Abstract
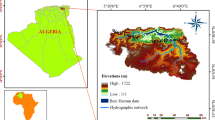
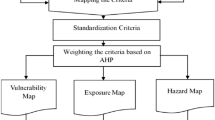
A highly visible form of soil erosion is gully, a significant geomorphological feature, resulting from water erosion and causing land degradation and deterioration. In arid and semi-arid environment, gully erosion is conceived as an important source of sediment supply washing out the top fertile soil and exposing lower soil layers. The present study is conducted on the lateritic terrain of Rupai watershed of eastern plateau fringe of India, where water erosion is a serious concern. In order to prepare a gully erosion vulnerability mapping, the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) model coupled with geospatial technology is adopted taking into account thirteen bio-physical factors. It is revealed that around 49% area of the watershed belongs to high to very high gully erosion vulnerability zone (GEVZ) followed by moderate risk zone of 31.64%. This model is validated performing an accuracy assessment, which is calculated to be 90.91%, and the value of Kappa co-efficient is 0.86. It is imperative to estimate the average annual soil loss alongside of delineating GEVZ; thus, the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model is used with geospatial technology. It unveils that the average estimated soil loss of the watershed varies from < 15 to 431 t ha−1 y−1. Around 29% of the study area experiences high to very high (57 to > 147 t ha−1 y−1) soil erosion risk, where 68% area endures low level of soil erosion risk (< 15 t ha−1 y−1). The study of gully morphology depicts gully depth ranging from < 1 to 5 m (small to medium gully) with V and U shapes. Results obtained from this study may help in planning and management of land use and soil erosion conservation.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Akadiri PO, Olomolaiye PO, Chinyio EA (2013) Multi-criteria evaluation model for the selection of sustainable materials for building projects. Autom Constr 30:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2012.10.004
Al-Abadi AM, Al-Ali AK (2018) Susceptibility mapping of gully erosion using GIS-based statistical bivariate models: a case study from Ali Al-Gharbi district, Maysan Governorate, Southern Iraq. Environ Earth Sci 77(6):249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7434-2
Al-Bawi AJ, Al-Abadi AM, Pradhan B, Alamri AM (2021) Assessing gully erosion susceptibility using topographic derived attributes, multi-criteria decision-making, and machine learning classifiers. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 12(1):3035–3062. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.1994024
Alexakis DD, Hadjimitsis DG, Agapiou A (2013) Integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and precipitation data for the assessment of soil erosion rate in the catchment area of “Yialias” in Cyprus. Atmos Res 131:108–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.02.013
Amiri M, Pourghasemi HR, Ghanbarian GA, Afzali SF (2019) Assessment of the importance of gully erosion effective factors using Boruta algorithm and its spatial modelling and mapping using three machine learning algorithms. Geoderma 340:55–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.12.042
Arabameri A, Razaei K, Pourghasemi HR, Lee S, Yamani M (2018) GIS-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: a comparison among three data-driven models and AHP knowledge-based technique. Environ Earth Sci 77(17):628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7808-5
Arabameri A, Pourghasemi HR (2019) Spatial modeling of gully erosion using linear and quadratic discriminant analyses in GIS and R.’ Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences, Elsevier 299–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815226-3.00013-2
Aslam B, Maqsoom A, Alaloul WS, Musarat MA, Jabbar T, Zafar A (2021) Soil erosion susceptibility mapping using a GIS-based multi-criteria decision approach: case of District Chitral, Pakistan. Ain Shams Eng J 12(2):1637–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.09.015
Assefa E, Hans-Rudolf B (2016) Farmers’ perception of land degradation and traditional knowledge in Southern Ethiopia—resilience and stability. Land Degrad Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2364
Aulakh MS, Sidhu GS (2015) Soil degradation in India: causes, major threats, and management options. In: MARCO Symposium 2015 - Next Challenges of Agro-Environmental Research in Monsoon Asia, 151–56. Tsukuba, Japan: National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences (NIAES)
Avand M, Janizadeh S, Naghibi SA, Pourghasemi HR, Bozchaloei SK, Blaschke T (2019) A comparative assessment of random forest and K-nearest neighbor classifiers for gully erosion susceptibility mapping. Water 11(10):2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102076
Ayalew L, Yamagishi H, Ugawa N (2004) Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based weighted linear combination, the Case in Tsugawa Area of Agano River, Niigata Prefecture, Japan. Landslides 1(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-003-0006-9
Ayele GK, Gessess AA, Addisie MB, Tilahun SA, Tenessa DB, Langendoen EJ et al (2015) The economic cost of upland and gully erosion on subsistence agriculture for a watershed in the Ethiopian highlands. Afr J Agric Resour Econ 10(4):265–278
Azareh A, Rahmat O, Rafiei-Sardooi E, Sankey JB, Lee S, Shahabi H, Ahmad BB (2019) Using the USLE: chances, challenges and implications of soil erosion modelling. Sci Total Environ 655:684–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.235
Balasubramani K, Mohan V, Kumaraswamy K, Saravanabavan V (2015) Estimation of soil erosion in a semi-arid watershed of Tamil Nadu (India) using revised universal soil loss equation (Rusle) model through GIS. Model Earth Syst Environ 1(3) https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0015-4
Bastola S, Dialynas YG, Bras RL, Noto LV, Istanbulluoglu E (2018) The role of vegetation on gully erosion stabilization at a severely degraded landscape: a case study from Calhoun Experimental Critical Zone Observatory. Geomorphology 308:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.12.032
Bawa AK (2017) Mitigating land degradation due to water erosion. Natl Acad Agric Sci, Policy Paper 88:1–19
Benjmel K, Amraoui F, Boutaleb S, Ouchchen M, Tahiri A, Touab A (2020) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in crystalline terrain using remote sensing, GIS techniques, and multicriteria data analysis (case of the Ighrem Region, Western Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Water 12:471. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020471
Bensekhria A, Bouhata R (2022) Assessment and mapping soil water erosion using RUSLE approach and GIS tools: case of Oued El-Hai Watershed, Aurès West, Northeastern of Algeria. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 11(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020084
Bera B, Bhattacharjee S, Chamling M, Ghosh A, Sengupta N (2021) Fluoride hazard and risk enumeration of hard rock unconfined aquifers in the extended part of Chhota Nagpur Gneissic complex. J Geol Soc India 97(2):199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1651-0
Besler H (1987) Slope properties, slope processes and soil erosion risk in the tropical rain forest of Kalimantan Timur (Indonesian Borneo). Earth Surf Proc Land 12(2):195–204
Bijukchhen SM, Kayastha P, Dhital MR (2013) A comparative evaluation of heuristic and bivariate statistical modelling for landslide susceptibility mappings in Ghurmi-Dhad Khola, East Nepal. Arab J Geosci 6(8):2727–2743
Bouhadeb CE, Menani MR, Bouguerra H, Derdous O (2018) Assessing soil loss using GIS based RUSLE methodology. Case of the Bou Namoussa Watershed – North-East of Algeria. J Water Land Dev 36(1):27–35. https://doi.org/10.2478/jwld-2018-0003
Bu CF, Cai QG, Zhang XC, Cheng QJ, Wu S (2009) Mechanism and erosion effect of development of soil crust of loess. Acta Pedologica Sinica 46(1):16–23
Bull LJ, Kirkby MJ (2002) Dryland rivers: hydrology and geomorphology of semi-arid channels. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, p 1–398
Çelik R (2019) Evaluation of groundwater potential by GIS-based multicriteria decision making as a spatial prediction tool: case study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin. Water 11:2630
Chakrabarty A (2011) Ecotourism development and security restructuring: a GIS based planning for peaceful dissuasion of Anarchism in Forest Provinces of India. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 21:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.07.006
Charlton RO (2008) Fundamentals of fluvial geomorphology, 1st edn. Routledge, Abingdon, p 1–264
Choubin B, Solaimani K, Rezanezhad F, Roshan MH, Malekian A, Shamshirband S (2019) Streamflow regionalization using a similarity approach in ungauged basins: application of the geo-environmental signatures in the Karkheh River Basin, Iran. Catena 182:104128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104128
Conforti M, Aucelli PCP, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F (2011) Geomorphology and GIS analysis for mapping gully erosion susceptibility in the Turbolo Stream Catchment (Northern Calabria, Italy). Nat Hazards 56(3):881–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9598-2
Dai FC, Lee CF (2002) Landslide characteristics and slope instability modeling using GIS, Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Geomorphology 42(3–4):213–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00087-3
Dandapat K, Hazari R, Bhunia GS, Shit PK (2020) The potential gully erosion risk mapping of River Dulung Basin, West Bengal, India using AHP method’. In Gully Erosion Studies from India and Surrounding Regions, Advance in Science, Technology & Innovation., 93–107. Springer International Publishing, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23243-6_6
Das B, Paul A, Bordoloi R, Tripathi OP, Pandey PK (2018) Soil erosion risk assessment of hilly terrain through integrated approach of RUSLE and geospatial technology: a case study of Tirap district, Arunachal Pradesh. Model Earth Syst Environ 4(1):373–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0435-z
Das B, Bordoloi R, Thungon LT, Paul A, Pandey PK, Mishra M, Tripathi OP (2020) An integrated approach of GIS, RUSLE and AHP to model soil erosion in West Kameng Watershed, Arunachal Pradesh. J Earth Syst Sci 129(1):94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-1356-6
de Lima JLMP, Singh VP (2002) The influence of the pattern of moving rainstorms on overland flow. Adv Water Resour 25(7):817–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00067-2
de Neergaard A, Magid J, Mertz O (2008) Soil erosion from shifting cultivation and other smallholder land use in Sarawak, Malaysia. Agr Ecosyst Environ 125(1):182–190
Deng L, Shangguan ZP, Li R (2012) Effects of the grain-for-green program on soil erosion in China. Int J Sedim Res 27(1):120–127
Dolui G, Chatterjee S, De Chatterjee N (2016) Geophysical and geochemical alteration of rocks in granitic profiles during intense weathering in Southern Purulia District, West Bengal, India. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, 132(2): 4–22 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0188-5
El Maaoui MA, Sfar Felfoul M, Boussema MR, Snane MH (2012) Sediment yield from irregularly shaped gullies located on the Fortuna Lithologic Formation in Semi-Arid Area of Tunisia. CATENA 93(2012):97–104
Erener A, Mutlu A, Sebnem Düzgünc H (2016) A comparative study for landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA), logistic regression (LR) and association rule mining (ARM). Eng Geol 203:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.09.007
Fadul HM, Salih AA, Imad-eldin AA, Inanaga S (1999) ‘Use of remote sensing to map gully erosion along the Atbara River, Sudan. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 1(3):175–180
FAO (2017) The future of food and agriculture – trends and challenges. Rome. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i6583e.pdf. 30 Jan 2022
Ganasri BP, Ramesh H (2016) Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS - a case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci Front 7(6):953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
Gao P (2013) Rill and gully development processes. In MountainandHillslope Geomorphology. TreatiseonGeomorphology. San Diego: Academic Press, 7, pp 122–31
Gayen A, Saha S, Pourghasemi HR (2020) Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and its validation by FR probability model. Geocarto Int 35(15):1750–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1581272
Ghosh, D, Karmakar M, Banerjee M, Mandal M (2020c) Evaluating the rate of change and predicting the future scenario of spatial pattern using markov chain model: a study from Baghmundi C.D. Block of Purulia District, West Bengal. Società Italiana Di Fotogrammetria e Topografia (SIFET), 2020c. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-020-00345-0
Ghosh D, Mandal M, Karmakar M, Banerjee M, Mandal D (2020b) Application of geospatial technology for delineating groundwater potential zones in the Gandheswari Watershed, West Bengal. Sustain Water Resour Manag 6(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00372-0
Ghosh D, Karmakar M, Banerjee M, Mandal M (2021c) Application of geospatial technology and plant diversity indices to assess the temporal change of forest covers across the Ajodhya Hills of West Bengal, India. Forest Resources Resilience and Conflicts, Elsevier, pp 139–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822931-6.00010-1.
Ghosh D, Mandal M, Karmakar M et al (2021b) The prevalence of undernutrition among the Santal children and quality of life of their households: a study from hilly region of West Bengal, India. Spatial Inform Res 29(5):775–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-021-00391-9
Ghosh D, Mandal M, Banerjee M, Karmakar M (2020a) Impact of hydro-geological environment on availability of groundwater using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and geospatial techniques: a study from the Upper Kangsabati River Basin. Groundw Sustain Dev 11:100419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100419
Ghosh S, Guchhait SK, Illahi RA, Subhankar B, Suvendu R (2021) Geomorphic character and dynamics of gully morphology, erosion and management in Laterite Terrain: few observations from Dwarka – Brahmani Interfluve, Eastern India. Geol Ecol Landscapes. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2020.1812148
Gómez-Gutiérrez A, Conoscenti C, Angileri SE, Rotigliano E, Schnabel S (2015) Using topographical attributes to evaluate gully erosion proneness (susceptibility) in two mediterranean basins: advantages and limitations. Nat Hazards 79(1):291–314
Government of India. ‘Census of India. (2011)’, n.d. http://censusindia.gov.in/
Government of West Bengal (2014) District statistical handbook Purulia. ‘Department of planning & statistics.’
Guaita-Martínez JM, de Castro-Pardo M, Perez-Rodríguez F, Martín Martín JM (2019) Innovation and multi-level knowledge transfer using a multi-criteria decisionmaking method for the planning of protected areas. J Innov Knowledge 4(4):256–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2019.01.001
Guerra CA, Maes J, Geijzendorffer I, Metzger MJ (2016) “An assessment of soil erosion prevention by vegetation in Mediterranean Europe: current trends of ecosystem service provision.” Ecol Ind 60:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.06.043
Guo M, Wang W, Wang T, Wang W, Kang H (2020) Impacts of Different Vegetation Restoration Options on Gully Head Soil Resistance and Soil Erosion in Loess Tablelands. Earth Surf Proc Land 45(4):1038–1050. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.4798
Guru B, Seshan K, Bera S (2017) Requency Ratio Model for Groundwater Potential Mapping and Its Sustainable Management in Cold Desert, India. J King Saud Univ Sci 29:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.08.003
Harvey AM (1992) Process Interactions, Temporal Scales and the Development of Hillslope Gully Systems: Howgill Fells, Northwest England. Geomorphology 5(3–5):323–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-555X(92)90012-D
Huggett RJ (2007) Fundamentals of Geomorphology’, Second. London, Madison Avenue, N.Y.: Routledge
Ibáñez J, Contador JL, Schnabel S, Valderrama JM (2016) Evaluating the Influence of Physical, Economic and Managerial Factors on Sheet Erosion in Rangelands of SW Spain by Performing a Sensitivity Analysis on an Integrated Dynamic Model. Sci Total Environ 544:439–449
Igwe O, Ugwuoke Ikechukwu J, Onwuka S, Ozioko O (2020) GIS-Based Gully Erosion Susceptibility Modeling, Adapting Bivariate Statistical Method and AHP Approach in Gombe Town and Environs Northeast Nigeria’. Geoenvironmental Disasters. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-020-00166-8
Ionita I, Fullen MA, Zgłobicki W, Poesen J (2015) Gully Erosion as a Natural and Human-Induced Hazard. Nat Hazards 79(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1935-z
Iro S (2020) Determining Causes of Gully Erosion and Associated Rates of Change in South-East Nigeria, Using a Remote Sensing and GIS Methodology. Am J Environ Sci 16(5):96–111. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2020.96.111
Allan JL, Watson DG, Hansen WF (2007) Using LiDAR Data to Map Gullies and Headwater Streams under Forest Canopy: South Carolina, USA. Catena 71(1):132–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2006.10.010
Kakembo V, Xanga WW, Rowntree K (2009) Topographic Thresholds in Gully Development on the Hillslopes of Communal Areas in Ngqushwa Local Municipality, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Geomorphology 110:118–95
Kale VS, Gupta A (2010) Introduction to geomorphology, 1st edn. Universities Press (India) Private Limited, Hyderabad, p 1–267
Karaburun A (2010) Estimation of C Factor for Soil Erosion Modeling Using NDVI in Buyukcekmece Watershed. Ozean J Appl Sci 3(1):77–85
Karmakar M, Banerjee M, Mandal, M, Ghosh D (2021) Application of AHP for groundwater potential zones mapping in plateau fringe terrain: study from Western Province of West Bengal. In: Shit PK, Bhunia GS, Adhikary PP, Dash CJ (eds) Groundwater and society. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64136-8_9
Kebede YS, Sinshaw BG, Endalamaw NT, Atinkut HB (2020) Modeling Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS at Watershed Level in the Upper Beles Ethiopia. Environ Challenges 2:100009
Kheir RB, Cerdan O, Abdallah C (2006) Regional Soil Erosion Risk Mapping in Lebanon. Geomorphology 82(3–4):374–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.05.012
Kirkby MJ, Bracken LJ (2009) Gully Processes and Gully Dynamics. Earth Surface Processes Landforms. J Br Geomorphological Res Group 34(14):1841–1851
Li X, Zhou Y, Tina Bo, Kuang R, Wang L (2015) GIS-Based Methodology for Erosion Risk Assessment of the Muddy Coast in the Yangtze Delta”. Ocean Coast Manag 108:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2014.09.028
Li Z, Cai CX, Shi ZHF, Wang TW (2005) Aggregate Stability and Its Relationship with Some Chemical Properties of Red Soils in Subtropical China. Pedosphere 15:129–36
Lim KJ, Sagong M, Engel BA, Tang Z, Choi J, Kim K-S (2005) GIS-Based Sediment Assessment Tool. Catena 64(1):61–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2005.06.013
Luvai A, Obiero J, Omuto C (2022) Soil Loss Assessment Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2022:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2122554
Mandal M, Modak P, Karmakar M, Ghosh D (2018) Tribal People of Purulia and Their Quality of Life. Eastern Geographer. Eastern Geographer 24(1):126–135
Marondedze AK, Schütt B (2020) Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. Sustainability 12:8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
Mokarram M, Zarei AR (2021) Determining Prone Areas to Gully Erosion and the Impact of Land Use Change on It by Using Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Algorithm in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Geoderma 403 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115379
Moore ID, Grayson RB, Ladson AR (1991) Digital Terrain Modelling: A Review of Hydrological, Geomorphological, and Biological Applications. Hydrol Process 5:3–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050103
Moore ID, Burch GJ (1986) Physical Basis of the Length-Slope Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50(5):1294–1298. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000050042x
Murmu P, Kumar M, Lal D (2019) Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Geospatial Techniques and Analytical Hierarchy Process in Dumka District, Jharkhand. India’. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100239
Naqvi HR, Laishram MD, Masood AS (2012) Soil Loss Prediction and Prioritization Based on Revised Universal Soil Loss Estimation (RUSLE) Model Using Geospatial Technique. Int J Environ Protect 2(3):39–43
Nasiri M (2013) GIS Modelling for Locating the Risk Zone of Soil Erosion in a Deciduous Forest. J for Sci 59(2):87–91
Nefeslioglu HA, Duman TY, Durmaz S (2008) Landslide Susceptibility Mapping for a Part of Tectonic Kelkit Valley (Eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey). Geomorphology 94:401–418
Neissi L, Albaji M, Boroomand Nasab S (2020) Combination of GIS and AHP for Site Selection of Pressurized Irrigation Systems in the Izeh Plain, Iran. Agric Water Manag. 231:106004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106004
Nekhay O, Arriaza M, Boerboom L (2009) Evaluation of Soil Erosion Risk Using Analytic Network Process and GIS: A Case Study from Spanish Mountain Olive Plantations. J Environ Manag 90(10):3091–3104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.022
Oh HJ, Lee S, Chotikasathien W, Kim CH, Kwon JU (2009) Predictive landslide susceptibility mapping using spatial information in the Pechabun area of Thailand. Environ Geol 57(3):641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1342-9
Pal SC, Chakrabortty R, Malik S, Das B (2018) Application of Forest Canopy Density Model for Forest Cover Mapping Using LISS-IV Satellite Data: A Case Study of Sali Watershed, West Bengal. Model Earth Syst Environ 4(2):853–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0445-x
Panditharathne DLD, Abeysingha NS, Nirmanee KGS, Mallawatantri A (2019) Application of Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (Rusle) Model to Assess Soil Erosion in “Kalu Ganga” River Basin in Sri Lanka. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2019:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4037379
Pathak P, Wani SP, Sudi R (2006) Gully control in SAT watersheds. Global theme on agroecosystems report no. 1 International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru, India 2(1):1-28
Pham BT, Bui DT, Pourghasemi HR, Indra P, Dholakia MB (2017) Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in the Uttarakhand Area (India) Using GIS: A Comparison Study of Prediction Capability of Naïve Bayes, Multilayer Perceptron Neural Networks, and Functional Trees Methods. Theoret Appl Climatol 2(1):255–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1702-9
Pimentel D (2006) Soil Erosion: A Food and Environmental Threat. Environ Dev Sustain 8:119–37
Poesen J, Nachtergaele J, Verstraeten G (2003) Gully Erosion and Environmental Change: Importance and Research Needs’ Translated by C Valentin. Catena 50(2):91–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(02)00143-1
Punniyamoorty M, Mathiyalagan P, Lakshmi G (2012) A Combined Application of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in Supplier Selection. Benchmark 19:70–92. https://doi.org/10.1108/14635771211218362
Rahmati O, Pourghasemi HR, Melesse AM (2016) Application of GIS-Based Data Driven Random Forest and Maximum Entropy Models for Groundwater Potential Mapping: A Case Study at Mehran Region, Iran. CATENA 137:360–372
Ranzi R, Le TH, Rulli MC (2012) A RUSLE Approach to Model Suspended Sediment Load in the Lo River (Vietnam): Effects of Reservoirs and Land Use Changes. J Hydrol 422–423:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.12.009
Razavi-Termeh, Sadeghi-Niaraki A, Vahid S, Soo MC (2020) Gully Erosion Susceptibility Mapping Using Artificial Intelligence and Statistical Models. Geomatics, Nat Hazards Risk 11(1):821–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2020.1753824
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In Agriculture Handbook 537. Washington, District of Columbia, USA: Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service
Rodrigo-Comino J, Cerdà A (2018) Improving stock unearthing method to measure soil erosion rates in vineyards. Ecol Indicator 85:509–517
Rowntree KM (1991) Morphological characteristics of gully networks and their relationship to host materials, Baringo District, Kenya. GeoJournal 23(1):19–27
Rozos D, Bathrellos GD, Skillodimou HD (2011) Comparison of the implementation of rock engineering system and analytic hierarchy process methods, upon landslide susceptibility mapping, using GIS: a case study from the Eastern Achaia County of Peloponnesus, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 63(1):49–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0687-z
Saaty TL, Vargas LG (1982) The logic of priorities, applications in business, energy, health, transportation. Kluwer-Nijhoff Publishing, Boston
Saaty TL (1990) How to Make a Decision: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Saha A, Ghosh P, Mitra B (2018) GIS Based Soil Erosion Estimation Using Rusle Model: A Case Study of Upper Kangsabati Watershed, West Bengal, India. Int J Environ Sci Nat Resour 13(5):119–26. https://doi.org/10.19080/IJESNR.2018.13.555871
Sałabun W, Watróbski J, Shekhovtsov A (2020) Are MCDA Methods Benchmarkable? A Comparative Study of TOPSIS, VIKOR, COPRAS, and PROMETHEE II Methods. Symmetry 12(9):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091549
Schmoldt DL (2011) The Analytic Hierarchy Process in Natural Resource and Environmental Decision Making. Springer, Dordrecht; London.
Selby MJ (1985) Earth’s Changing Surface Great Clarendon Street Oxford, OX2 6DP. Oxford University Press, United Kingdom
Sharda VN, Mandal D, Ojasvi PR (2013) Identification of soil erosion risk areas for conservation planning in different states of India. J Environ Biol 34(2):219–26
Shimabukuro YE, Duarte V, Arai E, Freitas RM, Lima A, Valeriano DM, Brown IF, Maldonado MLR (2009) Fraction images derived from Terra Modis Data for mapping burnt areas in Brazilian Amazonia. Int J Remote Sens 30(6):1573–1546. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160802509058
Singh SK, Laari PB, Mustak S et al (2018) Modelling of Land Use Land Cover Change Using Earth Observation Data-Sets of Tons River Basin, Madhya Pradesh, India. Geocarto Internationa 33:1202–1222. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2017.1343390
Singh G, S Chandra, R Babu (1981) Soil loss and prediction research in India. Tech Bull T-12/D-9, Dehradun, India: Central Soil and Water Conservation Research and Training Institute
Siva G, Nasir N, Selvakumar R (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in Sengipatti for Thanjavur district using analytical hierarchy process. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 80:012063. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/80/1/012063
Stock JD, Dietrich WE (2006) Erosion of steepland valleys by debris flows. Geol Soc Am Bull 118(9–10):1125–1148. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25902.1
Summerfield MA (1991) Global geomorphology: an introduction to the study of landforms. Routledge, Abingdon, pp 1–560
Tang Q, Yong Xu, Bennett SJ, Li Y (2015) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Yangou Watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ Earth Sci 73(4):1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3523-z
Thakkar H, Bhattacharyya S (2006) Reservoir siltation in India: latest studies.’ SANDRP 4, no. 7–8. www.sandrp.in OR www.narmada.org/sandrp
Thapa P (2020) Spatial estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE modeling: a case study of Dolakha District Nepal. Environ Syst Res 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-020-00177-2
Thomas J, Sabu J, Thrivikramji KP (2018) Assessment of soil erosion in a monsoon-dominated mountain river basin in India using RUSLE-SDR and AHP. Hydrol Sci J 63(4):542–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2018.1429614
Tilahun SA, Guzman CD, Zegeye AD, Ayana ES, Collick AS, Yitaferu B, Steenhuis TM (2014) Spatial and temporal patterns of soil erosion in the semi-humid Ethiopian highlands: a case study of Debre Mawi watershed. In: Melesse A, Abtew W, Setegn S (eds) Nile River Basin. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02720-3_9
Valentin C, Poesen J, Yong L (2005) Gully erosion: impacts, factors and control. CATENA 63:132–153
Vijith H, Dodge-Wan A, Hurmain D (2018) Impacts of land use changes and land cover alteration on soil erosion rates and vulnerability of tropical mountain ranges in Borneo’. Remote Sens Appl: Soc Environ 12:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.09.003
Vijith H, Dodge-Wan D (2017) Spatio-temporal changes in rate of soil loss and erosion vulnerability of selected region in the tropical forests of Borneo during last three decades. Earth Sci Inform. 11(2):171–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-017-0321-7
Vijith H, Seling LW, Dodge-Wan D (2018a) Estimation of soil loss and identification of erosion risk zones in a forested region in Sarawak, Malaysia, Northern Borneo.” Environment,’. Dev Sustain 20(3) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9946-4
Vrieling A (2006) Satellite Remote Sensing for Water Erosion Assessment: A Review. CATENA 65(1):2–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2005.10.005
Wang F, Sahana M, Pahlevanzadeh B, Pal SC, Shit PK, Jalil Piran MD, Janizadeh S, Band SS, Mosavi A (2021) Applying different resampling strategies in machine learning models to predict head-cut gully erosion susceptibility. Alexandria Eng J 60(6):5813–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.04.026
Waris M, Panigrahi S, Mengal A, Soomro MI, Mirjat NH, Ullah M, Khan A, Azlan ZS (2019) An application of analytic hierarchy process (AHP) for sustainable procurement of construction equipment: multicriteria-based decision framework for Malaysia.. Math Probl Eng, 2019: 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6391431
Wei W, Chen L, Bojie Fu, Huang Z, Dongping Wu, Gui L (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the Semi-Arid Loess Hilly Area, China. J Hydrol 335(3–4):247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.11.016
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses- a guide to conservation planning. Agriculture Handbook No. 537, Science and Education Administration, United States Department of Agriculture, Washington D.C.
Xie Z, Chen G, Meng X, Zhang Yi, Qiao L, Tan L (2017) A comparative study of landslide susceptibility mapping using weight of evidence, logistic regression and support vector machine and evaluated by SBAS-InSAR monitoring: Zhouqu to Wudu Segment in Bailong River Basin China. Environ Earth Sci 76(8):313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6640-7
Xu X-L, Liu W, Kong Y-P, Zhang K-L, Bofu Yu, Chen J-D (2009) Runoff and water erosion on road side-slopes: effects of rainfall characteristics and slope length. Transp Res Part d: Transp Environ 14(7):497–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2009.05.006
Yang A, Wang C, Pang G, Long Y, Wang L, Cruse RM, Yang Q (2021) Gully erosion susceptibility mapping in highly complex terrain using machine learning models. Int J Geo_Inform 10(680) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100680
Yeh HF, Cheng YS, Lin HI, Lee CH (2016) Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River, Taiwan. Sustain Environ Res 26(1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2015.09.005
Zabihi M, Mirchoolia F, Motevallia A, Darvishana AK, Pourghasemib HR, Zakeria MA, Sadighia F (2018) Spatial modelling of gully erosion in Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran. Catena 161:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.010
Zhou P, Luukkanen O, Tokola T, Nieminen J (2008) Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. CATENA 75(3):319–325
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Sk. Firoz for his constant support during the field investigation. They are also indebted to all the national and international organizations for providing freely available database. They are also grateful to Dr. Pravat Kumar Shit, Assistant Professor, Department of Geography, Raja N. L. Khan Women’s College (Autonomous), Medinipur, West Bengal, India; Dr. Sk. Mafizul Haque, Assistant Professor, Department of Geography, University of Calcutta, Kolkata, India; and Dr. Sandipan Ghosh, Assistant Professor, Department of Geography, Chandrapur College, Purba Barddhaman, West Bengal, India, for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Partha Modak conducted field work, collected secondary data, analysed it, prepared maps and partially drafted the first manuscript. Mrinal Mandal formulated the idea and design of this research work, conducted field, partially drafted the first manuscript and critically revised and edited the final manuscript. Susanta Mandi conducted field and partially drafted the first manuscript and prepared graphs and edited field photographs. Biswajit Ghosh conducted field and helped in analysing data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modak, P., Mandal, M., Mandi, S. et al. Gully erosion vulnerability modelling, estimation of soil loss and assessment of gully morphology: a study from cratonic part of eastern India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 116656–116687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22118-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22118-5