evaluating the genesis and dominant processes of groundwater salinization by using hydrochemistry and multiple isotopes in a mining city. Environ Pollut 283:117381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117381
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dansgaard W (1953) The abundance of 18O in atmospheric water and water vapour. Tellus 5:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2153-3490.1953.tb01076.x
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2153-3490.1964.tb00181.x
Egbueri JC, Ezugwu CK, Unigwe CO, Mgbenu CK (2020) Multidimensional analysis of the contamination status, corrosivity and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater from parts of the Anambra Basin Nigeria. Anal Lett 54:2126–2156. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1843049
Ge T, Chu TT, Liu GJ, Fan X, Wu D (2014) Characterisics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of deep ground water in the Panxie mining area in Huainan Coalfield. J U Sci Technol Chin 44:112–118. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2014.02.006
Gibson JJ, Reid R (2014) Water balance along a chain of tundra lakes: a 20-year isotopic perspective. J Hydrol 519:2148–2164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.10.011
Gibson JJ, Edwards T, Birks SJ, Amour NA, Buhay WM, McEachern P, Wolfe BB, Peters DL (2005) Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrol Process 19:303–327. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5766
Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Edwards TWD (2008) Global prediction of δA and δ2H-δ18O evaporation slopes for lakes and soil water accounting for seasonality. Glob Biogeochem Cycl 22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GB002997
Gonfiantini R (1978) Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature 271:534–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/271534a0
Gonfiantini R, Wassenaar LI, Araguas-Araguas L, Araguas LA, Aggarwal PK (2018) A unified Craig-Gordon isotope model of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during fresh or saltwater evaporation. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 235:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.05.020
Guo ZJ, Song HZ (2005) Groundwater chemical composition presence form and its SI value calculation. Resour Environ Eng 19(3):200–203. https://doi.org/10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2005.03.011
Guo C, Chen Y, Xia W (2020) Eutrophication and heavy metal pollution patterns in the water suppling lakes of China’s south-to-north water diversion project. Sci Total Environ 711:134543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134543
Halder J, Decrouy L, Vennemann TW (2013) Mixing of Rhne River water in Lake Geneva (Switzerland–France) inferred from stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope profiles. J Hydrol 477:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.026
Han DM, Song XF, Currell MJ, Cao GL, Zhang YH, Kang YH (2011) A survey of groundwater levels and hydrogeochemistry in irrigated fields in the Karamay Agricultural Development Area, northwest China: implications for soil and groundwater salinity resulting from surface water transfer for irrigation. J Hydrol 405:217–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.052
Hao S, Li FD, Li YH, Gu CK, Zhang QY, Qiao YF, Jiao L, Zhu N (2019) Stable isotope evidence for identifying the recharge mechanisms of precipitation surface water and groundwater in the Ebinur Lake basin. Sci Total Environ 657:1041–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.102
Hao YR, Wang P, Zhang MZ (2020) Hydrochemical characteristic and its driving force of groundwater in the covered karst in Pearl River Basin. Ecol Environ Sci 29(2):337–344. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.02.015
Horita J, Wesolowski DJ (1994) Liquid-vapor fractionation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes of water from the freezing to the critical temperature. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:3425–3437. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(94)90096-5
Hu JS (2011) The hydrogeological characteristics of each aquifer-bearing aquifer in the Cenozoic of Zhangji mining area of Huainan coalfield were discussed. Sci Technol Inform 26:155. https://doi.org/10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2011.26.002
Hui HJ, Chen B, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF (2002) Models of oxygen isopote transport in the process of fluid-rock interactions. Earth Sci Front 04:431–439
Jiang Q, Xu GQ, Liang XY (2007) Based on the principal component and cluster analysis to assess the water quality of the groundwater in Huainan mine area. Energy Enviro Prot 16(02):51–53
Katz BG, Coplen TB, Bullen TD et al (1997) Use of chemical and isotopic tracers to characterize the interactions between ground water and surface water in mantled karst. Groundwater 35(6):1014–1028. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1997.tb00174.x
Kong LJ, Jiang CL, Zheng LG, Cheng H, Fang LB (2017) Characters of hydrochemistry and their influenced factors of different waters in the Linhuan coal mining subsidence area of Huaibei City. J Lake Sci 29:1158–1167. https://doi.org/10.18307/2017.0513
Krishan G, Prasad G, Anjali Kumar CP, Patidar N, Yadav BK, Kansal ML, Singh S, Sharma LM, Bradley A, Verma SK (2020) Identifying the seasonal variability in source of groundwater salinization using deuterium excess - a case study from Mewat, Haryana, India. J Hydrol Reg Stud 31:100724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2020.100724
Kura NU, Ramli MF, Sulaiman WNA et al (2013) Evaluation of factors influencing the groundwater chemistry in a small tropical island of Malaysia. Int J Env Res Pub He 10(5):1861–1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10051861
Li G, Zhang XP, Song S (2016) Research progress of δD and δ18O in different water bodies in China. J Meteorol Environ 32:132–138. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2016.04.018
Li QY, Wu JL, Shen BB, Zeng HA (2018) Water chemistry and stable isotopes of different water types in Tajikistan. Environ Process 5:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0312-9
Li JM, Yu JH, Zhang WZ (2019a) Spatial distribution and governance of coal-mine subsidence in China. J Nat Resour 34(4):867–880
Li ZK, Xia MH, Dong SG, Liu XB, Wang C, Zhou YZ (2019) Analysis of chemical characteristics and evolution characteristics of shallow groundwater in Luoyang Basin. Earth Environ 47:57–63. https://doi.org/10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2019.47.012
Liao D, Pang Z, Xiao W (2020) Constraining the water cycle model of an important karstic catchment in southeast Tibetan Plateau using isotopic tracers (2H, 18O, 3H, 222Rn). Water 12(12):3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123306
Liu JY, Zhang FP, Fei Q et al (2018) Influence of below-cloud secondary evaporation on stable isotope composition in precipitation in Northwest China. Chin J Appl Ecol 29(5):1479–1488. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201805.028
Liu SJ, Liu YF, Wang K, Li XN (2022) Effects of reservoir and urban construction on hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics in Huangshui River Basin. Yangtze River 53(04):53–58. https://doi.org/10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2022.04.009
Lu CY, Li H, Sun QY, Wang H, Yan L, Zhang B (2016) Reserch on the distributed “river-subsidence area-groundwater” coupling simulation of coal mining subsidence area: II: application. Adv Water Sci 27:366–376. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2016.03.004
Ma YB, Xu Q, Gao DQ, Zhang BB (2018) Composition of hydrogen and oxygen isotope in precipitation and source apportionment of water vapor in the wetland forest area of Tangpu reservoir Zhejiang Province. For Res 31(3):37–44. https://doi.org/10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2018.03.006
Ma SJ, Qu SM, Gou JF (2022) Study on isotope effect in different research periods in the lower reach of the Yangtze River. Water Res Power 40(09):10–13. https://doi.org/10.20040/j.cnki.1000-7709.2022.20212582
Maurya P, Kumari R, Mukherjee S (2019) Hydrochemistry in integration with stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to assess seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Kachchh district, Gujarat, India. J Geochem Explor 196:42–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.09.013
Mayo AL, Loucks MD (1995) Solute and isotopic geochemistry and ground water flow in the central Wasatch Range. Utah J Hydro 172(1–4):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-E
McGuire KJ, McDonnell JJ (2006) A review and evaluation of catchment transit time modeling. J Hydrol 330:543–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.04.020
Ogrinc N, Kanduc T, Stichler W, Vreca P (2008) Spatial and seasonalvariations in δ18O and δD values in the River Sava in Slovenia. J Hydrol 359:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.010
Qian H, Wu JH, Zhou YH, Li PY (2014) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol Process 28:3554–3562. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9915
Qin W, Han D, Song X, Liu S (2021) Environmental isotopes (δ18O, δ2H, 222Rn) and hydrochemical evidence for understanding rainfall-surface water-groundwater transformations in a polluted karst area. J Hydrol 592:125748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125748
Sheikhy Narany T, Ramli MF, Aris AZ, Sulaiman WNA, Juahir H, Fakharian K (2014) Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using classic integrated geochemical methods and geostatistical techniques, in Amol-Babol Plain, Iran. Sci World J 2014:419058. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/419058
Shen YJ, Peng XH (2014) Stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in the precipitation of Yingtan. Ecol Environ Sci 23(1):101–105. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2014.01.008
Shen ZL, Zhu WH, Zhong ZS (1993) Fundamentals of hydrogeochemistry. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Shi PJ, Huang YN, Ji WJ, Xiang W, Jaivime E, Zhi L (2018) Impacts of deep-rooted fruit trees on recharge of deep soil water using stable and radioactive isotopes. Agr Forest Meteorol 300:108325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108325
Song X, Bei YP, Yuan BQ, Cao DM (2022) Influence of floating photovoltaic power plants on water ecological environment in coal mining subsidence water area of Huainan City. Water Resour Prot 38(05):204–211
Soulsby C, Birkel C, Geris J, Dick J, Tunaley C, Tetzlaff Z (2015) Stream water age distributions controlled by storage dynamics and nonlinear hydrologic connectivity: modeling with high-resolution isotope data. Water Resour Res 51:7759–7776. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017888
Stumpp C, Klaus J, Stichler W (2014) Analysis of long-term stable isotop-ic composition in German precipitation. J Hydrol 517:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.034
Sun PF, Yi QT, Xu GQ (2014) Characteristics of water chemistry and their influencing factors in subsidence waters in the Huainan and Huaibei mining areas, Anhui Province. J Chin Coal Soc 39:1345–1353. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.0959
van der Sleen P, Zuidema PA, Pons TL (2017) Stable isotopes in tropical tree rings: theory, methods and applications. Funct Ecol 31(9):1674–1689. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12889
Vystavna Y, Hejzlar J, Kopáček J (2017) Long-term trends of phosphorus concentra-tions in an artificial lake: socio-economic and climate drivers. PLoS ONE 12:0186917. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186917
Wang HB, Li L (2011) Cenozoic loose beds groundwater exploitation assurance level assessment in Zhuji west coalmine Huainan City Coal. Geol China 23(02):42–44
Wang T, Zhang JR, Liu X, Wang L (2013a) Variations of stable isotopes in precipitation and water vapor sources in Nanjing area. J China Hydrol 33(4):25–31
Wang TT, Yi QT, Hu YB, Yan JP, Yu HJ, Dong XL (2013) Eutrophication and nutrient enrichment bioassays in the waters of the Huainan and Huaibei coal mining subsidence areas, Anhui Province. J Lake Sci 25:916–926. https://doi.org/10.18307/2013.0616
Wang JH, Lu CY, Sun QY, Xiao WH, Cao GL, Li H, Yan LJ, Zhang B (2017) Simulating the hydrologic cycle in coal mining subsidence areas with a distributed hydrologic model. Sci Rep 7:518–528. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39983
Wang BL, Zhang HT, Liang X, Li XD, Wang FS (2019) Cumulative effects of cascade dams on river water cycle: evidence from hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. J Hydrol 568:604–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.11.016
Wassenaar LI, Athanasopoulos P, Hendry MJ (2011) Isotope hydrology of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia, Canada. J Hydrol 411:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.09.032
Wei KQ, Lin RY (1994) Influence of monsoon climate on isotopic composition of rainwater in China. Chin J Geochem 23:32–41. https://doi.org/10.19700/j.0379-1726.1994.01.004
Wei CC, Ren SM, Yang PL (2021) Effects of irrigation methods and salinity on CO2 emissions from farmland soil during growth and fallow periods. Sci Total Environ 752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141639
Wu XQ, Zhou DW, An SK, Lu CH (2015) Evolvement trend of land and water systems in Huainan Panxie mining area and its countermeasures. J Chin Coal Soc 40:2927–2932. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.1087
Wu X, An YH, Wei SB (2021) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of shallow groundwater in Dingxin valley, lower reaches of Heihe River. J Arid Land Resour Environ 35(09):103–109. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.248
Yang KH, Han GL (2020) Controls over hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of surface water and groundwater in the Mun River catchment, northeast Thailand: implications for the water cycle. J Hydrol 28:1021–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-02106-9
Yang Q, Mu H, Guo J, Bao X, Martin JD (2019) Temperature and rainfall amount effects on hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope in precipitation. Quatern Int 519:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2019.01.027
Yang J, Dudley BD, Montgomery K, Hodgetts W (2020) Characterising spatial and temporal variation in 18O and 2H content of New Zealand river water for better understanding of hydrologic processes. Hydrol Process 34:5474–5488. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13962
Yuan H, Yang S, Wang B (2022) Hydrochemistry characteristics of groundwater with the influence of spatial variability and water flow in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20685-1
Zannoni D, Steen-Larsen HC, Rampazzo G, Dreossi G (2019) The atmospheric water cycle of a coastal lagoon: An isotope study of the interactions between water vapor, precipitation and surface waters. J Hydrol 572:630–644. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.20847.07846
Zhang YH, Wu YQ, Wen XH (2006) Application of environ-mental isotopes in water cycle. Adv Water Sci 5:738–747
Zhang YH, Wu YQ (2007) Variation of δ18O in water in Heihe river basin. Adv Water Sci 6:864–870
Zhang L, Yi QT, Li H, Xu X, Wang XM (2015) Water quality and water environmental capacity for the small subsidence lakes in the Huainan and Huaibei coal mine areas, Anhui Province. Chin J Ecol 34:1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.20150311.028
Zhang B, Zhao D, Zhou PP, Qu S, Liao F, Wang GC (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and dominant water–rock interactions in the Delingha area, Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Water 12:836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030836
Zheng SH, Hou FG, Ni BL (1983) A study on stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of atmospheric precipitation in my coconut. Chin Sci Bull 28: 801–806. CNKI:SUN:KXTB.0.1983–13–010
Zheng LG, Chen X, Dong XL, Wei XP, Jiang CL, Tang Q (2019) Using δ34S-SO4 and δ18O-SO4 to trace the sources of sulfate in different types of surface water from the Linhuan coal-mining subsidence area of Huaibei, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 181:231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.001
Zheng T, Jiao TL, Hu B et al (2021) Hydrochemical characteristics and origin of groundwater in the central Guohe river basin. Environ Sci 42(02):766–775. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202006037
Zhou XP, Peng YX, Ma L, Liu MC, Qian JZ (2019) Indication founction of hydrogen and oxygen isotopic to groundwater of Huainan Panji mine area. J Hefei Univ Technol 42(04):536–540
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of the Department of Education of Anhui Province (KJ2021A0085) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chunlu Jiang: methodology, formal analysis, software, writing original draft, and visualization. Chenghong Jiang, Junzhen Zha, Hui Liu, and Dou Liu: data curation, validation, writing, review, and editing. Liugen Zheng: supervision and conceptualization. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No ethical approval was necessary for this study.
Consent to participate
All participants in this study consent to participation.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to this publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Jiang, C., Zha, J. et al. Water chemistry and stable isotope characteristics of subsidence lakes in coal mining areas, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43152–43167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25285-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25285-1