Abstract
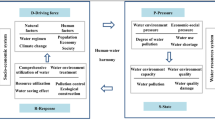
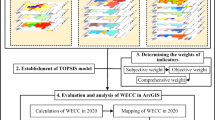
The Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion (MRPSNWD) is a major strategic project to alleviate the serious shortage of water resources in northern China, and it benefited 14 large- and medium-sized cities in Henan, Hebei, Beijing, and Tianjin. Most of the predecessors used qualitative analysis to study the impact of the MRPSNWD on the water-receiving cities (WRCs), and they only considered one aspect of economy, society, resources, and environment, which could not fully reflect the impact of the MRPSNWD on the water-receiving cities. Therefore, based on the data of economic and social resources and environment of the water-receiving cities in the MRPSNWD from 2010 to 2019, an evaluation model based on entropy weight–analytic hierarchy process (AHP) fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method was constructed to account for the impacts on the economy-society-resources-environment of the water-receiving cities after the operation of the MRPSNWD and scientifically evaluated the comprehensive benefits of the MRPSNWD. The evaluation results revealed that the economic and environmental impacts of the MRPSNWD on the water-receiving cities were more obvious than those on society and resources. As far as water-receiving cities were concerned, the impact of the Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion on Zhengzhou, Shijiazhuang, Tianjin, and Beijing was generally higher than that of other cities. As far as the Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion was concerned, its overall impact on water-receiving cities was relatively slow.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data used in this research work has been presented.
References
Chen XW, Hu XF (2005) Analysis and countermeasures of water environment safety in the core water source area of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. China Environ Manag Series (3):13–16
Chu YP (2020) Research on entropy weight-AHP fuzzy comprehensive evaluation based on foundation pit engineering monitoring [D]. Nanchang University, Jiangxi
Deng ZG, Guo PZ, Yu T (2021) Analysis of the impact of emergency water supply on the north extension of the first phase of the east route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on Dezhou City[J]. Haihe Water Resour (06):5–7.
Du ZY, Ge LL,Ng Alex Hay-Man, Lian XG,Zhu QGZ,Horgan FG.,Zhang Q (2021) Analysis of the impact of the South-to-North water diversion project on water balance and land subsidence in Beijing, China between 2007 and 2020[J]. J Hydrol 603(PB):5–9.
Feng GY, Lv JC, Cui XS (2006) Research on the method of evaluating the water quality of Danjiangkou Reservoir combined with water quantity and water quality [[C]. Proc 2006 Acad Ann Meeting Chin Soc Hydr Res 2006 Hydr Sym (1):122–126
Feng T, Liu X, Zhong Y et al (2018) Research of combination forecasting model based on improved analytic hierarchy process[J]. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 1:1–8
Gao YN, Gao JF (2010) Comprehensive evaluation of the impact of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on the ecological environment of the middle and lower reaches of the Han River[J]. Adv Geog Sci 29(01):59–64
Giri RK, Shang W, Wang Z, Langford J (2019) China’s south-to-north water diversion project empowers sustainable water resources system in the north[J]. Sustainability 11(13):3735
Hu BQ (2010) Basis of fuzzy theory [M]. Wuhan University Press, Hubei
Jia SF (2003) How to View the Social and Economic Impact of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. Impact Sci Soc (3): 32–37.
Jiang JQ (2019) Analysis of current situation of water resources in China and study on countermeasures for sustainable development [J]. Smart City 5(01):44–45
Kattel GR, Shang W, Wang Z et al (2019) China’s south-to-north water diversion project empowers sustainable water resources system in the north[J]. Sustainability 11(13):3735
Li QZ (2001) Analysis of the social benefits of the western route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on the development of the western region [J]. Water Conservancy Econ 19(4):39–41
Li Y, Wang X, Zhou B et al (2015) Analysis on the background characteristics and variation trend of water quantity and water quality in the middle and lower reaches of the Han River before water transfer from the middle route [J]. Hydrology 35(5):82–90
Li DL, Zuo QT, Wu QS, Li QW, Ma JX (2021) Achieving the tradeoffs between pollutant discharge and economic benefit of the Henan section of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project through water resources-environment system management under uncertainty[J]. J Clean Prod 321:2–8
Li ZJ, Hou Y, Wang HF, Yu B (2021b) Evaluation of water resources security in Jinan City based on AHP-entropy weight method and fuzzy model[J]. Jilin Water Resour (09):6–9+22.
Li HY, Fu JB, Chu Y, Zhai PH (2022) Evaluation of the operation effect of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion based on the harmony of human and water: a case study of a typical water receiving area in Henan[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion Water Conservancy Sci Technol 20(01):93–101
Liu MK, Guo J (2020) Comparisons and improvements of eco-compensation standards for water resource protection in the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. Water Supply 20(8):17–21
Liu J, Li M, Wu M et al (2020) Influences of the south–to-north water diversion project and virtual water flows on regional water resources considering both water quantity and quality[J]. J Clean Prod 244:118920
Long D, Yang W, Scanlon BR et al (2020) South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels[J]. Nat Commun 11(1):1–10
Long Y, Li Y, Lei X et al (2021) A study on comprehensive evaluation methods for coordinated development of water diversion projects based on advanced SWOT analysis and coupling coordination model[J]. Sustainability 13(24):13600
Matos JP, Cohen LT, Boillat JL, et al.(2010) Analysis of flow regime changes due to operation of large reservoirs on the Zambezi River[C]//6th International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulics. Taylor & Francis Group, (CONF): 337–342.
Peng H, Guo SL (2003) Effects of South-to-North Water Diversion on algae growth in the Lower Han River and countermeasures [J]. Environ Sci Technol 3:1–3
Peng Z, Yin J, Zhang L et al (2020) Assessment of the socio-economic impact of a water diversion project for a water-receiving area[J]. Pol J Environ Stud 29(2):1771–1784
Quigley TM, Haynes RW, Hann WJ (2001) Estimating ecological integrity in the interior Columbia River basin[J]. For Ecol Manage 153(1–3):161–178
Tortajada C (2000) Environmental impact assessment of water projects in Mexico[J]. Int J Water Resour Dev 16(1):73–87
Wang QN, Ma YF (2008) Research on the water environment in the water source area of southern Shaanxi in the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project [J]. J Water Resour Water Eng 19(1):77–80
Wang YS, Yang YY (2005) China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. People’s Yangtze River 36(7):2–5
Wang S, Ge L, Cai S, Wu L (2018) Hybrid interval AHP-entropy method for electricity user evaluation in smart electricity utilization[J]. J Modern Power Syst Clean Energy 6(4):701–711
Wang F, Liu GW, Chen ZL, Cui QG, Li GH, Liu GY (2021) Water enrichment evaluation of long and deep buried tunnel based on GIS and AHP-entropy weight method[J]. J Railway Eng 38(10):66–72
Wu J, Huang H, Cao Q (2013) Research on AHP with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application in multi-criteria decision making problems[J]. Appl Math Model 37(24):9898–9906
Xie P, Dou M, Xia J (2005) Calculation model of probability of occurrence of algal blooms in the Han River under different water transfer schemes of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. J Hydr Con (6):727–732
Xu ZF, Xu T, Pu QC (2011) Protection and management of water resources in Danjiangkou Reservoir Area and upstream[J]. People’s Yangtze River 42(2):16–20
Yan B, Chen L (2013) Coincidence probability of precipitation for the middle route of South-to-North water transfer project in China[J]. J Hydrol 499:19–26
Yang Z, Huang X, Fang G et al (2021) Benefit evaluation of East Route Project of South to North Water Transfer based on trapezoid cloud model[J]. Agric Water Manag 254:106960
Yin DC, Yin ZJ, Yang CH et al (2017) Key hydrological thresholds and scheduling strategies to control spring diatom blooms in the middle and lower reaches of the Han River [J]. China Water Resources 9:31–34
Zhang ZW, Jiang HJ, Li CG et al (2012) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of water safety in the core water source areas of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project [J]. South-to-North Water Diversion Water Conservancy Sci Technol 10(3):16–21
Zhao X (2003) Influence of South-to-North Water Diversion on Urban Ecological Environment of Handan City and Countermeasures [J]. Hebei Water Conservancy Hydropower Technol S1:50–52
Zhao S, Liu W, Zhu M et al (2021) A priority-based multi-objective framework for water resources diversion and allocation in the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. Socioecon Plann Sci 78:101085
Zhao J, Bi YJ, Han YP, Yu J, Zuo P (2019) Research on the social and economic benefit of the Henan section of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J].J Northwest Univ (Natl Sci Ed) 49(06):855–866.
Zhou C, Li GP (2015) Willingness to pay and influencing factors of ecological compensation in the basin: taking Zhengzhou City, the water-receiving area of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project as an example [J]. Econ Geog 35(6):38–46
Zuo HF, Huang YF, Wei JH, Fu XD, Wang GQ (2008) Potential risk analysis of inferior groundwater along the Middle Route of South-to-North Water Diversion on water quality[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion Water Conservancy Sci Technol (05):1–3+12.
Funding
Thanks to the support from the Introduction of High-end Foreign Experts Program in Henan Province (grant no: HNGD2022039) and the training program for young key teachers in Henan Province’s Higher Education (2019GGJS098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ken Sun designed the research; Ken Sun and Yufeng Hua wrote and revised the paper; Wenbo He, Tianshu Yan, and Chang Liu analyzed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, K., Hua, Y., He, W. et al. Impact assessment on the economy, society, resource, and environment in the water-receiving cities of the Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 90378–90390 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22044-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22044-6