Abstract
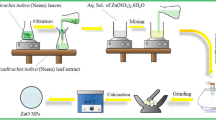
Zinc and magnesium oxide nanoparticles were fabricated using green synthesis method for the sequestration of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) from the aqueous medium. The biogenically prepared ZnO@EC and MgO@EC nanoparticles were successfully loaded on the Eucalyptus. The prepared nanomaterials were characterized using various techniques such as FESEM, TGA, XRD, EDX, FTIR, BET, and elemental mapping. FE-SEM analysis has revealed the surface morphology of ZnO nanoparticles, which were rod-like and spherical in shape, whereas MgO nanoparticles were of irregular shape. Batch mode was selected to remove the hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using the prepared nanomaterials. The Cr(VI) adsorption was carried out under optimized conditions, viz., pH (3.0), adsorbent dose (0.05 g), contact time (150 min), temperature (25 ± 2 °C), and initial concentration (50 mg/L). The experimental results were compared using the different isotherm models; The observations have indicated that experimental data fit better with Freundlich (R2 = 0.99) and Langmuir (R2 = 0.99) isotherms, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity of ZnO@EC and MgO@EC for Cr(VI) was found to be 49.3 and 17.4 mg/g, respectively. The regeneration study of the adsorbents was conducted using different desorbing agents viz., ethanol, NaOH, and NaCl. The desorbing agent NaOH performed better and showed removal percentage of 34.24% and 20.18% for ZnO@EC and MgO@EC, respectively, after the three reusability cycles. The kinetics of reaction was assessed using the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models. The experimental data of both the nanomaterials ZnO@EC and MgO@EC obeyed pseudo-second-order model with correlation coefficient values 0.999 and 0.983, respectively. The thermodynamic study confirmed that adsorption was feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic. The adsorbents were tested for spiked real water which confirms their applicability and potential in real water systems also. The results indicated fair removal of chromium suggesting applicability of both adsorbents.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors have included all the relevant data and the source of freely available data in the manuscript.
References
Abshirini Y, Esmaeili H, Foroutan R (2019) Enhancement removal of Cr(VI) ion using magnetically modified MgO nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 6(12):125513
Ahlawat W, Kataria N, Dilbaghi N, Hassan AA, Kumar S, Kim KH (2020) Carbonaceous nanomaterials as effective and efficient platforms for removal of dyes from aqueous systems. Environ Res 181:108904
Amde M, Yao J, Liu JF, Tan ZQ (2020) Nano-selenium functionalised zinc oxide nanorods: a superadsorbent for mercury (II) removal from waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 122495
Athar T, Hakeem A, Ahmed W (2012) Synthesis of MgO nanopowder via non aqueous sol–gel method. Adv Sci Lett 7(1):27–29
Bagheri M, Younesi H, Hajati S, Borghei SM (2015) Application of chitosan-citric acid nanoparticles for removal of chromium (VI). Int J Biol Macromol 80:431–444
Baig U, Rao RAK, Khan AA, Sanagi MM, Gondal MA (2015) Removal of carcinogenic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions using newly synthesised and characterised polypyrrole–titanium (IV) phosphate nanocomposite. Chem Eng 280:494–504
Bansal M, Garg R, Garg VK, Garg R, Singh D (2022) Sequestration of heavy metal ions from multi-metal simulated wastewater systems using processed agricultural biomass. Chemosphere 296:133966
Bilici Z, Işık Z, Aktaş Y, Yatmaz HC, Dizge N (2019) Photocatalytic effect of zinc oxide and magnetite entrapped calcium alginate beads for azo dye and hexavalent chromium removal from solutions. J Water Process Eng 31:100826
Chauhan AK, Kataria N, Garg VK (2020) Green fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles using Eucalyptus spp. leaves extract and their application in wastewater remediation. Chemosphere, 247, 125803
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK (2010) Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J Environ Manage 91(11):2238–2247
Dehghani MH, Sanaei D, Ali I, Bhatnagar A (2016) Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using treated waste newspaper as a low-cost adsorbent: kinetic modeling and isotherm studies. J Mol Liq 215:671–679
Farooqi ZH, Akram MW, Begum R, Wu W, Irfan A (2021) Inorganic nanoparticles for reduction of hexavalent chromium: physicochemical aspects. J Hazard Mater 402:123535
Fendorf S, Wielinga BW, Hansel CM (2000) Chromium transformations in natural environments: the role of biological and abiological processes in chromium (VI) reduction. Int Geol Rev 42(8):691–701
Flower H, Rains M, Lewis D, Zhang JZ, Price R (2017) Saltwater intrusion as potential driver of phosphorus release from limestone bedrock in a coastal aquifer. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 184:166–176
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Garg VK, Kataria N (2016) Nanomaterial-based sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions from water in book: advanced nanomaterials for wastewater remediation. Publisher: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, pp. 179-200
Gupta VK, Chandra R, Tyagi I, Verma M (2016) Removal of hexavalent chromium ions using CuO nanoparticles for water purification applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 478:54–62
Herlekar M, Barve S, Kumar R (2014) Plant-mediated green synthesis of iron nanoparticles. J Nanopart 2014:140614. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/140614
Ho YS, McKay G (2000) The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Res 34:735–742
Hu J, Chen G, Lo IM (2005) Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Res 39(18):4528–4536
Islam MA, Angove MJ, Morton DW (2019) Recent innovative research on chromium (VI) adsorption mechanism. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 12:100267
Jorfi S, Barzegar G, Ahmadi M, Soltani RDC, Takdastan A, Saeedi R, Abtahi M (2016) Enhanced coagulation-photocatalytic treatment of acid red 73 dye and real textile wastewater using UVA/synthesised MgO nanoparticles. J Env Manage 177:111–118
Joshi S, Kataria N, Garg VK, Kadirvelu K (2020) Pb2+ and Cd2+ recovery from water using residual tea waste and SiO2@ TW nanocomposites. Chemosphere 257:127277
Kataria N, Chauhan AK, Garg VK, Kumar P (2022a) Sequestration of heavy metals from contaminated water using magnetic carbon nanocomposites. J Hazard Mater Adv 6:100066
Kataria N, Bhushan D, Gupta R, Rajendran S, Teo MYM, Khoo KS (2022b) Current progress in treatment technologies for plastic waste (bisphenol A) in aquatic environment: occurrence, toxicity and remediation mechanisms. Environmental Pollution, 120319
Khalafi T, Buazar F, Ghanemi K (2019) Phycosynthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles toward organosulfur pollutants. Sci Rep 9(1):6866
Khan TA, Nazir M, Ali I, Kumar A (2017) Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using guar gum–nano zinc oxide biocomposite adsorbent. Arab J Chem 10:S2388–S2398
Khare N, Bajpai J, Bajpai AK (2018) Graphene coated iron oxide (GCIO) nanoparticles as efficient adsorbent for removal of chromium ions: preparation, characterisation and batch adsorption studies. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 10:148–162
Kurniawan TA, Sillanpaa ME, Sillanpaa M (2012) Nanoadsorbents for remediation of aquatic environment: local and practical solutions for global water pollution problems. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(12):1233–1295
Lace A, Ryan D, Bowkett M, Cleary J (2019) Chromium monitoring in water by colorimetry using optimised 1, 5-diphenylcarbazide method. Int J Env Res Pub He 16(10):1803
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 24:1–39
Li LX, Xu D, Li XQ, Liu WC, Jia Y (2014) Excellent fluoride removal properties of porous hollow MgO microspheres. New J Chem 38(11):5445–5452
Maremeni LC, Modise SJ, Mtunzi FM, Klink MJ, Pakade VE (2018) Adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium by diphenylcarbazide-grafted Macadamia nutshell powder. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018
Meng A, Xing J, Li Z, Li Q (2015) Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation, adsorption property, and recyclability. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(49):27449–27457
Nriagu JO, Nieboer E (Eds.) (1988) Chromium in the natural and human environments (Vol. 20). John Wiley & Sons
Owlad M, Aroua MK, Daud WAW, Baroutian S (2009) Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: a review. Water, Air, Soil Poll 200(1–4):59–77
Parlayici S, Eskizeybek V, Avcı A, Pehlivan E (2015) Removal of chromium (VI) using activated carbon-supported-functionalised carbon nanotubes. J Nanostructure Chem 5(3):255–263
Patil HR, Murthy ZVP (2016) Vanadium-doped magnesium oxide nanoparticles formation in presence of ionic liquids and their use in photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Acta Metall Sin- Engl 29(3):253–264
Paul ML, Samuel J, Das SB, Swaroop S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2012) Studies on Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions by nanoalumina. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(46):15242–15250
Pourmortazavi SM, Taghdiri M, Makari V, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M (2015) Procedure optimisation for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Eucalyptus oleosa. Spectrochim Acta a: Mol Biomol Spectrosc 136:1249–1254
Sankararamakrishnan N, Jaiswal M, Verma N (2014) Composite nanofloral clusters of carbon nanotubes and activated alumina: an efficient sorbent for heavy metal removal. Chem Eng 235:1–9
Schlur L, Calado JR, Spitzer D (2018) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanorods or nanotubes on one side of a microcantilever. R Soc Open Sci 5(8):180510
Singh S, Naik TSK, Anil AG, Khasnabis S, Nath B, Basavaraju U, Ramamurthy PC (2022) A novel CaO nanocomposite cross linked graphene oxide for Cr(VI) removal and sensing from wastewater. Chemosphere 301:134714
Siriwardane IW, Udangawa R, de Silva RM, Kumarasinghe AR, Acres RG, Hettiarachchi A, de Silva KN (2017) Synthesis and characterisation of nano magnesium oxide impregnated granular activated carbon composite for H2S removal applications. Mater Des 136:127–136
Temkin MJ, Temkin V, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modification to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physiochim USSR 12:217–222
Xiao Z, Zhang H, Xu Y, Yuan M, Jing X, Huang J, Sun D (2017) Ultra-efficient removal of chromium from aqueous medium by biogenic iron-based nanoparticles. Sep Purif Technol 174:466–473
Zhang JZ (2011) Avoiding spurious correlation in analysis of chemical kinetic data. Chem Commun 47(24):6861–6863
Zhang JZ, Huang XL (2011) Effect of temperature and salinity on phosphate sorption on marine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 45(16):6831–6837
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amit Kumar Chauhan: conceptualization, investigation, resources, writing-original draft.
Navish Kataria: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, writing-original draft.
Renuka Gupta: validation, supervision, resources, writing-review and editing.
Vinod Kumar Garg: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
No prior ethical approval was necessary for the study.
Consent to participate
No human subjects included in the study. Consent is not required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Preprint server
The manuscript has been submitted to a preprint server prior to submission on ESPR.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, A.K., Kataria, N., Gupta, R. et al. Biogenic fabrication of ZnO@EC and MgO@EC using Eucalyptus leaf extract for the removal of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) ions from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 124884–124901 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24967-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24967-6